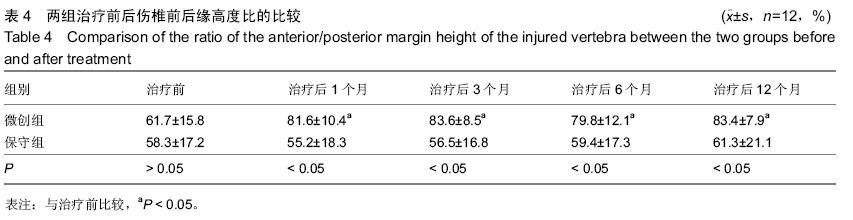
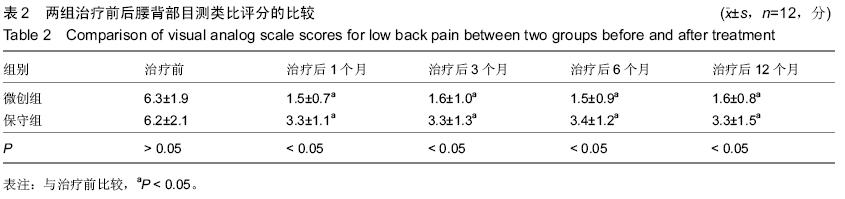
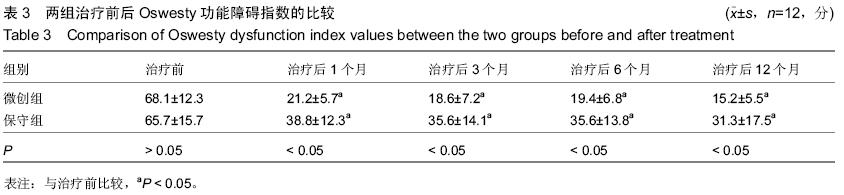
| [1] Matsumoto T,Takano T,Saito H,et al.Vitamin D analogs and bone: preclinical and clinical studies with eldecalcitol. Bonekey Rep.2014;3:513.[2] Maricic M.Use of DXA-based technology for detection and assessment of risk of vertebral fracture in rheumatology practice.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014; 16(8):436.[3] Zhou Z,Chen C,Zhang J,et al.Safety of denosumab in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or low bone mineral density: a meta-analysise.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(5):2113-2122.[4] Huang Z,Wan S,Ning L,et al.Is unilateral kyphoplasty as effective and safe as bilateral kyphoplasties for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures? A meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(9): 2833-2842.[5] Zaryanov AV,Park DK,Khalil JG,et al.Cement augmentation in vertebral burst fractures.Neurosurg Focus.2014;37(1):E5.[6] Feurer E,Chapurlat R.Emerging drugs for osteoporosis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2014;19(3):385-395.[7] Chen H,Kubo KY.Bone three-dimensional microstructural features of the common osteoporotic fracture sites.World J Orthop.2014;5(4):486-495.[8] Savage JW,Schroeder GD,Anderson PA. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2014;22(10):653-664.[9] Fujiwara S,Hamaya E,Sato M,et al. Systematic review of raloxifene in postmenopausal Japanese women with osteoporosis or low bone mass (osteopenia).Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:1879-1893.[10] Tian J,Xiang L,Zhou D,et al.The clinical efficacy of vertebroplasty on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2014;12(12): 1249-1253.[11] Shi-Ming G, Wen-Juan L,Yun-Mei H,et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A metaanalysis.Indian J Orthop. 2015 ;49(4):377-387.[12] Martín-López JE,Pavón-Gómez MJ,Romero-Tabares A,,et al.Stentoplasty effectiveness and safety for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: A systematic review.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101(5):627-632.[13] Lorentzon M,Cummings SR.Osteoporosis: the evolution of a diagnosis.J Intern Med. 2015;277(6): 650-661.[14] No YJ,Roohani-Esfahani SI,Zreiqat H. Nanomaterials: the next step in injectable bone cements. Nanomedicine (Lond).2014;9(11):1745-1764.[15] Rahaman MN,Bal BS,Huang W.Review: emerging developments in the use of bioactive glasses for treating infected prosthetic joints.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;41:224-231.[16] Cauley JA,Chalhoub D,Kassem AM,et al.Geographic and ethnic disparities in osteoporotic fractures.Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(6):338-351.[17] Rossini M,Zanotti R,Viapiana O,et al.Bone involvement and osteoporosis in mastocytosis.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am.2014;34(2):383-396.[18] Nuti R,Caffarelli C,Guglielmi G,et al.Undiagnosed vertebral fractures influence quality of life in postmenopausal women with reduced ultrasound parameters.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7): 2254-2261.[19] Sone T,Ito M,Fukunaga M,et al.The effects of once-weekly teriparatide on hip geometry assessed by hip structural analysis in postmenopausal osteoporotic women with high fracture risk.Bone.2014;64:75-81.[20] Papanastassiou ID,Filis A,Gerochristou MA, et al. Controversial issues in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral fractures.Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:934206.[21] Kammerlander C,Zegg M,Schmid R,et al.Fragility fractures requiring special consideration: vertebral fractures.Clin Geriatr Med.2014;30(2):361-372.[22] Castro-Mateos I,Pozo JM,Cootes TF,et al.Statistical shape and appearance models in osteoporosis.Curr Osteoporos Rep.2014;12(2):163-173.[23] Qu B,Ma Y,Yan M,et al.The economic burden of fracture patients with osteoporosis in western China.Osteoporos Int.2014;25(7):1853-1860.[24] Ensrud KE,Taylor BC,Peters KW,et al.Implications of expanding indications for drug treatment to prevent fracture in older men in United States: cross sectional and longitudinal analysis of prospective cohort study. BMJ.2014;349:g4120.[25] Zhang YZ,Kong LD,Cao JM,et al.Incidence of subsequent vertebral body fractures after vertebroplasty.J Clin Neurosci.2014;21(8):1292-1297.[26] Kroon F,Staples M,Ebeling PR,et al.Two-year results of a randomized placebo-controlled trial of vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures.J Bone Miner Res.2014;29(6):1346-1355.[27] Zhou Z,Chen C,Zhang J,et al.Safety of denosumab in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or low bone mineral density: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(5):2113-2122.[28] Gerdhem P.Osteoporosis and fragility fractures: Vertebral fractures.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27(6):743-755.[29] Misra D,Zhang Y,Peloquin C,et al.Incident long-term warfarin use and risk of osteoporotic fractures: propensity-score matched cohort of elders with new onset atrial fibrillation.Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(6): 1677-1684.[30] Olsen CF,Bergland A.The effect of exercise and education on fear of falling in elderly women with osteoporosis and a history of vertebral fracture: results of a randomized controlled trial.Osteoporos Int. 2014; 25(8):2017-2025.[31] van Griensven M,Biberthaler P.Therapy of osteoporotic fractures - new therapeutic options.MMW Fortschr Med. 2014;156(18):48-50.[32] Savage JW,Schroeder GD,Anderson PA.Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(10):653-664.[33] Kim HJ,Yi JM,Cho HG,et al.Comparative study of the treatment outcomes of osteoporotic compression fractures without neurologic injury using a rigid brace, a soft brace, and no brace: a prospective randomized controlled non-inferiority trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(23):1959-1966.[34] Benoist M.The Michel Benoist and Robert Mulholland yearly European Spine Journal Review: a survey of the "medical" articles in the European Spine Journal, 2014. Eur Spine J.2015;24(1):12-21. [35] Yang H,Pan J,Wang G.A review of osteoporotic vertebral fracture nonunion management.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(26 Spec No.):B4-6. [36] Brincat M,Gambin J,Brincat M,et al.The role of vitamin D in osteoporosis.Maturitas.2015;80(3):329-332. [37] Lorentzon M,Cummings SR.Osteoporosis: the evolution of a diagnosis.J Intern Med. 2015;277(6): 650-661.[38] Griffith JF. Identifying osteoporotic vertebral fracture.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015;5(4):592-602. [39] Lems WF,Geusens P.Established and forthcoming drugs for the treatment of osteoporosis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26(3):245-251[40] Giangregorio LM,MacIntyre NJ,Heinonen A,et al.Too Fit To Fracture: a consensus on future research priorities in osteoporosis and exercise.Osteoporos Int.2014;25(5):1465-1472. |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)