| [1] Buchvald P, Barsa P, Suchomel P.Odontoid fracture combined with lateral atlanto-axial dislocation. Report of two cases. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012;79(5):459-462.[2] Forterre F, Precht C, Riedinger B, et al. Biomechanical properties of the atlantoaxial joint with naturally-occurring instability in a toy breed dog. A comparative descriptive cadaveric study. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2015. [Epub ahead of print][3] Hein C, Richter HP, Rath SA. Atlantoaxial screw fixation for the treatment of isolated and combined unstable jefferson fractures - experiences with 8 patients. Acta Neurochir Wien. 2002;144:1187-1192.[4] Yamamoto H, Kurimoto M, Hayashi N, et al. Atlas burst fracture (Jefferson fracture) requiring surgical treatment after conservative treatment--report of two cases. No Shinkei Geka. 2002;30:987-991.[5] 5 Sen MK, Steffen T, Beckman L, et al. Atlantoaxial fusion using anterior transarticular screw fixation of C1-C2: technical innovation and biomechanical study. Eur Spine J. 2005;14: 512-518.[6] Suchomel P, Stulik J, Klezl Z, et al. Transarticular fixation of C1-C2: a multicenter retrospective study. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2004;71:6-12.[7] Mixter SJ,Osgood RB.Traumatic Lesions of the Atlas and Axis. Ann Surg. 1910;5(2):193-207.[8] Yue B, Kwak DS, Kim MK, et al. Morphometric trajectory analysis for the C2 crossing laminar screw technique. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(5):828-832.[9] Ruf M, Melcher R,Harms J. Transoral reduction and osteosynthesis C1 as a function-preserving option in the treatment of unstable Jefferson fractures. Spine. 2004;29: 823-827.[10] Brasiliense LB, Lazaro BC, Reyes PM, et al. Stabilization of the atlantoaxial joint with C1-C3 lateral mass screw constructs: biomechanical comparison with standard technique. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(2 Suppl Operative):422-428.[11] Wang MY, Samudrala S. Cadaveric morphometric analysis for atlantal lateral m ass screw placement. Neurosurgery. 2004; 54:1436-1439,1439-1440.[12] Mendes GA, Dickman CA, Rodriguez-Martinez NG, et al. Endoscopic endonasal atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation technique: an anatomical feasibility and biomechanical study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(5): 470-477.[13] Yeom JS, Kafle D, Nguyen NQ, et al. Routine insertion of the lateral mass screw via the posterior arch for C1 fixation: feasibility and related complications. Spine J. 2012;12(6): 476-483.[14] Hong X, Dong Y, Yunbing C, et al. Posterior screw placement on the lateral mass of atlas: an anatomic study. Spine. 2004; 29:500-503. [15] Nitising A, Jetjumnong C, Tisavipat N, et al. Posterior C1-C2 fusion using C1 lateral mass and C2 pars screw with rod fixation: techniques and outcomes. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011; 94(7):794-800.[16] Stulik J, Vyskocil T, Sebesta P, et al. Harms technique of C1-C2 fixation with polyaxial screws and rods. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2005;72:22-27.[17] Radcliff KE, Hussain MM, Moldavsky M, et al. In vitro biomechanics of the craniocervical junction-a sequential sectioning of its stabilizing structures. Spine J. 2015;15(7): 1618-1628.[18] Saari A, Itshayek E, Cripton PA.Cervical spinal cord deformation during simulated head-first impact injuries. J Biomech. 2011;44(14):2565-2571.[19] Dugailly PM, Sobczak S, Moiseev F, et al.Musculoskeletal modeling of the suboccipital spine: kinematics analysis, muscle lengths, and muscle moment arms during axial rotation and flexion extension. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(6):E413-422.[20] Lee SH, Kim ES, Eoh W. Modified C1 lateral mass screw insertion using a high entry point to avoid postoperative occipital neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci.2013;20(1):162-167.[21] 曹正霖,钟世镇,徐达传.寰枢椎的解剖学测量及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2000,18(4):2993-2301.[22] Joaquim AF,Ghizoni E,Rubino PA,et al. Lateral mass screw fixation of the atlas: surgical technique and anatomy. World Neurosurg. 2010;74(2-3):359-362.[23] Goel A,Desai KI,Muzumdar DP.Atlantoaxial fixation using plate and screw method: a report of 160 treated patients. Neurosurgery. 2002;51(6):1351-1356.[24] Eshra MA. C2 pars/pedicle screws in management of craniocervical and upper cervical instability. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(2):156-160.[25] 杨双石,刘景发,欧阳钧.寰枢关节固定不同术式的生物力学评价及临床意义[J].中华创伤杂志,1998,14(2):531-533 .[26] 瞿东滨,金大地,欧阳钧,等.几种寰枢椎后路内固定术的生物力学评价[J].医用生物力学,1999,14(4):199-200.[27] Richter M,Schmidt R,Claes L,et al.Posterior atlantoaxial fixation: biomechanical in vitro comparison of six different techniques.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(16):1724-1732.[28] Aryan HE,Newman CB,Nottmeier EW,et al.Stabilization of the atlantoaxial complex via C-1 lateral mass and C-2 pedicle screw fixation in a multicenter clinical experience in 102 patients: modification of the Harms and Goel techniques.J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(3):222-229.[29] 滕文臣,滕文臣,锡林•宝勒日,等.寰枢椎不稳后路钢丝内固定术相关应用解剖学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(1):52-56.[30] Kothe R,Ruther W,Schenider E, et al. Biomechanical analysis of transpedicular screw fixation N the subaxial cervical spine. Spine. 2004;29(7):1689-1875.[31] Abumi K,Itoh H,Taneichi H,et al.Transpedicular screw fixation for traumatic lesions of the middle and lower cervical spine:description of the techniques and preliminary report. J Spinal Disord. 1994;7:19-28.[32] Yoshida M, Neo M, Fujibayashi S. Comparison of the anatomical risk for vertebral artery injury associated with the C2-pedicle screw and atlantoaxial transarticular screw. Spine. 2006;31(15):513-517.[33] 刘铁龙,章允志,严望军,等.钢丝与不同钛缆内固定系统固定寰枢椎失稳的抗扭转生物力学比较研究[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(8): 570-572.[34] Weis JC,Cunningham BW,Kanayama M,et al.In vitro biomechanical comparison of multistrand cables with conventional cervical stabilization.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(18):2108-2114.[35] 曹锡文,刘文和,胡伟文,等.后路钛缆与钢丝内固定治疗少儿寰枢椎不稳的临床对照试验[J].中国骨伤,2007,20(12):812-814.[36] Menendez JA,Wright NM.Techniques of posterior C1-C2 stabilization.Neurosurgery. 2007;60(1):103-111.[37] 傅捷.后路经关节螺钉内固定治疗寰枢椎不稳定的疗效评价[J].重庆医科大学学报,2010,35(4):620-621.[38] Jeanneret B,Geghard JS,Margerl F.Transpedicular screw fixation of ar-ticular mass fracture separation:results of an anatomical study and oper-ative technique.J Spinal Disord. 1994;7:222-229.[39] 蔡贤华,陈庄洪,黄继锋,等.后路改良经关节螺钉内固定术治疗寰枢椎不稳定[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(3):161-163.[40] Melcher RP,Puttlitz CM,Kleinstueck FS,et al.Biomechanical testing of posterior atlantoaxial fixation techniques.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(22):2435-2440.[41] Paramore CG,Dickman CA,Sonntag VK.The anatomical suitability of the C1-2 complex for transarticular screw fixation. J Neurosurg.1996;85(2):221-224.[42] Wright NM,Lauryssen C.Vertebral artery injury in C1-2 transarticular screw fixation: results of a survey of the AANS/CNS section on disorders of the spine and peripheral nerves. American Association of Neurological Surgeons/ Congress of Neurological Surgeons. J Neurosurg. 1998;88(4): 634-640.[43] Wang C,Yan M,Zhou H,et al. Atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation with morselized autograft and without additional internal fixation: technical description and report of 57 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(6):643-646.[44] Resnick DK,Benzel EC.C1-C2 pedicle screw fixation with rigid cantilever beam construct: case report and technical note. Neurosurgery. 2002;50(2):426-428.[45] Kotani Y,Cunningham BW,Abumi K,et al.Biom echaical analysis of cervical stabilization systems:An assessment of transpedicle screw fixa-tion in the cervical spine. Spine. 1994; 19:2929-2539.[46] Xu R,Kang A,Ebraheim NA,et al. Anatomic relation between the cervical pedicle and the adjacent neural structure. Spine. 1999;24:451-454.[47] 曾周景,叶建华,唐桂阳,等.寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗齿状突骨折合并寰枢椎脱位[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(7): 617-619.[48] 窦维新,焦绪民.经后路寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗寰枢椎不稳24例分析[J].中国基层医药,2010,17(5):648-649.[49] 马维虎,刘观燚,孙韶华,等.经后路寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗C1-2不稳[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(1):47-51.[50] 郝定均,贺宝荣,许正伟,等.寰椎椎弓根螺钉和侧块螺钉技术的临床疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(12):1297-1303.[51] 常志强,张沛,吴一民,等.寰椎椎弓根螺钉置入的应用解剖及生物力学评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(26):4185-4189. |
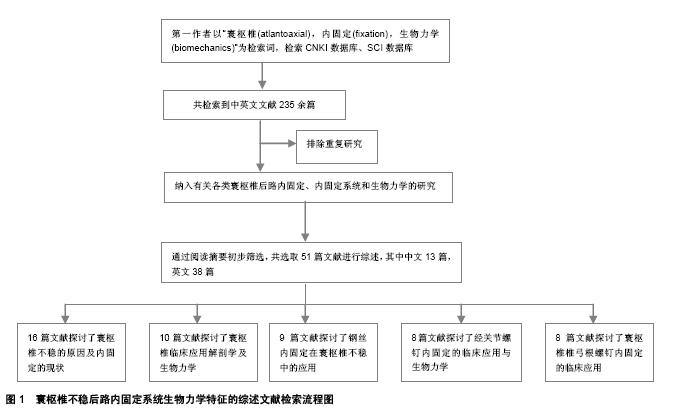
.jpg)