中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (37): 5983-5987.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.37.015
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
中成药无敌丹对骨关节炎软骨细胞活力和软骨细胞凋亡的影响
孟亚轲1,刘 岩1,王宏瑞1,刘建国2,郭永飞1
- 1解放军第二军医大学附属长征医院骨科,上海市 200003; 2解放军第二军医大学药学院药理教研室,上海市 200082
Effect of Wudi Dan on vitality and apoptosis of cartilage chondrocytes after osteoarthritis
Meng Ya-ke1, Liu Yan1, Wang Hong-rui1, Liu Jian-guo2, Guo Yong-fei1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Changzheng Hospital of Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China; 2Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200082, China
摘要:
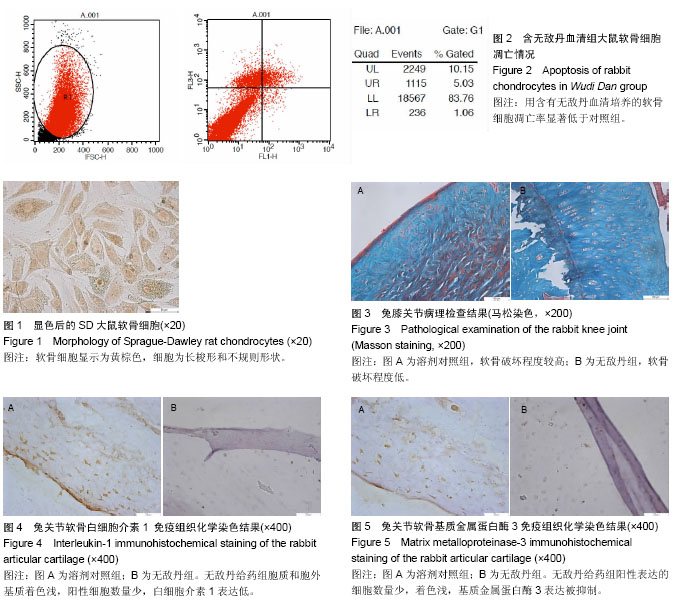
背景:研究发现,无敌丹能够抑制病变关节局部的炎症反应,保护关节软骨。 目的:验证无敌丹对家兔软骨细胞活力和软骨细胞凋亡的影响及对家兔骨关节炎病变的治疗效果。 方法:用含无敌丹的血清培养基培养大鼠软骨细胞,通过与溶剂对照组对比,观察无敌丹对软骨细胞活力及凋亡的影响;采用改良Hulth法构建兔膝骨关节炎模型,无敌丹给药组给予无敌丹;溶剂对照组给予生理盐水,2次/d,连续给药4周。观察无敌丹对兔膝骨关节炎的治疗作用;镜下观察关节局部的软骨细胞情况;用免疫组织化学的方法检测软骨中白细胞介素1、基质金属蛋白酶3的水平。 结果与结论:无敌丹血清培养的软骨细胞凋亡率显著低于对照组;兔膝关节病理检查显示溶剂对照组软骨破坏程度较高,无敌丹组软骨破坏程度低;免疫组织化学染色显示无敌丹给药组胞质和胞外基质着色浅,阳性细胞数量少,白细胞介素1表达低;无敌丹给药组阳性表达的细胞数量少,着色浅,基质金属蛋白酶3表达被抑制。结果表明,无敌丹能够有效保护家兔骨关节炎病变部位关节软骨,减少炎症反应,对于骨关节炎有很好的治疗作用,其机制可能与抑制软骨细胞凋亡、减少细胞因子的生成及抑制基质金属蛋白酶的蛋白表达有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: