| [1] 赵永生.老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折的微创治疗对策[D].济南:山东大学,2013.
[2] Svejme O, Ahlborg HG, Nilsson JÅ, et al. Early menopause and risk of osteoporosis, fracture and mortality: a 34-year prospective observational study in 390 women. BJOG. 2012; 119(7):810-816.
[3] Komemushi A, Tanigawa N, Kariya S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29(4):580-585.
[4] 江天蔚,王澍.单侧椎弓根旁入路 PKP治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的疗效分析[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2015,19(1): 43-45.
[5] 甘锋平,谢兆林,江建中,等.中西医结合治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(16): 1715- 1716.
[6] Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M, et al. Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(19):2260-2265; discussion 2265-2267.
[7] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092.
[8] Bai B, Jazrawi LM, Kummer FJ, et al. The use of an injectable, biodegradable calcium phosphate bone substitute for the prophylactic augmentation of osteoporotic vertebrae and the management of vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(15):1521-1526.
[9] Garfin SR, Buckley RA, Ledlie J, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for symptomatic vertebral body compression fractures results in rapid, significant, and sustained improvements in back pain, function, and quality of life for elderly patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2213-2220.
[10] 徐晖,赵敬凯,陈鸥,等.后凸成形术中骨水泥量对相邻椎体终板影响的有限元分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(3):227-231.
[11] 冯杰,戴维享,王栋,等.单侧椎弓根旁入路与双侧椎弓根入路行椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的效果比较[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(34):60-64.
[12] 徐攀峰.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的临床应用[D].杭州:浙江大学,2008.
[13] 张伟.单侧椎弓根外入路与双侧椎弓根入路 PVP 治疗胸椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床对比研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2014.
[14] 刘仕友,路青林,郑伟,等.椎体后凸成形椎间盘骨水泥渗漏时行相邻椎体预防性强化的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(22): 4001-4005.
[15] 刘仕友.椎体后凸成形椎间盘骨水泥渗漏相邻椎体预防性强化的有限元分析[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[16] Lien SB, Liou NH, Wu SS. Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8): 1215- 1222.
[17] Zoarski GH, Snow P, Olan WJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long-term outcomes. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(2 Pt 1):139-148.
[18] De Negri P, Tirri T, Paternoster G, et al. Treatment of painful osteoporotic or traumatic vertebral compression fractures by percutaneous vertebral augmentation procedures: a nonrandomized comparison between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Clin J Pain. 2007;23(5):425-430.
[19] 刘中浩,彭国栋,林勇,等.肌间隙入路并伤椎植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,6(4):168-169.
[20] 陈柏龄,谢登辉,黎艺强,等.单侧PKP骨水泥注射过中线分布对压缩性骨折椎体两侧刚度的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(2): 118-121.
[21] 徐宝山,胡永成,闫广辉,等.经皮椎体成形术和后凸成形术的相关问题探讨[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(5):430-436.
[22] Molina GS, Campero A, Feito R, et al. Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures (VCF) : procedure description and analysis of the outcomes in 128 patients. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011;108:163-170.
[23] Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, et al. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(10):1897-1904.
[24] Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, et al. Initial outcome and efficacy of "kyphoplasty" in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1631-1638.
[25] Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Duncan TD, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures. Clin Imaging. 2002;26(1):1-5.
[26] Ryu KS, Park CK, Kim MC, et al. Dose-dependent epidural leakage of polymethylmethacrylate after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Neurosurg. 2002;96(1 Suppl):56-61.
[27] Voormolen MH, Mali WP, Lohle PN, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with optimal pain medication treatment: short-term clinical outcome of patients with subacute or chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. The VERTOS study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(3):555-560.
[28] Perry A, Mahar A, Massie J, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty with calcium sulfate cement in a cadaveric osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture model. Spine J. 2005;5(5):489-493.
[29] Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, et al. Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty- retrospective report of 245 cases 1. Radiology. 2003;226(2): 366-372.
[30] Zoarski GH, Snow P, Olan WJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long-term outcomes. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(2 Pt 1):139-148.
[31] Cheung G, Chow E, Holden L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with intractable pain from osteoporotic or metastatic fractures: A prospective study using quality-of-life assessment. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2006; 57(1):13-21.
[32] Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Fransen H, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: first short term results. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2003;147(32):1549-1553.
[33] Fessl R, Roemer FW, Bohndorf K. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: experiences and prospective clinical outcome in 26 consecutive patients with 50 vertebral fractures. Rofo. 2005; 177(6):884-892.
[34] Kumar K, Verma AK, Wilson J, et al. Vertebroplasty in osteoporotic spine fractures: a quality of life assessment. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005;32(4):487-495.
[35] Frey ME, Depalma MJ, Cifu DX, et al. Percutaneous sacroplasty for osteoporotic sacral insufficiency fractures: a prospective, multicenter, observational pilot study. Spine J. 2008;8(2):367-373.
[36] Winking M, Stahl JP, Oertel M, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate- vertebroplasty. A new and effective method of pain treatment in vertebral compression. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2003; 128(48):2525-2530.
[37] He SC, Teng GJ, Deng G, et al. Repeat vertebroplasty for unrelieved pain at previously treated vertebral levels with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):640-647.
[38] Khanna AJ, Reinhardt MK, Togawa D, et al. Functional outcomes of kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic and osteolytic vertebral compression fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(6):817-826.
[39] Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med. 2003;114(4):257-265.
[40] McGraw JK, Lippert JA, Minkus KD, et al. Prospective evaluation of pain relief in 100 patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty: results and follow-up. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(9 Pt 1):883-886.
[41] Wilhelm K, Stoffel M, Ringel F, et al. Preliminary experience with balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Rofo. 2003;175(12): 1690-1696.
[42] Alvarez L, Alcaraz M, Pérez-Higueras A, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: functional improvement in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(10):1113-1118.
[43] Legroux-Gérot I, Lormeau C, Boutry N, et al. Long-term follow-up of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Clin Rheumatol. 2004;23(4): 310-317.
[44] Tsou IY, Goh PY, Peh WC, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the management of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: initial experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2002; 31(1):15-20.
[45] Rousing R, Hansen KL, Andersen MO, et al. Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(5):478-482.
[46] Anselmetti GC, Corgnier A, Debernardi F, et al. Treatment of painful compression vertebral fractures with vertebroplasty: results and complications. Radiol Med. 2005;110(3):262-272.
[47] Kim C, Mahar A, Perry A, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an injectable radiopaque polypropylene fumarate cement for kyphoplasty in a cadaveric osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture model. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20(8):604-609.
[48] Lim TH, Brebach GT, Renner SM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an injectable calcium phosphate cement for vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(12):1297- 1302.
[49] Wu XT, Jiang XJ, Zhang SD, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of vertebroplasty using calcium sulfate cement for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Chin J Traumatol. 2007;10(6): 327-333.
[50] Sietsma MS, Hosman AJ, Verdonschot NJ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the vertebral jack tool and the inflatable bone tamp for reduction of osteoporotic spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(18):E640-644.
[51] Tohmeh AG, Mathis JM, Fenton DC, et al. Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(17):1772-1776.
[52] Tomita S, Kin A, Yazu M, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty with calcium phosphate cement in a simulated osteoporotic compression fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2003;8(2):192-197.
[53] Kayanja MM, Togawa D, Lieberman IH. Biomechanical changes after the augmentation of experimental osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the cadaveric thoracic spine. Spine J. 2005;5(1):55-63.
[54] Bai B, Jazrawi LM, Kummer FJ, et al. The use of an injectable, biodegradable calcium phosphate bone substitute for the prophylactic augmentation of osteoporotic vertebrae and the management of vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(15):1521-1526. |
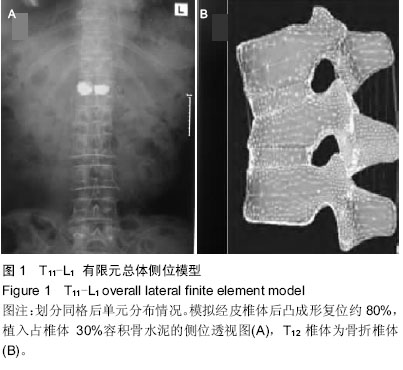
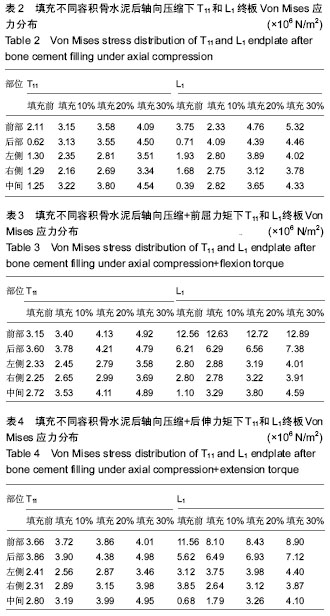
.jpg)
.jpg)