中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4304-4308.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.008
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
以线栓法构建脑梗死模型大鼠的微血管新生及电针干预效应
金哲峰,石 磊,杜元灏
- 天津中医药大学第一附属医院,天津市 300193
Effects of electroacupuncture intervention on angiogenesis in rat models of cerebral infraction constructed by suture method
Jin Zhe-feng, Shi Lei, Du Yuan-hao
- First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China
摘要:
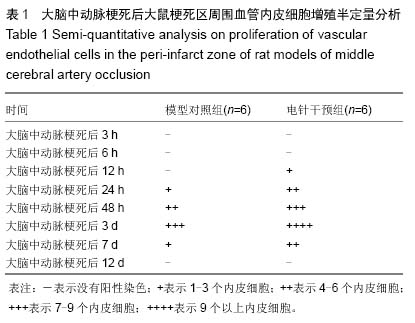
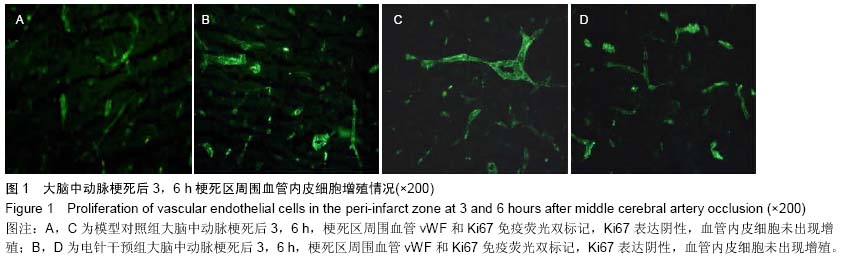
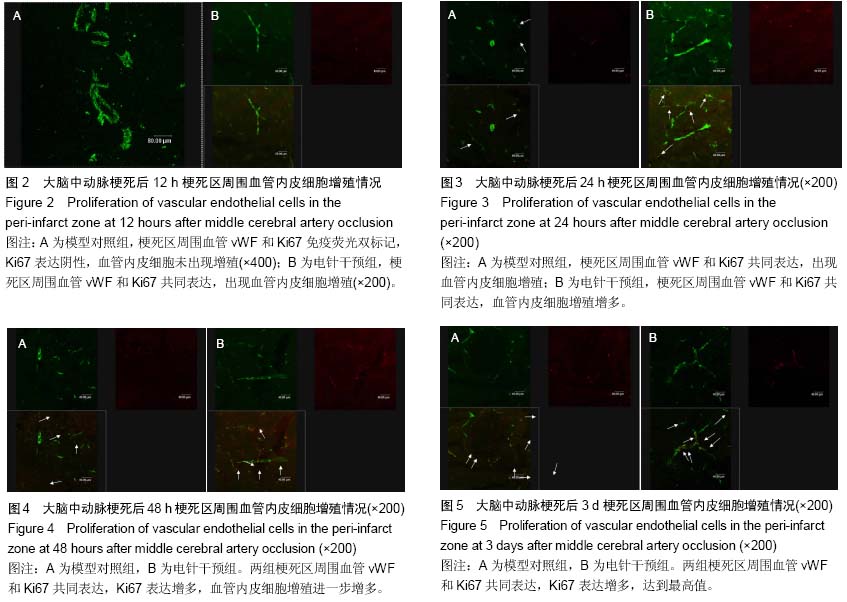
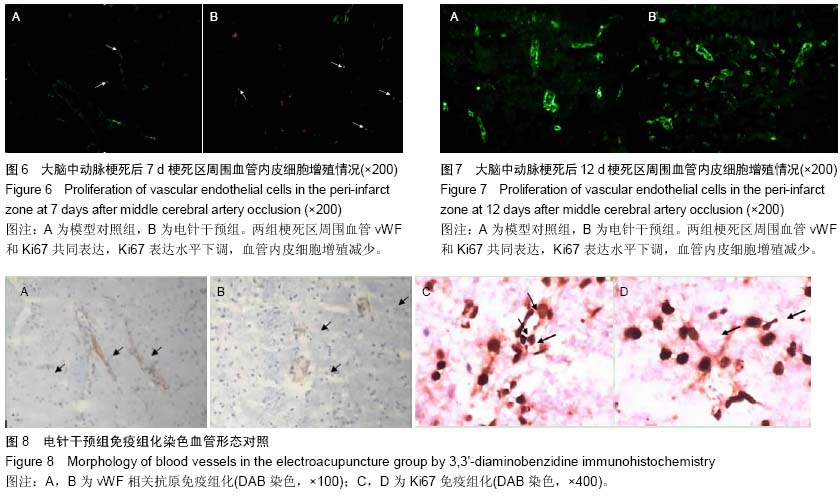
背景:脑梗死发生后缺血半暗带存在的状态决定了最终梗死灶的体积,在这一区域出现的选择性基因表达、蛋白合成减少、乳酸中毒和细胞毒性水肿,对神经细胞的抢救性治疗以及对神经血管单元的持续调节,成为后期神经功能恢复的结构和生理基础。 目的:以脑梗死后微血管新生过程为研究切入点,探索微血管新生随时间延续呈现的基本规律以及电针干预对局部血管增殖产生的影响。 方法:96只Wistar大鼠随机分为模型对照组和电针干预组,以线栓法复制大鼠大脑中动脉梗死模型,电针干预组在造模后即刻针刺人中穴,给予15 Hz,1 mA的电刺激,持续20 min。模型对照组同样抓取固定,但不进行任何治疗。在脑梗死后不同时间(3,6,12,24,48 h以及3,7,12 d)采用vWF、Ki67免疫荧光双标记检测血管的新生情况。 结果与结论:在大脑中动脉梗死后3,6,12 h,模型对照组梗死区周围无血管内皮细胞增殖标记,24 h出现血管内皮细胞增殖,48 h血管内皮细胞增殖增加,3 d时达到高峰,7 d时血管内皮细胞增殖水平下降,12 d时无血管内皮细胞增殖标记;在大脑中动脉梗死后3,6 h,电针干预组无血管内皮细胞增殖标记,12 h出现血管内皮细胞增殖,24,48 h血管内皮细胞增殖进一步增加,3 d时达到高峰,7 d时血管内皮细胞增殖水平下降,12 d时无血管内皮细胞增殖标记。与模型对照组比较,电针干预组血管内皮细胞增殖出现时间提前,血管内皮细胞增殖数量多于同时相模型对照组,而两组所有时相梗死区和梗死灶对侧半球均无血管内皮细胞增殖标记。结果表明电针干预可促进大脑中动脉梗死模型大鼠梗死区周围脑血管内皮细胞增殖,并将血管内皮细胞增殖出现时间提前,由此可改善脑梗死的预后。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
中图分类号: