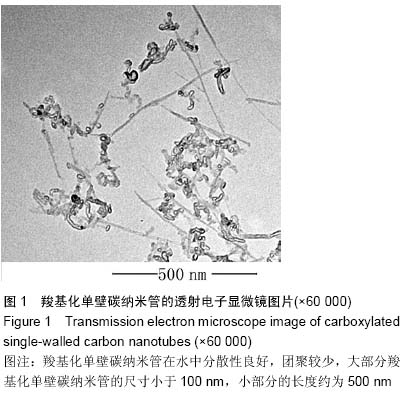
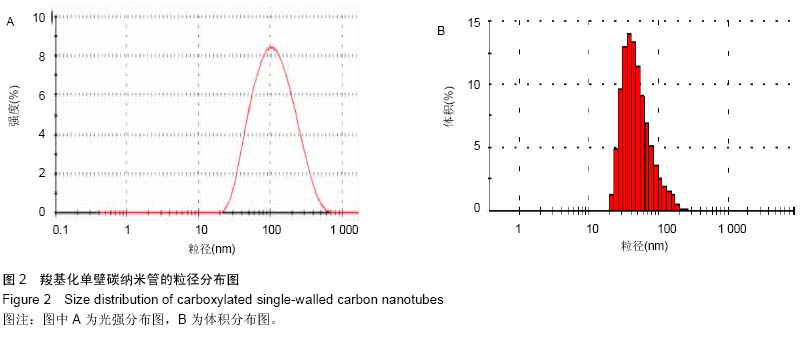
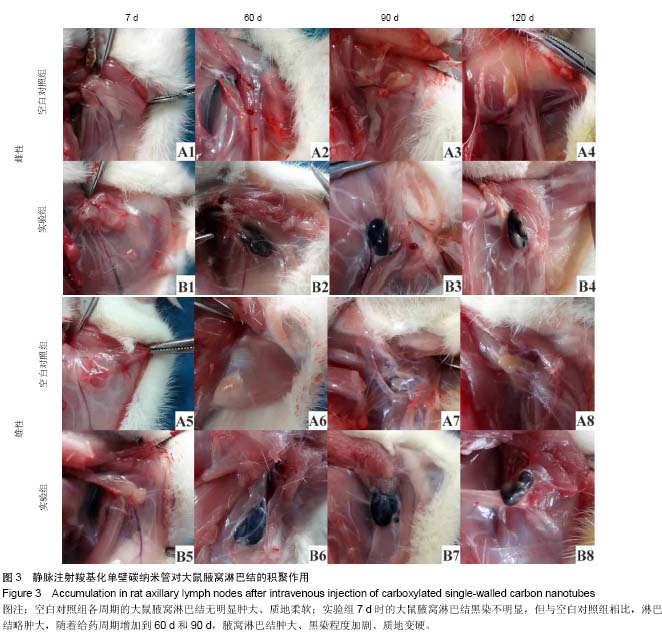
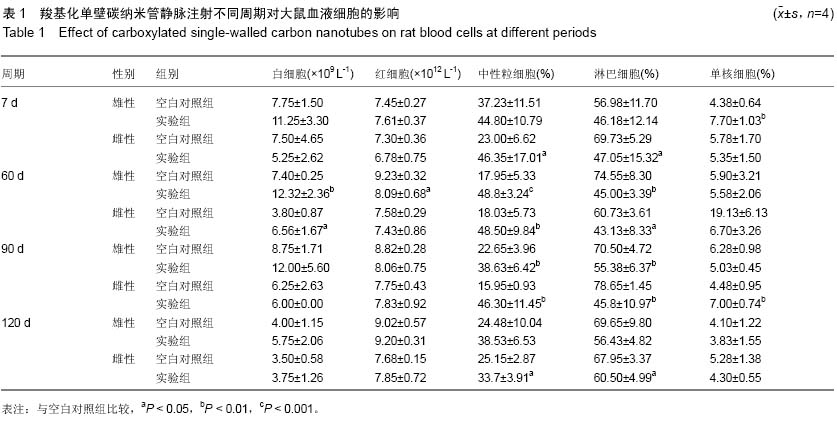
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (25): 3990-3995.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.25.011
• 膜生物材料 membrane biomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
静脉注射羧基化单壁碳纳米管在大鼠腋窝淋巴结的积聚
李苏宁1,秦 悦1,成晓静2,傅宣皓1,冯建海3,赖泽锋1,刘华钢1
- 广西医科大学,1药学院,
2医学实验中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;
3广西中医药大学药学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200
Accumulation of intravenously injected carboxylated single-walled carbon nanotubes in rat axillary lymph nodes
Li Su-ning1, Qin Yue1, Cheng Xiao-jing2, Fu Xuan-hao1, Feng Jian-hai3, Lai Ze-feng1, Liu Hua-gang1
- 1School of Pharmacy, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China;
2Medical Research Center, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China;
3School of Pharmacy, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
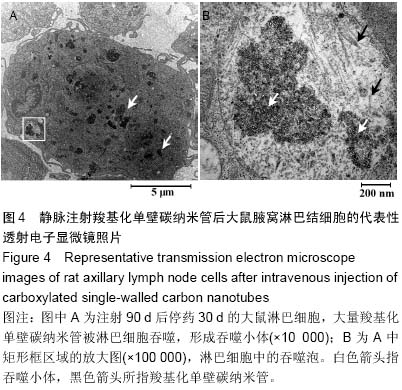
背景:基于碳纳米管的淋巴靶向示踪和治疗是肿瘤靶向诊疗的研究热点之一,评价碳纳米管对腋窝淋巴结的聚集作用,能够为开发淋巴特异性更高、生物兼容性更好的纳米示踪剂和药物载体提供实验依据。 目的:观察静脉注射羧基化单壁碳纳米管在SD大鼠腋窝淋巴结的积聚作用,并评价其对血液细胞的影响。 方法:将64只SD大鼠随机均分为两组,实验组尾静脉注射羧基化单壁碳纳米管2 mg/kg,空白对照组尾静脉注射5%葡萄糖溶液1 mL/kg,3次/周,设定7,60,90,120 d(120 d为给药90 d后停药30 d)共4个周期,每个周期结束时每组随机抽取8只大鼠,采集腹主动脉血液进行血常规检测,观察腋窝淋巴结变化,采集实验组120 d淋巴结标本进行透射电子显微镜观测。 结果与结论:与空白对照组相比,实验组7 d的腋窝淋巴结无明显黑染;随着给药周期的增加,实验组大鼠淋巴结肿大、质地变硬、黑染加深,伴随血液中性粒细胞百分数显著升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.001);停药30 d后,腋窝淋巴结缩小、黑染局部褪去,中性粒细胞百分数下降。停药30 d后,透射电子显微镜观测证实实验组大量羧基化单壁碳纳米管被淋巴细胞吞噬,形成大量吞噬泡。表明尾静脉注射羧基化单壁碳纳米管对SD大鼠腋窝淋巴结的短期靶向示踪作用较弱,长期静脉注射会逐渐在大鼠腋窝淋巴结形成积聚,并引起中性粒细胞增多;停止给药后,羧基化单壁碳纳米管能够被淋巴结缓慢清除。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: