| [1] Langer R,Tirrell DA.Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature.2004; 428(6982):487-492.
[2] Navarro M,Ginebra MP,Planell JA,et al.Development and cell response of a new biodegradable composite scaffold for guided bone regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2004; 15(4):419-422.
[3] Kim HW,Kim HE,Salih V.Stimulation of osteoblast responses to biomimetic nanocomposites of gelatin-hydroxyapatite for tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials.2005;26(25): 5221-5230.
[4] Sinha A,Das C,Sharma BK,et al.Poly (vinyl alcohol)- hydroxyapatite biomimetic scaffold for tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Biomimetic Supramol Sys.2007;27(1):70-74.
[5] Zhou YF,Hutmacher DW,Varawan SL,et al.In vitro bone engineering based on polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate composites.Polym Int.2007;56(3):333-342.
[6] Zhang RY,Ma PX.Poly(alpha-hydroxyl acids) hydroxyapatite porous composites for bone-tissue engineering. I. Preparation and morphology.J Biomed Mater Res.1999; 44(4):446-455.
[7] Slater SC,Gallaher T,Dennis D,et al.Polyhydroxybutyrate. Natural biocompatible and biodegradable polyesters produced by bacteria.J Bacteria.1988;170(10):4431-4436.
[8] Doyle C,Tanner ET,Bonfield W.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of polyhydroxybutyrate to and of polyhydroxybutyrate reinforced with hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials.1991;12(11): 841-847.
[9] Boeree NR,Dove J,Cooper JJ,et al.Development of a degradable composite for orthopaedic use: mechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite-polyhydroxybuty- rate composite material.J Biomaterials.1993;14(10):793-796.
[10] Barham PJ,Kelley A,Otnn EL,et al.Crystallization and morphology a bacterial thermoplastic:poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. J Mater Sci.1981;19:2781-2794.
[11] Ma ZW,Kotaki M,Yong T,et al.Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering.Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2527-2536.
[12] Taylor GI.Electrically driven jets. Proc R Soc London Ser A.1969;313:453-475.
[13] Fong H,Reneker DH.Electrospinning and formation of nano-fibers.In:Salem DR, editor. Structure formation in polymeric fibers. Munich: Hanser,2001:225-246.
[14] Huang ZM,Zhang YZ,Kotaki M.A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites.ComposSci Technol.2003;63:2223-2253.
[15] Deitzel JM,Kleinmeyer J,Harris DT.The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles.Polymer.2001;42:261-272.
[16] Demir MM,Yilgor I,Yilgor E,et al.Electrospinning of polyurethane fibers. Polymer.2002;43:3303-3309.
[17] Casper CL,Stephens JS,Chase D,et al.Using humidity and molecular weight to control the surface morphology of electrospun fibers.Abstr Pap Am Chems.2003;226: U430- U430, 496-POLY Part 2.
[18] Zong X,Kim K,Fang D,et al.Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer. 2002; 43(16):4403-4412.
[19] Liu W,Wu ZQ,Reneker DH.Structure and morphology of poly (meta-phenylene isophthalamide) nanofibers produced by electrospinning. Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc.2000;220: U260- U260.
[20] Deitzel JM,Kleinmeyer JD,Hirvonen JK.Controlled deposition of electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) fibers.Polymer.2001;42: 8163-8170.
[21] 方壮熙,张璐,韩涛,等.PHBV电纺纤维结构与形态的研究[J].高分子学报,2004,48(4):500-505.
[22] Barham PJ,Kelley A,Otnn EL,et al.Crystallization and morphology a bacterial thermoplastic: poly-3-hydroxybntyrate. J Mater Sci.1981;19:2781. |
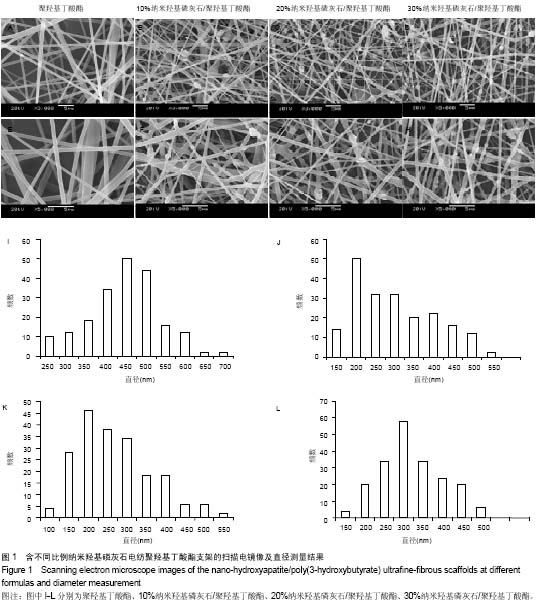
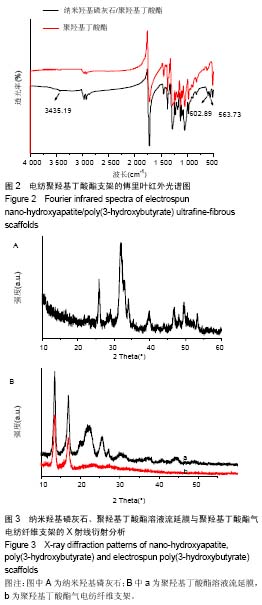
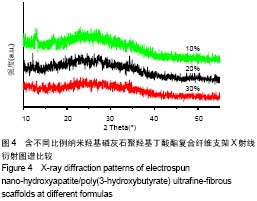
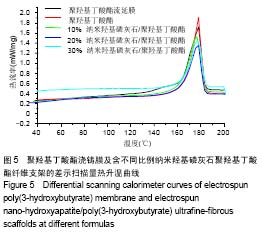
.jpg)