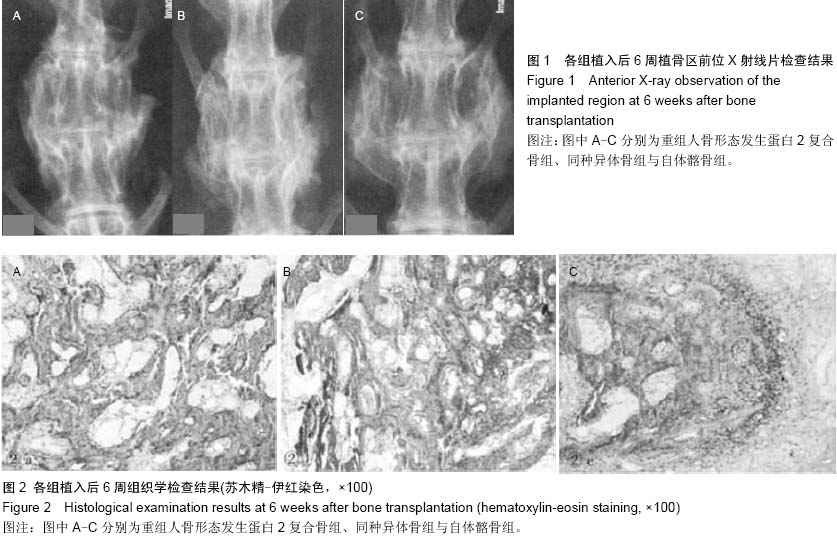
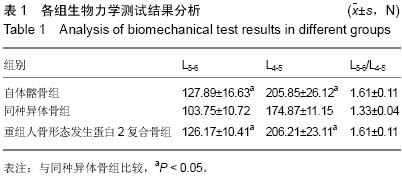
| [1] 杨毅,金格勒,唐周舟,等.复合骨在兔腰椎融合过程中相关基因表达调控的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(2):245-247.
[2] 唐周舟,金格勒,李忠伟,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2/异体骨复合骨用于兔腰椎融合的显微CT研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2009, 26(1):109-111.
[3] 金格勒,王武昌,曹力,等.rhBMP-2/异体骨复合骨应用于兔腰椎植骨融合的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(12): 1165-1168.
[4] 王磊磊,金格勒,任龙龙,等.不同植骨材料在腰椎融合过程中的应用及转化生长因子β的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(16):2885-2888.
[5] 金格勒,任龙龙,杨小丰,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2/异体骨复合骨用于兔腰椎融合的正电子发射计算机体层摄影-CT研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1065-1068.
[6] 王磊磊.rhBMP-2用于兔腰椎融合过程中相关因子的表达[D].新疆医科大学,2011.
[7] 李忠伟,金格勒,唐周舟,等.外源性重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2应用于兔腰椎植骨融合中细胞增殖的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2009,11(5):464-468.
[8] 金格勒,王武昌,曹力,等.rhBMP-2/异体骨复合骨用于兔腰椎融合的实验研究[C].//第二届全国骨关节结核病专题研讨会论文集, 2008:334-341.
[9] 杨毅.组织工程骨用于兔腰椎融合过程中相关基因表达[D].新疆医科大学,2010.
[10] 邓伟,金格勒,殷剑,等.磁共振监测骨形态发生蛋白2及异体骨体内植入的早期血管化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(50): 9331- 9336.
[11] 唐周舟.组织工程骨用于兔腰椎融合的BMP-2表达和显微CT研究[D].新疆医科大学,2009.
[12] 李忠伟.外源性rhBMP-2应用于兔腰椎植骨融合中细胞增殖的实验研究[D].新疆医科大学,2009.
[13] 王武昌,马原,金格勒,等.rhBMP-2用于兔腰椎融合的实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2009,32(8):1060-1062.
[14] Burkus JK.Surgical treatment of the painful motion segment:matching technology with indications.Spine.2005; 30(16Suppl):7-15.
[15] Kim DH,Louis J,Beta SC,et al.Bone graft in spinal fusion surgery. Cur Opin Orthop.2003;14:127-137.
[16] 唐周舟,金格勒,李忠伟,等.rhBMP-2/异体骨复合骨用于兔腰椎融合的显微CT研究[C].//第二届全国骨科修复与移植学术研讨会论文集,2008:314-322.
[17] 黄晖,杨志.骨形态发生蛋白在骨组织工程中的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(2):340-343.
[18] 金格勒,王武昌,盛伟斌,等.rhBMP-2/异体骨复合骨用于兔腰椎融合的实验研究[C].//中国科协第六届青年学术年会卫星会议-新疆第六届青年学术年会暨首届博士生论坛论文集,2006: 1089-1092.
[19] 朱志海,曹鹏,梁裕,等.腹腔镜下多孔自固化磷酸钙人工骨复合重组人骨形态发生蛋白2在山羊腰椎体间融合中的作用[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(21):1503-1506.
[20] 吴波文,李志忠,谭颖,等.壳聚糖-磷酸钙/rhBMP-2复合材料在兔腰椎椎间融合的应用[J].广东医学,2009,30(6):879-882.
[21] 崔福斋,廖素三,关凯,等.矿化胶原基骨材料与BMP-2复合用于兔腰椎横突间融合[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2003,1(1):1-5.
[22] 陈亮,顾勇,陈晓庆,等.丝素蛋白增强型磷酸钙复合rhBMP-2用于绵羊腰椎椎体间融合的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2010, 30(7):677- 683.
[23] 罗军,肖荣驰.复合人工骨用于兔腰椎横突间植骨的生物学评价[J].中国基层医药,2011,18(1):1-3.
[24] 李忠伟,金格勒,唐周舟,等.外源性rh-BMP2应用于兔腰椎植骨融合中细胞增殖的实验研究[C].//第二届全国骨科修复与移植学术研讨会论文集,2008:295-302.
[25] 马金梁,黄帆,汪洋,等.双表达重组腺病毒介导的骨形态发生蛋白2-9复合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66融合器用于山羊椎间融合的效果评价[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2012,38(6):1086-1090.
[26] 崔泳.rhBMP-2复合物与自体骨移植后腰椎融合率的系统评价[D].新疆医科大学,2007.
[27] 盛俊东,刘兴炎,白孟海,等.牛骨形态发生蛋白对骨质疏松性椎体骨折愈合过程中局部血管内皮生长因子表达的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(14):2695-2698.
[28] 袁振灿,郑燕平,刘新宇,等.不同植骨材料椎间融合效果的实验研究[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(3):276-279,283.
[29] 黄凯.脱钙骨基质纳米化条件及其复合重组人骨形态发生蛋白作为骨移植替代物的实验研究[D].第二军医大学,2011.
[30] 罗军.rhBMP-2/20%β-TCP/PDLLA(重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2/20%β-磷酸三钙/消旋聚乳酸)复合物用于腰椎后外侧融合的实验研究[D].桂林医学院,2010.
[31] 崔少千.BMP-2基因修饰的骨髓基质干细胞复合纳米骨促进兔腰椎融合的实验研究[D].中国医科大学,2007.
[32] 臧业峰,刘亚,邱玉金,等.兔腰椎融合术中BMP和bFGF对骨髓间充质干细胞的作用[J].潍坊医学院学报,2008,30(6):530-532.
[33] 袁振灿.不同植骨材料椎间融合效果的实验研究[D].山东大学, 2008.
[34] 肖荣驰,李宁宁,罗军,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白2人工骨复合物在腰椎横突间植骨融合中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(34):6697-6700.
[35] 马兴,胡蕴玉,熊卓,等.新型仿生活性人工骨诱导兔腰椎横突间脊柱融合研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(11):1387-1389.
[36] 李琦,曾炳芳.骨移植替代物在脊柱融合中应用研究进展[J].国外医学:骨科学分册,2005,26(1):49-51.
[37] 杨发军.rhBMP-2、HA及其复合物在兔腰椎后外侧融合的实验研究[D].北京大学,2001.
[38] Itoh H,Ebar S,Kamuar M,et al.Experiment lspinalufsion with ues of ecrombinnat humna bone morphogenetie Portein-2.Spine. 1999;24:1402-1415.
[39] Minmaide A,Kawkaami M,Hashizume H,et al.Evaluation of carriesr of bone moprhogenetic portein for spinalufsion. Spine. 2001;26:933-939.
|