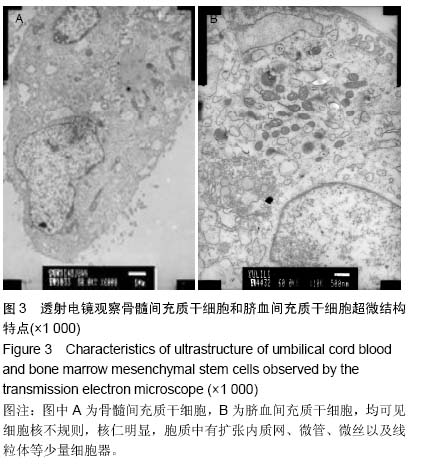
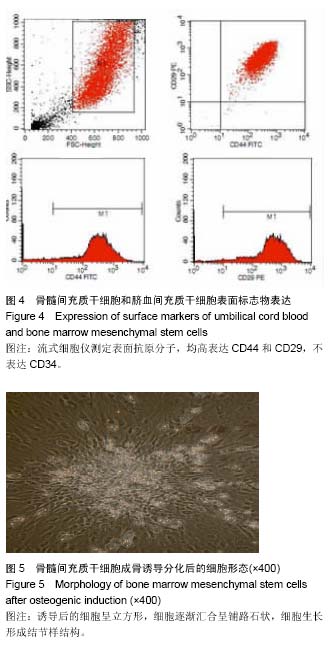
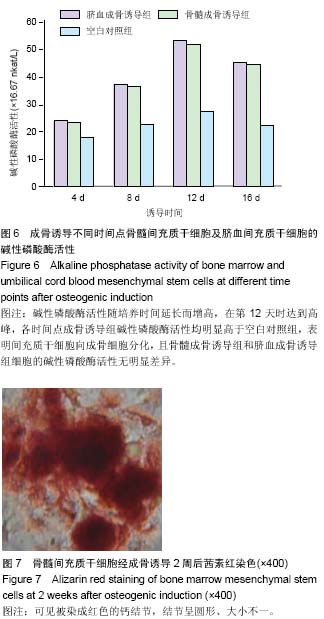
| [1] Tonti GA, Mannello F. From bone marrow to therapeutic applications: different behaviour and genetic/epigenetic stability during mesenchymal stem cell expansion in autologous and foetal bovine sera. Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(8): 1023-1032.
[2] 吴艳,于洁,张磊,等.再生障碍性贫血患儿骨髓间充质干细胞体外造血支持作用的研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2008,10(4): 455-459.
[3] Rogers I, Casper RF. Umbilical cord blood stem cells. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;18(6):893-908.
[4] Yang SE, Ha CW, Jung M, et al. Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells developed in cultures from UC blood. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(5):476-486.
[5] Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2001;226(6):507-520.
[6] Lee MW, Choi J, Yang MS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;320(1):273-278.
[7] Honig S. Osteoporosis - new treatments and updates. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2010;68(3):166-170.
[8] Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, et al. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell. 2001;107(4):513-523.
[9] Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature. 2000;407(6803): 530-535.
[10] Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ, et al. Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brains of albino rats--similarities to astrocyte grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3908-3913.
[11] Ventura C, Cantoni S, Bianchi F, et al. Hyaluronan mixed esters of butyric and retinoic Acid drive cardiac and endothelial fate in term placenta human mesenchymal stem cells and enhance cardiac repair in infarcted rat hearts. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14243-14252.
[12] 徐丽丽,匡弢,张佳.体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化:两种方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45): 7821-7826.
[13] 姚旺祥,裴国献,刘勇,等.兔胎盘源性间充质干祖细胞的分离方法比较[J].生物医学工程与临床,2007,11(2):85-87.
[14] 杨乃龙,张红艳,孙晓娟,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的体外分离纯化及成骨能力的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(11):824-828.
[15] 谷祖华,徐丽丽,苗志敏,等.脐血与骨髓间充质干细胞生物学性状的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36): 7078-7082.
[16] Deng W, Obrocka M, Fischer I, et al. In vitro differentiation of human marrow stromal cells into early progenitors of neural cells by conditions that increase intracellular cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282(1):148-152.
[17] Derubeis AR, Cancedda R. Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in bone engineering: limitations and recent advances. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(1):160-165.
[18] Chung CH, Golub EE, Forbes E, et al. Mechanism of action of beta-glycerophosphate on bone cell mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992;51(4):305-311.
[19] Bruder SP, Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE. Growth kinetics, self-renewal, and the osteogenic potential of purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive subcultivation and following cryopreservation. J Cell Biochem. 1997;64(2): 278-294.
[20] Tabata Y. Tissue regeneration based on tissue engineering technology. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2004;44(3):111-124.
[21] Phinney DG, Kopen G, Isaacson RL, et al. Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of commonly used strains of inbred mice: variations in yield, growth, and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1999;72(4):570-585.
[22] Aubin JE. Osteoprogenitor cell frequency in rat bone marrow stromal populations: role for heterotypic cell-cell interactions in osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1999; 72(3): 396-410.
[23] White A, Lamb PW, Barrett JC. Frequent downregulation of the KAI1(CD82) metastasis suppressor protein in human cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 1998;16(24):3143-3149.
[24] Kumar S, Mahendra G, Nagy TR, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of recombinant adeno-associated virus 2-transduced murine mesenchymal stem cells and development of an immunocompetent mouse model for ex vivo osteoporosis gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2004;15(12): 1197-1206.
[25] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3318-3325.
[26] Gruber R. Cell biology of osteoimmunology. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2010; 160(17-18): 438-445.
[27] 冉博.大鼠骨髓基质细胞在体外诱导成骨成脂分化的实验研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古医学院, 2009.
[28] Phinney DG. Biochemical heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cell populations: clues to their therapeutic efficacy. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(23):2884-2889.
[29] 魏毅东,徐亚伟,陈艳清,等.骨髓间质干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死的实验研究[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2008,29(4):13-16.
[30] Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, et al. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301.
[31] Kim SW, Han H, Chae GT, et al. Successful stem cell therapy using umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells for Buerger's disease and ischemic limb disease animal model. Stem Cells. 2006;24(6):1620-1626.
[32] Pittenger MF, Martin BJ. Mesenchymal stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics. Circ Res. 2004;95(1):9-20.
[33] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.
[34] 段轶滗,乔鑫,税青林.脐血间充质干细胞的培养及诱导分化的研究进展[J].西南军医,2009,11(5):939-941.
[35] Mori M, Sadahira Y, Awai M. Characteristics of bone marrow fibroblastic colonies (CFU-F) formed in collagen gel. Exp Hematol. 1987;15(11):1115-1120. |