设计:细胞学体内观察实验。
时间及地点:实验于2011年3月至2012年9月在中山大学北校区动物实验中心、中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院中心实验室及广东省人民医院(广东省医学科学院)中心实验室完成。
材料:
实验动物:雌性成年Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠83只(6-8周龄,平均体质量约250 g,SPF级)用于建立辐射小肠损伤模型;雌性SD幼鼠10只(三四周龄,体质量60-80 g,SPF级)用于获取骨髓间充质干细胞,均由中山大学北校区实验中心提供。所有动物经检疫符合实验动物标准。
细胞株:大鼠小肠隐窝上皮细胞IEC-6,购于American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)。辐射损伤的IEC-6用于诱导间充质干细胞,模拟间充质干细胞在小肠辐射炎症环境下的诱导激活。
主要试剂与材料:DMEM-F12培养基、胎牛血清(美国Hycolne公司);TrypLEExpress胰酶替代物(美国Invitrogen公司);小鼠抗大鼠CD29-FITC,CD34-FITC,CD44-FITC,CD45-FITC和CD90-FITC单克隆抗体(美国Biolegend公司);5 ku离心超滤管(Millipore公司);D-木糖试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所,批号20100801)。
实验方法:
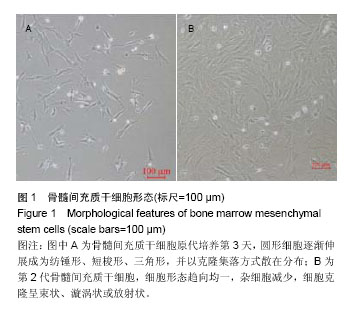
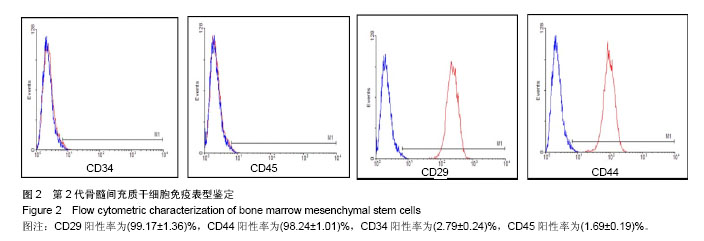
骨髓间充质干细胞的原代培养和鉴定:①原代分离:雌性SD幼鼠颈椎脱臼处死,完整提取双侧胫骨、股骨,无菌条件下暴露骨髓腔。用5 mL注射器反复冲洗骨髓腔内细胞,再用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的完全培养基重新悬浮细胞收集于25 cm2培养瓶中,置于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2、湿度90%的细胞培养箱内培养,此细胞记为原代。②原代培养:在文献[13]基础上加以改良,以改良的频繁换液法纯化骨髓间充质干细胞,4 h后首次全量更换培养液,随后3 d内每8 h全量更换1次。至原代的克隆集落长至约70%融合时(约3 d),用性质温和的TrypLEExpress胰酶替代物常温消化,避免胰酶-EDTA对原代骨髓间充质干细胞的消化损伤。收集原代分离后剩余的大鼠股骨和胫腓骨,钳碎后加入含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的完全培养基细胞培养箱孵育3 d,使用0.22 μm滤器过滤,此为原代和第1代细胞培养基,目的在于避免频繁换液造成骨髓间充质干细胞生长微环境破坏,以碎骨中丰富细胞因子模拟骨髓间充质干细胞生长微环境。原代细胞1︰1传代,37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2细胞培养箱继续培养,此为第1代。第2代以后细胞1︰3传代,随后使用常规含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的培养基继续培养。③免疫表型鉴定:待骨髓间充质干细胞生长至第2代时,取部分细胞悬液与CD29,CD34,CD45,CD90单抗充分混匀,室温避光孵育20 min,上流式细胞仪做细胞表型鉴定。
骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基的制备:①辐射炎症激活状态间充质干细胞条件培养基(MSC-CMIR)制备:辐射损伤的IEC-6用于诱导间充质干细胞,模拟间充质干细胞在小肠辐射炎症环境下的诱导激活。IEC-6细胞以3×104的密度种植于6孔Transwell板(0.4 μm;Costar,Cambridge,MA)上室,加入体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培育;第2代的骨髓间充质干细胞以5×104的密度接种于6孔Transwell板下室,加入体积分数为10%胎牛血清DMEM-F12培育,在辐射之前上室和下室分开培养。待细胞融合度达到70%-80%后,取上室的IEC-6细胞用PRIMUS®H直线加速器(X射线)以300 cGy/min的速率一次性照射,总剂量为10 Gy。辐射后上下室细胞共培养,弃去原来含血清的培养液,无血清DMEM-F12共培养24 h,随后将上室的IEC-6细胞移走,下室的骨髓间充质干细胞再次更换2 mL新鲜的无血清培养基培养48 h后收集该培养液,用5 ku离心超滤管3 000 r/min离心20 min;培养基浓缩约50倍,0.22 μm滤器过滤灭菌,此为辐射炎症激活状态间充质干细胞条件培养基,-20 ℃冷冻保存备用。②正常对照间充质干细胞条件培养基(MSC-CMNOR)制备:步骤同上,但不与辐射损伤IEC-6交互激活,共培养对象为正常IEC-6细胞,无血清DMEM-F12培养基孵育48 h后收集培养液,超滤后收集储存。
辐射损伤模型建立:大鼠麻醉后除腹部外均用铅砖覆盖屏蔽,采用PRIMUS® H直线加速器(X射线)以300 cGy/min的速率一次性照射,总剂量14.0 Gy进行腹部局部照射。随机将83只大鼠分为4组,正常对照组20只、辐射损伤组20只、MSC-CMNOR治疗组23只和MSC-CMIR治疗组20只。
小肠辐射损伤大鼠的治疗:造模后4 h内,各模型组大鼠采用尾静脉注射+植入式胶囊渗透压泵(Alzet microosmotic pumps,model 2ML1;DURECT Corp)腹腔植入的方式分别输注DMEM-F12、MSC-CMNOR和MSC-CMIR,每只大鼠每天尾静脉一次性注射200 μL,连续注射3 d,胶囊泵内含2 mL浓缩条件培养基,植入腹腔后以10 μL/h的速率匀速释放。
标本的留取:每组取10只大鼠,分别于造模后第1,3,5,7,14天处死后取材,开腹,将屈氏韧带以下的小肠段分为4份2.5 cm肠段,用PBS将肠腔冲洗干净,第1份投入液氮罐保存用于Real time-PCR检测小肠上皮干细胞标记物Lgr5及Bmi1(研究进展中);第2份用于Western Blots检测小肠上皮干细胞标记物Lgr5及Bmi1(研究进展中);第3份用40 g/L多聚甲醛固定,行苏木精-伊红染色常规病理检查和免疫组化检测;第4份用于制作标本行电镜观察超微结构改变以及用于检测短回路电流观察小肠分泌功能变化。上述各组大鼠于造模后第1,3,7天经内眦取血检测血清木糖水平。剩余每组约10只大鼠治疗后密切观察生存状态,记录死亡时间,进行生存分析。
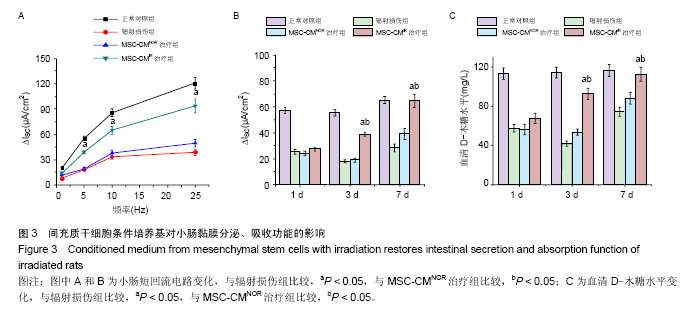
小肠黏膜分泌功能测定:采用恒温灌流装置体外测定小肠分泌功能,将肠段置于Ussing小室中进行电生理测定。黏膜标本垂直方向置于左、右两半小室的开口处,顶膜朝右,基膜朝左。加入充氧的Kreb缓冲液,实验参数:体积分数为95%O2,体积分数为5%CO2,pH 7.4,37 ℃。用连接于电位钳放大器的参考电极测量黏膜电位差,应用外来电流和液体电阻补偿使黏膜电位差被持续的钳在零电位,测得的跨上皮电流为短回路电流的变化(Short circuit variation, ?Isc)。通过检测?Isc评价小肠黏膜的分泌功能。
小肠黏膜吸收功能测定:采用木糖吸收实验检测小肠吸收功能。用去离子水将D-木糖溶解至50 g/L,按每只大鼠0.5 g/kg的剂量灌胃,2 h后取血,按照D-木糖测定试剂盒说明书测定各组大鼠血清木糖含量。
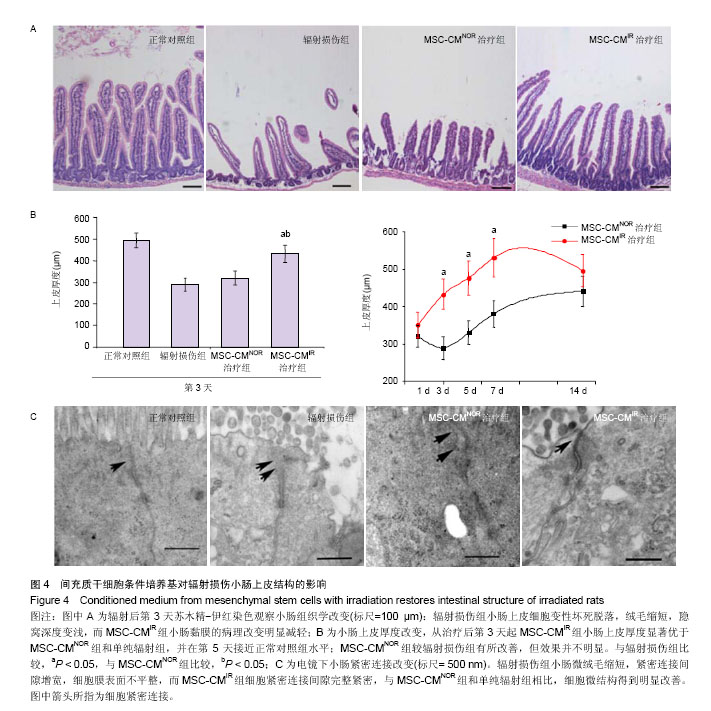
小肠黏膜形态学评估:①苏木精-伊红染色评估组织学改变:小肠组织石蜡切片常规脱蜡入水,苏木精染色5 min,返蓝30 min,伊红复染10 min,梯度乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封固,随后光镜观察,并测量小肠黏膜厚度。②透射电镜评估超微结构改变:标本投入4 ℃的3%戊二 醛-15 g/L多聚甲醛-0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液,用1%锇酸 4 ℃固定1.5 h。乙醇、丙酮脱水,环氧树脂618包埋。超薄切片90 mm,醋酸铀、枸橼酸铅各浅染1 min后,透射电镜观察紧密连接情况。
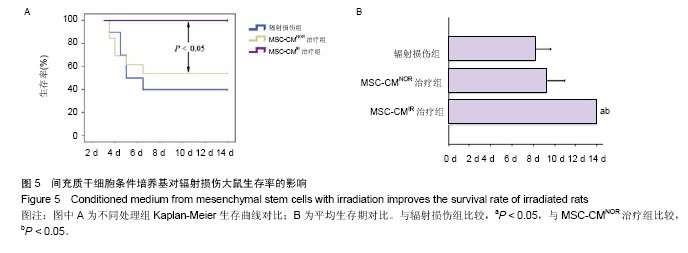
大鼠生存分析:治疗后每组约取10只密切观察大鼠生存状态,记录辐照后14 d内各组大鼠的存活情况,并用 Kaplan-Meier生存曲线作图。
主要观察指标:①骨髓间充质干细胞形态学和免疫学表型鉴定。②间充质干细胞条件培养基对辐射损伤小肠黏膜分泌、吸收功能的影响。③间充质干细胞条件培养基对辐射损伤小肠黏膜形态结构的影响。④间充质干细胞条件培养基对辐射损伤大鼠生存率的影响。
统计学分析:计量资料以x±s表示,均数的比较正态分布者组间比较用方差分析与t 检验,非正态分布者用秩和检验;生存分析采用Kaplan-Meier检验。采用SPSS 16.0统计软件进行统计分析,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。