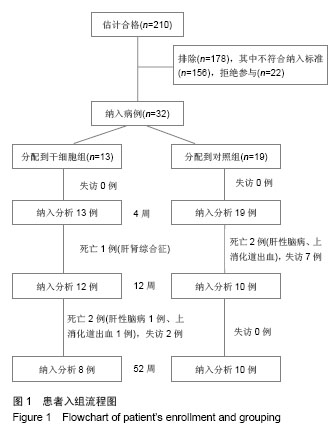
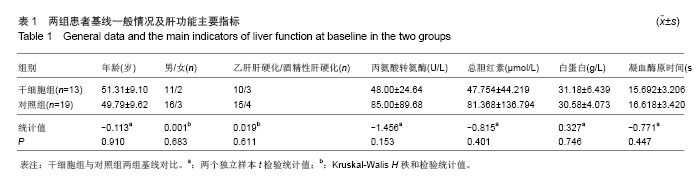
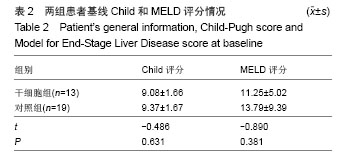
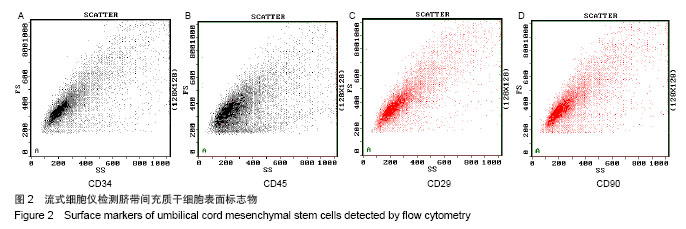
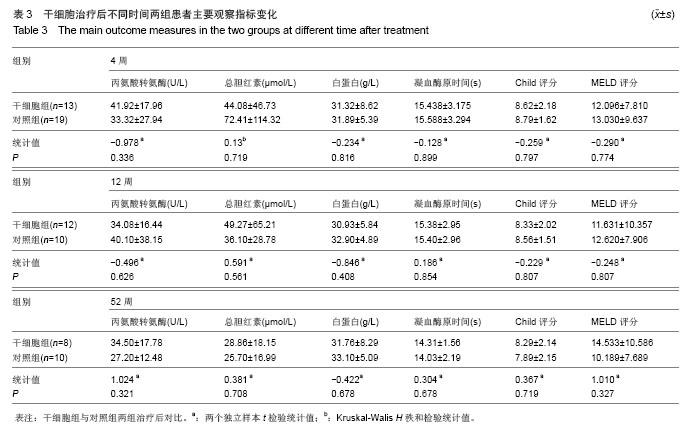
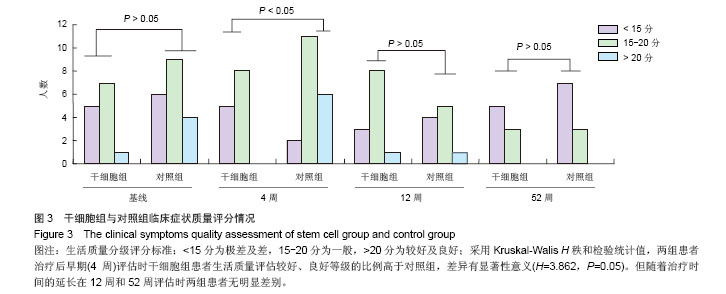
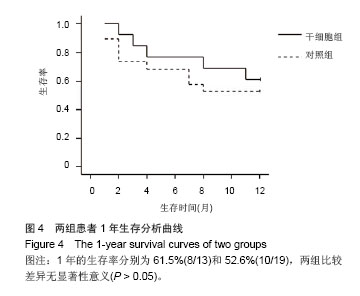
| [1]Gordon MY, Levicar N, Pai M, et al. Characterization and clinical application of human CD34+ stem/progenitor cell populations mobilized into the blood by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.Stem Cells. 2006;24(7):1822-1830.
[2]Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K, Mohyeddin-Bonab M, et al. Phase 1 trial of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis.Arch Iran Med. 2007;10(4):459-466.
[3]Liao X, AnCheng JY, Zhou QJ, et al.Therapeutic effect of autologous bone marrow-derived liver stem cells transplantation in hepatitis B virus-induced liver cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(123):406-409.
[4]Han Y, Yan L, Han G, et al.Controlled trials in hepatitis B virus-related decompensate liver cirrhosis: peripheral blood monocyte transplant versus granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor mobilization therapy.Cytotherapy. 2008;10(4):390-396.
[5]Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27 Suppl 2:112-120.
[6]Zoulim F, Radenne S, Ducerf C. Management of patients with decompensated hepatitis B virus associated [corrected] cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2008;14 Suppl 2:S1-7.
[7]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[8]Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD,et al.Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999;284 (5417): 1168-1170.
[9]Theise ND, Nimmakayalu M, Gardner R, et al. Liver from bone marrow in humans. Hepatology. 2000;32(1):11-16.
[10]Terai S, Sakaida I, Yamamoto N, et al. An in vivo model for monitoring trans-differentiation of bone marrow cells into functional hepatocytes.J Biochem. 2003;134(4):551-558.
[11]范敬静,李东良,何秀华,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞向肝样细胞的诱导及分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(14): 2491-2494.
[12]Li DL, He XH, Zhang SA, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. Pathobiology. 2013; 80(5):228- 234.
[13]何秀华,李东良,江军,等.移植途径对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞归巢及肝功能恢复的影响[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2011, 1(1): 57-62.
[14]李东良,何秀华,范敬静,等.骨髓动员与骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进极量肝切除大鼠肝再生作用的对照研究[J].解放军医学杂志, 2014,39(8):595-600.
[15]Chen H,Zhang Y,Yang ZJ,et al.Human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly-derived oligodendrocyte precursor-like cells for axon and myelin sheath regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(10): 890-899.
[16]van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo.Hepatology. 2008;47(5): 1634-1643.
[17]Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K, Bagheri M, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in decompensated cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2013;33(10):1490-1496. |