中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 213-219.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.02.010
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡中caspase-8基因变化与二乙酰吗啡的影响
苏丽萍1,刘小山2,王雪梅3,陈 晓1,张丽萍1,蒲红伟4,王治国5,王 华1,李凯超6
- 1新疆医科大学基础学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011;2广州中山大学医学院,法医学系,广东省广州市 510080;3新疆医科大学第一附属医院临床研究院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;4新疆医科大学第一附属医院科教中心,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011;5新疆维吾尔自治区司法鉴定科学技术研究所,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002;6新疆维吾尔自治区阿勒泰地区哈巴河县公安局法医室,新疆维吾尔自治区哈巴河县 836700
Effects of diacetylmorphine on caspase-8 gene in apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons
Su Li-ping1, Liu Xiao-shan2, Wang Xue-mei3, Chen Xiao1, Zhang Li-ping1, Pu Hong-wei4, Wang Zhi-guo5, Wang Hua1, Li Kai-chao6
- 1College of Basic Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Forensic Medicine, Medical School of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; 3Clinical Research Institute, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Center of Science and Education, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 5Institute of Forensic Science of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Bureau of Justice, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 6Forensic Room, the Public Security Bureau of Habahe County, Altay Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Habahe 836700, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
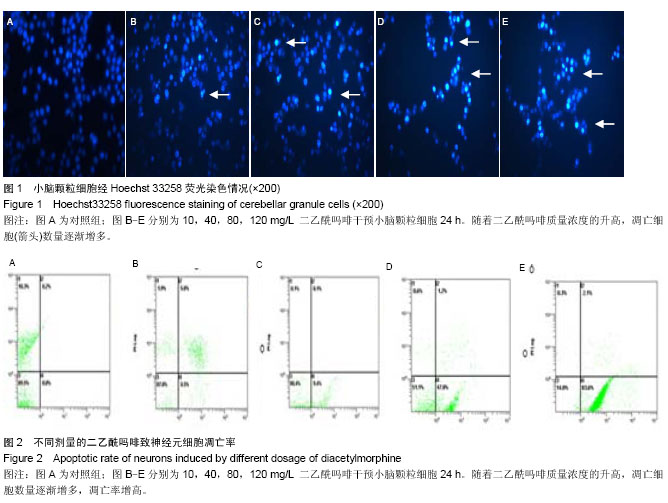
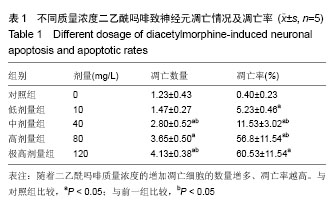
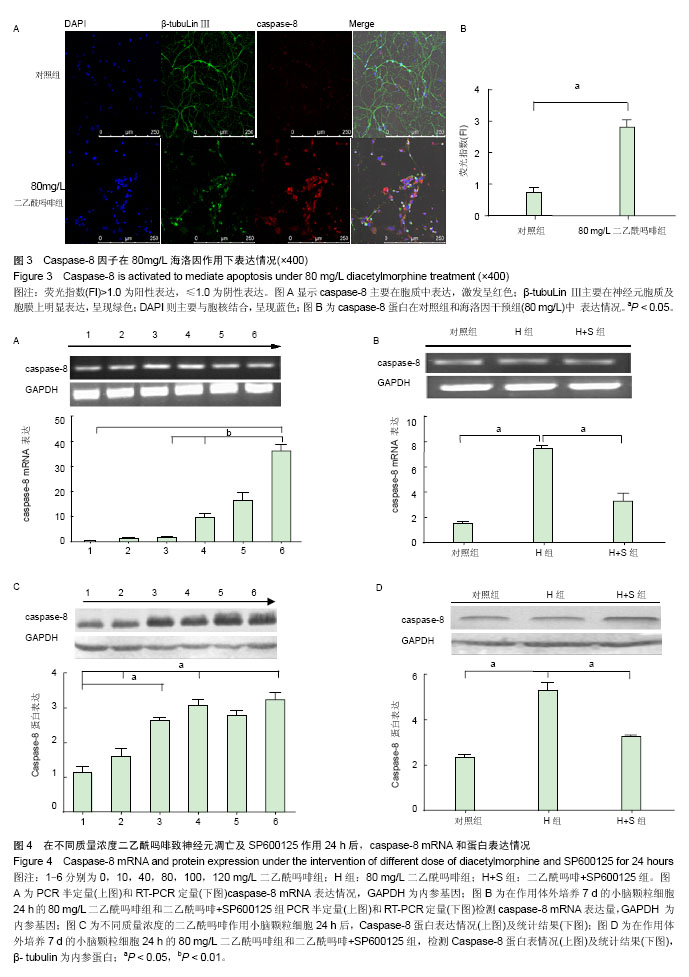
背景:半胱-天冬氨酸蛋白酶8(Caspase-8)是细胞凋亡过程起始的重要因子,二乙酰吗啡可致神经元细胞凋亡,其与二乙酰吗啡致小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡之间关系尚未见报道。 目的:验证二乙酰吗啡诱导小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡与caspase-8基因表达情况,明确caspase-8参与二乙酰吗啡致神经元凋亡过程。 方法:取出生7 d SD大鼠小脑颗粒神经元细胞进行体外培养,第7天后,以不同质量浓度的二乙酰吗啡(10,40,80,100,120 mg/L)和C-jun氨基末端激酶通路特异性抑制剂SP600125作用小脑颗粒神经元细胞24 h,并分对照组(0 mg/L二乙酰吗啡),80 mg/L二乙酰吗啡组,二乙酰吗啡+SP 600125组;采用Hoechst 33258 荧光染色观察细胞形态学改变,流式细胞仪测细胞凋亡率,免疫荧光、RT-PCR及Western Blotting检测caspase-8 mRNA和蛋白表达情况。 结果与结论:①施加不同质量浓度二乙酰吗啡致神经元细胞凋亡,凋亡细胞出现透亮深蓝色的凋亡小体,细胞核呈现固缩、凝聚及断裂,随给药浓度增加细胞凋亡率呈现升高趋势(P < 0.05)。②与对照组相比,在80 mg/L二乙酰吗啡干预时caspase-8 mRNA和蛋白表达明显明显表达(P < 0.05);caspase-8 mRNA随给药浓度增加呈现升高趋势(P < 0.05),二乙酰吗啡+SP600125组中caspase-8 mRNA和蛋白较80 mg/L二乙酰吗啡组明显下调(P < 0.05)。结果提示caspase-8参与二乙酰吗啡致小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡过程,同时也是C-jun氨基末端激酶信号通路中的重要候选促凋亡因子。
中图分类号: