设计:随机对照动物实验。
时间及地点:实验于2012年1月至2013年7月在辽宁医学院研究生学院骨科实验室完成。
材料:
实验动物:雄性新西兰大耳白兔25只,清洁级,体质量(3.0±0.5) kg,常规饲养,由辽宁医学院实验动物中心提供。实验过程中对动物的处置符合2009年《Ethical issues in animal experimentation》相关动物伦理学标准的条例。
实验试剂:DMEM、胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶、Ⅰ型胶原酶、Ⅱ型胶原酶、Western blot化学试剂盒、RT-PCR试剂盒、胎牛血清、腺病毒真核表达载体。
实验仪器:A101439电泳仪、电泳槽、1703940转膜仪、凝胶成像系统、CPH-500倒置相差显微镜、CX31-32C02荧光倒置显微镜。
溶液配制:
电泳缓冲液的配制:Tris-base 27 g,硼酸13.75 g,0.5 mol/L EDTA 10 mL加入475 mL三蒸水中,磁力搅拌器搅拌至完全溶解,加入三蒸水定容为500 mL,4 ℃保存,使用时稀释10倍。
1%琼脂糖凝胶的配制:电泳缓冲液稀释10倍后加入适量琼脂糖,在微波炉中加热使琼脂糖彻底稀释后将其放置于室温下,待其温度降至50 ℃时加入预先配制好的0.5 mg/L的溴化乙锭,使其与琼脂糖溶液充分混合,接着加入到胶槽内,放入电泳梳子。待琼脂糖溶液彻底成形后,取出电泳梳子。在电泳槽里加入适量的缓冲液,然后将准备好的胶槽置入其中,要注意缓冲液液面一定要高于所配制的凝胶高度。
磷酸盐缓冲液的配制:称取氯化钾0.2 g、氯化钠8.0 g、磷酸钠3.15 g、磷酸钾0.2 g,同时置于大量筒中,加入蒸馏水,使其总量1 L。用搅拌器使其充分溶解,保证配制的溶液pH值维持在中性。分装入试剂瓶中,瓶塞上插入注射针头,68 kPa高压锅中消菌30 min,取出后4 ℃保存备用。
DEPC水的配制:DEPC水1 mL加至999 mL蒸馏水中,充分混匀,所有RT-PCR反应中用到的相关用具均需用DEPC水浸泡过夜后使用。
0.1%Ⅰ型胶原酶的配制:PBS、Ⅰ型胶原酶、牛血清白蛋白的量分别为100 mL、100 mg、2.0 g。置于量筒中,充分混合,过滤,除菌后-20 ℃保存备用。
Western实验中所需试剂:①丙烯酰胺储存液:称取甲叉双丙烯酰胺和丙烯酰胺各1 g和29 g,加入量筒中,向其内倒入蒸馏水,使其刻度至1 L,一次性滤器滤过后,于避光环境下4 ℃保存。②普通缓冲液:电泳缓冲液的配制:900 mL蒸馏水加入Tris-base 30 g、SDS 10 g、Glycine 144 g,充分混合,调整pH为8.3,补充蒸馏水至1 L,4 ℃保存,稀释10倍使用;TBST缓冲液的配制:量取10×TBS 10 mL加入量筒中,倒入蒸馏水至刻度为100 mL,再加入0.1 mL的0.1%Tween-20,4 ℃保存待用。③10×TBS缓冲液的配制:称取NaCl和Tris-base各44 g和30 g,加入量筒中,倒入蒸馏水至刻度为0.4 L,调整pH为中性后再补充蒸馏水至刻度为0.5 L,4 ℃保存,稀释10倍使用。④电转缓冲液的配制:蒸馏水900 mL、Tris-base 30 g、SDS 3.7 g、Glycine 148 g,充分调匀,将pH值调节为8.0,4 ℃保存,稀释10倍后加入10%甲醇使用。⑤封闭液配制:100 mL TBST、脱脂奶粉5 g,4 ℃保存备用。
实验方法:
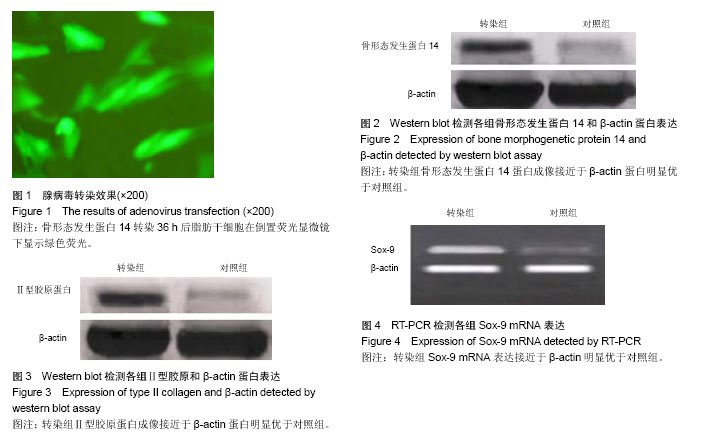
脂肪来源干细胞的提取、培养:新西兰大白兔1只,空气栓塞处死后,沿颈背部正中线切开,取颈后部脂肪组织置于无菌盘中,获得的脂肪组织应用PBS及青霉素、链霉素充分洗涤,使用无菌手术剪刀将洗涤后的脂肪组织剪碎成1 mm3左右大小;切碎的组织在37 ℃下加入0.15%Ⅰ型胶原酶酶促解离45 min。加入体积分数为10%胎牛血清培养基中止消化过程,再用200目滤网过滤,去除因脂肪组织块过大尚未消化的部分,滤后获得的细胞悬液装入离心管中,离心10 min,获得目的细胞;PBS充分中和清洗,应用滤网再次过滤,离心,弃上清;将沉淀的细胞以2×109 L-1的细胞浓度度重新悬浮于添加有体积分数为10%胎牛血清和10% KSR的DMEM/F12培养基中。细胞置于37 ℃恒温、湿润的细胞培养箱中孵育。5 d后首次换液,以后每三四天换液1次,待细胞长至80%左右时倒掉旧培养液,用PBS冲洗3次,向瓶中加入1 mL胰酶充分覆盖细胞,置于显微镜下观察,当大部分细胞漂浮于瓶中且悬浮的细胞突起消失时,加入含体积分数为10%胎牛血清培养基中和以终止消化,反复吹打瓶底贴壁细胞并将吹下来的细胞吹打均匀,补足培养基,放入细胞培养箱中。4 d后首次换液,以后每三四天换液1次。依上述传代方法将细胞传至第3代备用。
脂肪干细胞向脂肪细胞、软骨细胞、骨细胞分化:
向脂肪细胞分化:第3代脂肪干细胞用胰蛋白酶消化并按每25 cm2 5×105的密度平铺于培养瓶中。将细胞置于含 3 mL体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM/F12培养基中恒温孵育24 h。然后将细胞接种到脂肪诱导培养基中。每3 d更换1次培养液,直至培养两三周,采用红油O染色对其成脂分化进行评估。染色前将细胞用PBS漂洗,并在体积分数为4%的甲醛溶液中固定30 min,在30 ℃下置于2%的红油O试剂。最后应用PBS洗涤3次以去除过量的杂物。
向软骨细胞分化:第3代脂肪干细胞用胰蛋白酶消化并按每25 cm2 5×105的密度平铺于培养瓶中。将细胞置于含 3 mL体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM/F12培养基中恒温孵育24 h。然后将细胞接种到成软骨诱导培养基中。每3 d更换1次培养液,直至培养两三周。采用阿利辛蓝染色对其成软骨分化进行评估。染色前将细胞用PBS漂洗,并在体积分数为4%的甲醛溶液中固定30 min。在30 ℃室温下置于1%阿利辛蓝染色3 h。最后应用PBS洗涤3次以去除过量的杂物。
向骨细胞分化:第3代脂肪干细胞用胰蛋白酶消化并按每25 cm2 5×105的密度平铺于培养瓶中。将细胞置于含3 mL体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM/F12培养基中恒温孵育24 h。然后将细胞接种到成骨诱导培养基中培养。应用茜素红染色法对其成骨分化进行评估,染色前将细胞用PBS漂洗,并在体积分数为4%的甲醛溶液中固定15 min。在30 ℃室温下置于茜素红试剂中3-5 min。最后应用PBS洗涤3次以去除过量的杂物。
骨形态发生蛋白14转染脂肪干细胞:①转染组:取制备好的第3代脂肪干细胞接种于细胞培养板中,接种密度为5×105/孔,置于37 ℃恒温、湿润的细胞培养箱中孵育24 h,待细胞贴壁长满80%左右后吸去上清。Ad-CMV-BMP-14- IRES-hrGFP-1病毒液以感染复数(MOI)值为150转染脂肪干细胞,再补充2 mL无血清DMEM培养基。②对照组:在培养板中单纯接种脂肪干细胞不做任何处理。将所有培养板置于37 ℃恒温、湿润的细胞培养箱中孵育3 h,之后再加入含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基2 mL,继续培养两三天。腺病毒转染细胞成功后,于倒置显微镜下观察荧光成像清晰,细胞未发生变形且细胞聚合反应很少见。将转染成功的第3代脂肪干细胞接种于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2、100%饱和湿度培养箱中孵育5 d后,取标本进行检测。
Western blot检测骨形态发生蛋白14和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达:留取转染组、对照组贴壁生长的细胞应用PBS反复冲洗,加入蛋白裂解液裂解细胞,经离心后,测定上清液中蛋白含量;转膜,封闭,羊抗兔单克隆抗体作为一抗、辣根过氧化物酶标记的驴抗羊IgG作为二抗,使用Tween-20 PBS稀释,与滤膜共温浴,显色。将膜置于凝胶成像系统中以分析其目的条带与内参照,测各自的吸光度值。重复以上操作3次,计算净吸光度值。
RT-PCR检测Sox-9基因表达:TRIzol法提取转染组、对照组细胞总RNA:首先取1 μg RNA进行反转录,得到第1股cDNA,产物用于扩增目的基因。根据已知基因序列,设计合成引物序列,引物序列:sox-9上游5’-GAA CGC ACA TCA AGA CGG AG-3’,下游5’-TCT CGT TGA TTT CGC TGC TC-3’。所有反应结束后,取PCR反应液进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳40 min,观察电泳结果,置于凝胶成像系统中检测目的条带的吸光度值。重复以上操作3次。
Ⅰ型胶原海绵支架搭载脂肪干细胞复合体制备:转染 3 d后将脂肪干细胞消化为细胞悬液,将Ⅰ型胶原海绵支架(广州创尔生物技术有限公司)修整为直径4 mm长度2 mm的圆柱体放入培养瓶中,将两组细胞悬液用移液枪滴加至培养瓶中至完全覆盖支架,种植数量约为1×106个,恒温孵育3 d使细胞完全吸附于Ⅰ型胶原海绵支架中,制成细胞载体复合物。
兔关节软骨缺损修复:将24只成年新西兰大白兔随机分为3组,每组8只,20%速眠新1.0 mg/kg肌肉注射麻醉后,将大鼠仰卧固定于手术台上,双下肢备皮,常规消毒,铺无菌洞巾,取膝关节髌前内侧弧形切口,向两侧掀开皮肤、皮下筋膜,经髌骨内侧缘切开膝关节内侧支持韧带,将髌骨向外侧脱位,使股骨髁间髌骨滑车部充分显露,用直径4 mm钻头在股骨髁间窝关节负重面造成软骨及软骨下骨缺损,深度约3 mm,见创面有少量渗血为止。实验组于缺损区植入支架搭载经骨形态发生蛋白14转染后的脂肪干细胞,对照组于缺损区植入支架搭载脂肪干细胞,空白组植入单纯支架。分组处理后,复位髌骨,严密缝合膝关节囊内侧支持韧带,缝合皮肤切口,局部加压包扎。术后抗生素处理,肌注青霉素80×104 U,1次/d,连续3 d,分笼饲养,定期换药,按照标准动物饲养法饲养,于术后12周取材,对3组关节软骨分别进行大体观察、切片染色后组织学观察。
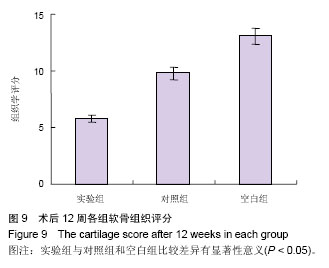
软骨修复的形态学检查及评分:于术后12周处死实验兔,取双侧膝关节股骨下端在内的关节面按Wakitani评分标准进行评价,该评分标准由5项指标组成:细胞形态完整性、基质染色是否清晰、表面是否光滑平整、新生软骨厚度及与周围是否融合。
软骨修复的组织学检查及评分:取手术修复的组织标本,PBS反复冲洗,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定1周,10% Formiacal脱钙液脱钙1个月,梯度乙醇脱水、二甲苯透明、常规石蜡包埋,选择损伤区中央部组织沿关节面横向做5 μm厚切片。对切片进行苏木精-伊红染色、甲苯胺蓝染色、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白免疫组化检测,显微镜下观察切片判断组织愈合情况。
.jpg)
苏木精-伊红染色:标本常规脱钙、石蜡包埋和切片,二甲苯及梯度乙醇脱蜡水化,分别进行苏木精染色,盐酸乙醇分化,促蓝液返蓝,伊红液染色,最后脱水、透明和封固,光镜下观察组织形态。
甲苯胺蓝染色:标本经甲醛固定、脱钙、石腊包埋、沿矢状面垂直于缺损区进行切片, 二甲苯及梯度乙醇脱蜡水化,甲苯胺蓝染色12 h,水洗2 min,脱水、透明和封固,光镜下观察组织形态。
免疫组织化学染色:PBS冲洗标本,滴加动物血清,封闭非特异性抗原,滴加一抗工作液37 ℃孵育1.0-2.0 h,冲洗,滴加二抗工作液室温下孵育30 min,再次冲洗后用显色剂显色冲洗,复染,脱水,透明,封固。
主要观察指标:①骨形态发生蛋白14转染的脂肪干细胞骨形态发生蛋白14和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达,Sox-9基因表达。②Ⅰ型胶原海绵支架搭载经骨形态发生蛋白14转染脂肪干细胞修复软骨缺损的形态学和组织学检测结果。
统计学分析:采用SPSS 18.0统计软件进行分析,数据以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用t 检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。

.jpg)