中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (30): 4810-4815.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.30.009
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
不同多肽修饰方法对纯钛微弧氧化膜层性能的影响
王 磊1,闫凤英2,陈建治3,王守彪4
- 1青岛大学医院口腔科,山东省青岛市 266071
2青岛科技大学材料科学与工程学院,山东省青岛市 266042
3浙江中医药大学口腔医学院,浙江省杭州市 310053
4青岛大学医学院基础学院,山东省青岛市 266071
Effect of different polypeptide modification methods on properties of micro-arc oxidation coatings covering pure titanium
Wang Lei1, Yan Feng-ying2, Chen Jian-zhi3, Wang Shou-biao4
- 1Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
2College of Material Science and Engineering, Qingdao University of Science & Technology, Qingdao 266042, Shandong Province, China
3College of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, Zhejiang Province, China
4School of Basic Medical Science, Medical College of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
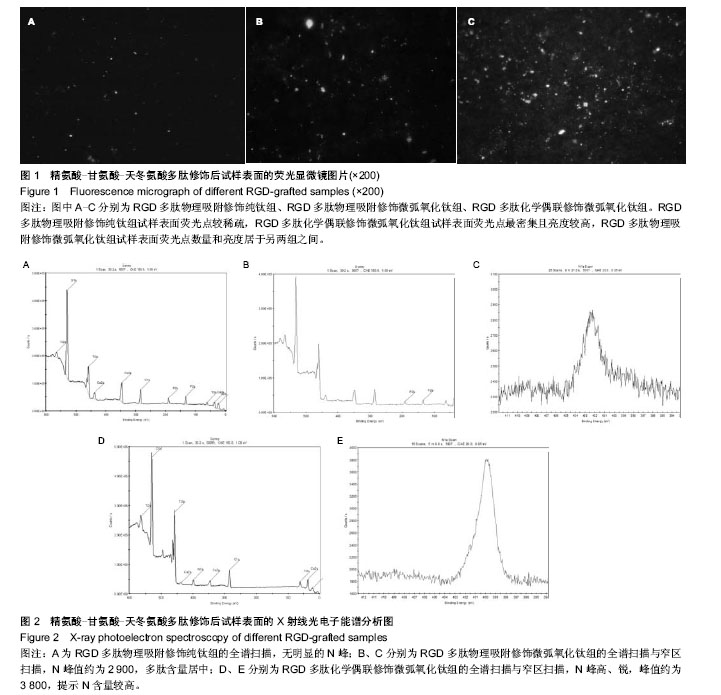
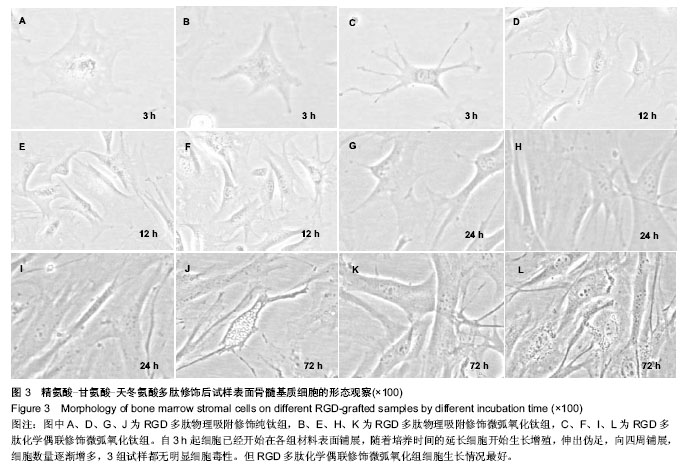
背景:理论上推测钛基-微弧氧化陶瓷膜-精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸(RGD)序列多肽的结合模式应具较好的力学和生物学性能。 目的:观察不同修饰方法固定RGD多肽后,钛基体微弧氧化膜层表面的微观结构和细胞增殖。 方法:取纯钛与微弧氧化纯钛试件共90枚,分3种方法固定RGD多肽,分别为RGD多肽物理吸附修饰纯钛组、RGD多肽物理吸附修饰微弧氧化组与RGD多肽化学偶联修饰微弧氧化组,每组30枚。应用荧光显微镜观察3组试件表面接枝效果,采用X射线光电子能谱扫描检测试样表面的RGD多肽含量。将3组试件分别与小鼠骨髓基质细胞培养,光镜观察各时间点的细胞黏附及增殖情况。 结果与结论:3组试样表面有大小不一、数量不等的绿色荧光亮点,在单位视野中,RGD多肽化学偶联修饰微弧氧化组荧光最强,提示此组试件接枝了更多的多肽。RGD多肽物理吸附修饰纯钛组试样表面仅含少量或微量多肽,RGD多肽物理吸附修饰微弧氧化组含多肽量居中,RGD多肽化学偶联修饰微弧氧化组含肽量最高。3组试件均无明显的细胞毒性,但RGD多肽化学偶联修饰微弧氧化组细胞生长情况最好。表明化学偶联法可以较好地将RGD多肽固定在含微弧氧化膜层的纯钛试样表面,无明显细胞毒性,有利于细胞的生长增殖。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)