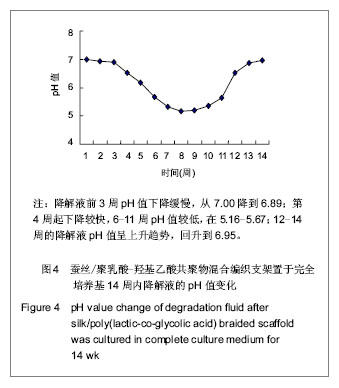
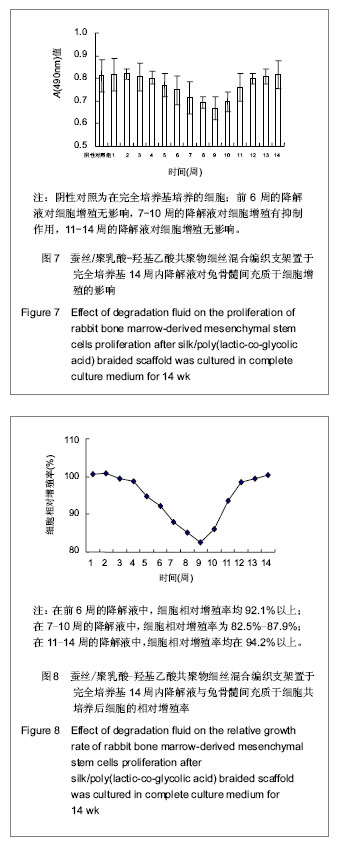
| [1] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi.2011;21(12):2868-2870.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等. 蚕丝-PLGA混合编织支架材料的细胞毒性检测[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2011,21(12):2868-2870.[2] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi.2012;22(2):237-239.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等. 蚕丝-PLGA编织支架生物安全性评价方法研究和应用[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2012,22(2):237-239.[3] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2006;10(13):44-46.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等.不同冻存时间与温度对兔骨髓基质干细胞存活率的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2006, 10(13):44-46.[4] Kim UJ,Park J,Kim HJ,et al.Three dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2775-2785.[5] Cao Y,Wang B.Biodegradation of silk biomaterials.Int J Mol Sci.2009;10(4):1514-1524.[6] Wang Y,Rudym DD,Walsh A,et al.In vivo degradation of three-dimensional silk fibroin scaffolds. Biomaterials.2008; 29(24-25):3415-3428.[7] Laurencin CT,Freeman JW.Ligament tissue engineering:an evolutionary materials science approach.Biomaterials. 2005; 26(36):7530-7536.[8] Altman GH,Horan RL,Lu HH,et al.Silk matrix for tissue engineered anterior cruciate ligaments.Biomaterials.2002; 23(20):4131-4141.[9] James AC,Helen HL,Frank KK,et al.Fiber-based tissue-engineered scaffold for ligament replacement:design considerations and in vitro evaluation. Biomaterials.2005; 26(13):1523-1532.[10] Mandal BB,Kundu SC.Biospinning by silkworms:Silk fiber matrices for tissue engineering applications.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(2):360-371.[11] Cooper JA Jr,Sahota JS,Gorum WJ 2nd,et al.Biomimetic tissue-engineered anterior cruciate ligament replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(9):3049-3054.[12] Seo YK,Yoon HH,Song KY,et al.Increase in cell migration and angiogenesis in a composite silk scaffold for tissue-engineered ligaments.J Orthop Res.2009;27(4): 495-503.[13] Fan H,Liu H,Toh SL,et al.Anterior cruciate ligament regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and silk scaffold in large animal model. Biomaterials.2009;30(28):4967-4977.[14] Li M,Ogiso M,Minoura N.Enzymatic degradation behavior of porous silk fibroin sheets.Biomaterials.2003;24(2):357-365.[15] Wang Y,Kim HJ,Karageorgiou V,et al.Stem cell-based tissue engineering with silk biomaterials. Biomaterials.2006;27(36): 6064-6082.[16] Fan H,Liu H,Wong EJ,et al.In vivo study of anterior cruciate ligament regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and silk scaffold. Biomaterials.2008;29(23):3324-3337.[17] Park BH,Zhou L,Jang KY,et al.Enhancement of tibial regeneration in a rat model by adipose-derived stromal cells in a PLGA scaffold.Bone.2012;51(3):313-323.[18] van Eijk F,Saris DB,Fedorovich NE,et al.In vivo matrix production by bone marrow stromal cells seeded on PLGA scaffolds for ligament tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(10):3109-3117.[19] van Eijk F,Saris DB,Creemers LB,et al.The effect of timing of mechanical stimulation on proliferation and differentiation of goat bone marrow stem cells cultured on braided PLGA scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(8):1425-1433.[20] Vaquette C,Slimani S,Kahn CJ,et al.A poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)knitted scaffold for tendon tissue engineering:an in vitro and in vivo study.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2010;21(13): 1737-1760.[21] Urita Y,Komuro H,Chen G,et al.Evaluation of diaphragmatic hernia repair using PLGA mesh-collagen sponge hybrid scaffold:An experimental study in a rat model.Pediatr Surg Int.2008;24(9):1041-1045.[22] Wang X,Sui S.Pulsatile culture of a poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) sandwiched cell/hydrogel construct fabricated using a step-by-step mold/extraction method.Artif Organs.2011; 35(6): 645-655.[23] Jenner JM,van Eijk F,Saris DB,et al.Effect of transforming growth factor-beta and growth differentiation factor-5 on proliferation and matrix production by human bone marrow stromal cells cultured on braided poly lactic-co-glycolic acid scaffolds for ligament tissue engineering. Tissue Eng.2007; 13(7):1573-1582.[24] Li S,Wu H,Hu XD,et al.Preparation of electrospun PLGA-silk fibroin nanofibers-based nerve conduits and evaluation in vivo. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol.2012;40(1-2): 171-178.[25] Sahoo S,Toh SL,Goh JC.PLGA nanofiber-coated silk microfibrous scaffold for connective tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;95(1):19-28.[26] Sahoo S,Toh SL,Goh JC.A bFGF-releasing silk/PLGA-based biohybrid scaffold for ligament/tendon tissue engineering using mesenchymal progenitor cells.Biomaterials. 2010;31 (11): 2990-2998.[27] Shao HJ,Chen CS,Lee IC,et al.Designing a three-dimensional expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold for tissue engineering.Artif Organs.2009;33(4): 309-317.[28] Sahoo S,Ouyang H,Goh JC,et al.Characterization of a novel polymeric scaffold for potential application in tendon/ligament tissue engineering.Tissue Eng.2006;12(1):91-99.[29] Stoll C,John T,Endres M,et al.Extracellular matrix expression of human tenocytes in three-dimensional air-liquid and PLGA cultures compared with tendon tissue:implications for tendon tissue engineering.J Orthop Res.2010;28(9):1170-1177.[30] Heidemann W,Jeschkeit-Schubbert S,Ruffieux K,et al.pH-stabilization of predegraded PDLLA by an admixture of water-soluble sodiumhydrogenphosphate--results of an in vitro- and in vivo-study.Biomaterials.2002;23(17):3567-3574. |




.jpg)