| [1] Monaco JL, Lawrence WT. Acute wound healing: An overview. Clinics in Plastic Surgery.2003; 30(1): 1-12.[2] Whitney JD. Overview: Acute and Chronic Wounds. Nursing Clinics of North America.2005; 40(2): 191-205.[3] Williams RL, Sroussi HY, Abercrombie JJ, et al. Synthetic decapeptide reduces bacterial load and accelerates healing in the wounds of restraint-stressed mice. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2012; 26(4):588-596.[4] Tian X, Zhang Z, Wang S ,et al. Copper–taurine (CT): A potential organic compound to facilitate infected wound healing. Medical Hypotheses.2009; 73(6):1048-1050. [5] de Romaña DL, Olivares M, Uauy R, et al. Risks and benefits of copper in light of new insights of copper homeostasis. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology. 2011; 25(1): 3-13.[6] Zhang NL,Liu JH,Sun FC.Shijie Yuansu Yixue. 2007,14(1): 41-43.张奶玲,刘景华,孙凤春.铜与人体健康的关系[J].世界元素医学, 2007,14(1): 41-43.[7] Hou JY,Hu XD.Siliao Yanjiu. 2010;1: 39-40.侯江泳,胡向东. 微量元素铜在动物机体中的作用研究进展[J].饲料研究, 2010,1: 39-40.[8] Shen J,Jiang QY,Zhong GQ.Huagong Jinzhan. 2006;6: 634-638.沈娟,蒋琪英,钟国清.牛磺酸配合物的合成与应用研究进展[J].化工进展, 2006,6: 634-638.[9] Dang DB, An B, Niu WJ, et al. Assembly of one novel polyoxometalate-based inorganic–organic compound from copper-Schiff base building block: Synthesis, crystal structure and spectral properties. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy. 2012; 91: 338-344.[10] Chattopadhyay T, Kogiso M, Asakawa M, et al. Copper(II)-coordinated organic nanotube: A novel heterogeneous catalyst for various oxidation reactions. Catalysis Communications. 2010;1(25) : 9-13.[11] Doan K, Bronaugh RL, Yourick JJ. In vivo and in vitro skin absorption of lipophilic compounds, dibutyl phthalate, farnesol and geraniol in the hairless guinea pig. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010; 48(1): 18-23. [12] NCCLS/CLIS.Performence standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing [M]. Fifteenth Inform Suppl.M100-S15, 2005:44-52.[13] Uppal SK, Ram S, Kwatra B, et al.Comparative evaluation of surface swab and quantitative full thickness wound biopsy culture in burn patients. Burns. 2007; 33(4): 460-463.[14] Liu ZZ,Chen ZG,Sun TZ,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2009; 18(3):328-331.刘丈忠,陈志刚,孙同柱,等. 大鼠深Ⅱ度烫伤创面愈合中血管形成与血流变化特点[J]. 中国美容医学,2009,18(3):328-331.[15] Park E, Lee SM, Jung IK,et al. Effects of genistein on early-stage cutaneous wound healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 410(3): 514-519.[16] Lehtola MJ, Miettinen IT, Keinänen MM, et al.Microbiology, chemistry and biofilm development in a pilot drinking water distribution system with copper and plastic pipes. Water Research. 2004; 38(17): 3769-3779.[17] Borkow G, Gabbay J. Copper as a biocidal tool. Curr Med Chem. 2005; 12:2163-2175.[18] Borkow G, Zatcoff RC, Gabbay J.Reducing the risk of skin pathologies in diabetics by using copper impregnated socks. Medical Hypotheses. 2009; 73(6): 883-886.[19] Sen CK, Khanna S, Venojarvi M, et al.Copper-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression and wound healing.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2002; 282(5): H1821-H1827. [20] Lansdown AB.Metallothioneins: potential therapeutic aids for wound healing in the skin. Wound Repair Regen. 2002; 10:130-132.[21] Mel'nikova VI, Izvol'skaia MS, Voronova SN,et al. Reparative regeneration of rat skin under influence of hollow cathode lamp (HCL) with manganese and copper line spectrum emission. Tsitologiia. 2010; 52(3):204-210.[22] Abe K,Matsuki N.Measurement of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction activity and lactate dehydrogenase release using MTT. Neurosci. Res.2000; 38(4):325-329.[23] Hamid R, Rotshteyn Y, Rabadi L, et al. Comparison of Alamar blue and MTT assays for high through-put screening. Toxicol. In Vitro. 2004; 18(5): 703-710.[24] Zhou LG.Beijing:Zhongguo Nongye Kexue Jishu Chubanshe. 2005: 63-85.周立刚.植物抗菌化合物[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社, 2005: 63-85. |
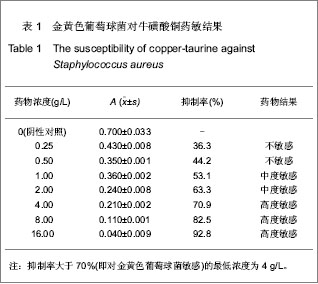
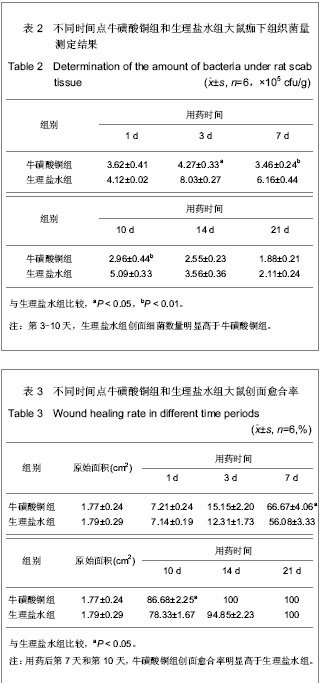
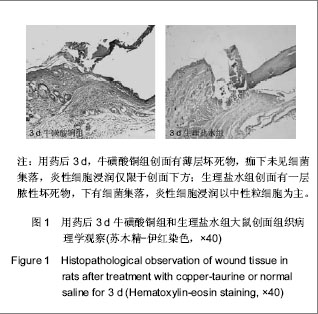
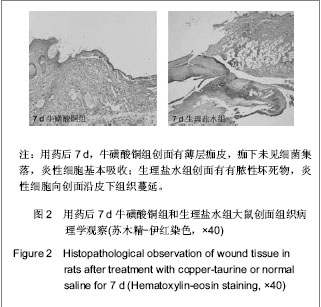

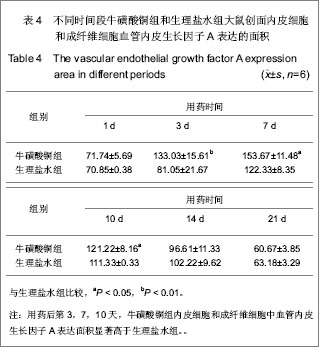
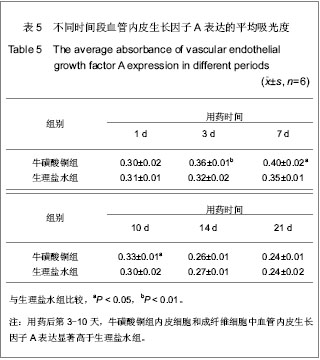
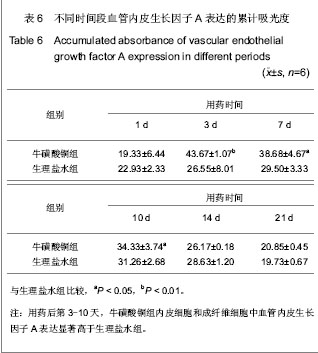

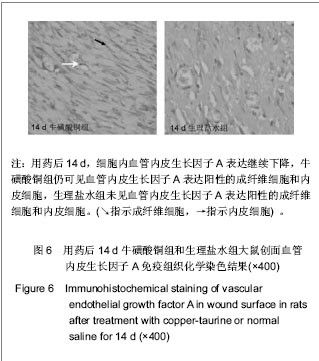
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 表示。P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义,P < 0.01为差异有非常显著性意义。
表示。P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义,P < 0.01为差异有非常显著性意义。