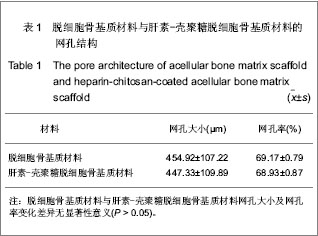
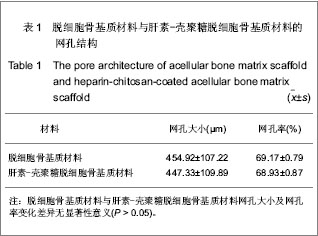
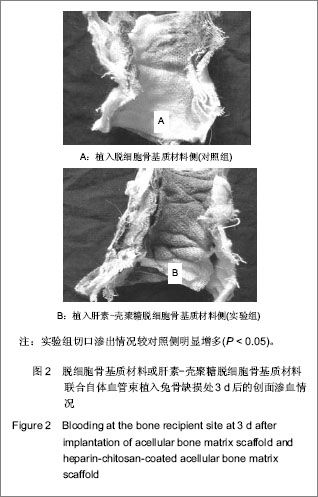
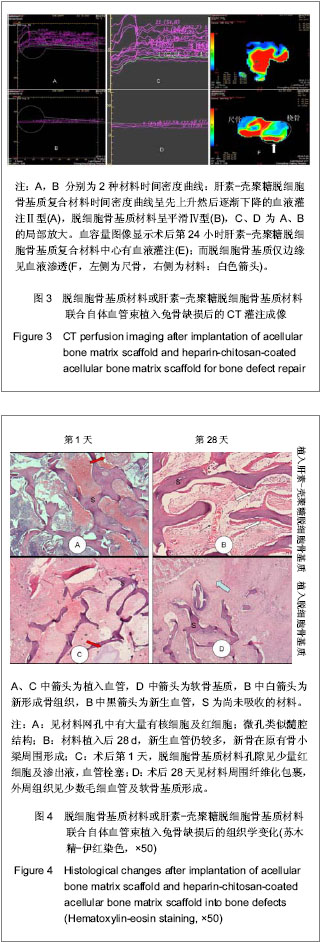
| [1] Reichert JC,Carvalho C,Mulhaupt R,et al.The challenge of establishing preclinical models for segmental bone defect research.Biomaterials.2009;30(12):2149-2163.[2] Lasanianos NG,Kanakaris NK,Giannoudis PV.Current management of long bone large segmental defects. Orthopaed Trauma.2010;24(2):149-163.[3] Ikada Y.Challenges in tissue engineering.J R Soc Interface. 2006;3(10):589-601.[4] Griffith LG,Naughton G. Tissue engineering- current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science.2002;295: 1009-1014.[5] Khetani SR,Bhatia SN. Engineering tissues for in vitro applications.Curr Opin Biotechnol.2006;17:524-531.[6] MacNeil S. Progress and opportunities for tissue-engineered skin. Nature. 2007;445:874-880.[7] Jain RK,Au P,Tam J,et al.Engineering vascularized tissue. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(7):821-829.[8] Rouwkema J,Rivron NC,van Blitterswijk CA.Vascularization in tissue engineering.Trends Biotechnol.2008;26:434-441.[9] Demirdogen B,Elcin AE,Elcin YM.Neovascularization by bFGF releasing hyaluronic acid-gelatin microspheres: in vitro and in vivo studies.Growth Factors.2010;28(6):426-436.[10] Laschke MW,Rucker M,Jensen G,et al.Improvement of vascularization of PLGA scaffolds by inosculation of in situ-preformed functional blood vessels with the host microvasculature. Ann Surg.2008;248(6):939-948.[11] Chen X,Aledia AS,Ghajar CM,et al.Prevascularization of a fibrin-based tissue construct accelerates the formation of functional anastomosis with host vasculature. Tissue Eng A. 2009;15:1363-1371.[12] Lokmic Z,Stillaert F,Morrison WA,et al. An arteriovenous loop in a protected space generates a permanent, highly vascular, tissue-engineered construct. J FASEB.2007;21(2):511-522.[13] Polykandriotis E,Arkudas A,Beier JP,et al. Intrinsic axial vascularization of an osteoconductive bone matrix by means of an arteriovenous vascular bundle. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120:855-868.[14] Novosel EC,Kleinhans C,Kluger PJ.Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Del Rev.2011;63 (4-5): 300-311.[15] Gorbet MB,Sefton MV.Biomaterial associated thrombosis: roles of coagulation factors, complement, platelets and leukocytes.Biomaterials. 2004;25(26):5681-5703.[16] Meng S,Liu ZJ,Shen L.The effect of a layer-by-layer chitosan-heparin coating on the endothelialization and coagulation properties of a coronary stent system. Biomaterials.2009;30:2276-2283.[17] Sun XJ,Peng W,Ren ML,et al.Heparin-chitosan-coated acellular bone matrix enhances perfusion of blood and vascularization in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(19-20):2369-2378.[18] Shastri VP. Future of regenerative medicine: challenges and hurdles. Artif Organs.2006;30(10): 828-834.[19] Borselli C,Ungaro F,Oliviero O,et al.Bioactivation of collagen matrices through sustained VEGF release from PLGA microspheres. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(1):94-102.[20] Yang J,Zhou W,Zheng W,et al. Effects of myocardial transplantation of marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected with vascular endothelial growth factor for the improvement of heart function and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Cardiology.2007; 107(1):17-29.[21] Sekine H,Shimizu T,Hobo K,et al.Endothelial cell coculture within tissue-engineered cardiomyocyte sheets enhances neovascularization and improves cardiac function of ischemic hearts.Circulation.2008;118: S145-S152.[22] Tanaka Y,Tsutsumi A,Crowe DM,et al.Generation of an autologous tissue (matrix) flap by combining an arteriovenous shunt loop with artificial skin in rats: preliminary report. Br J Plast Surg.2000;53(1):51-57.[23] Yang J,Yamato M,Shimizu T,et al. Reconstruction of functional tissues with cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28(34): 5033-5043.[24] Santos MI,Tuzlakoglu K,Fuchs S,et al.Endothelial cell colonization and angiogenic potential of combined nano- and micro-fibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008;29(32):4306-4313.[25] Nilsson PH, Engberg AE, Bäck J,et al.The creation of an antithrombotic surface by apyrase immobilization.Biomaterials.2010;31(16):4484-4491.[26] 26.Sperling C,Salchert K,Streller U,et al.Covalently immobilized thrombomodulin inhibits coagulation and complement activation of artificial surfaces in vitro. Biomaterials.2004;25(21):5101-5113.[27] Venkatesan J,Kim SK. Chitosan composites for bone tissue engineering--an overview. Mar Drugs.2010; 8(8): 2252-2266.[28] Vogler EA,Siedlecki CA. Contact activation of blood–plasma coagulation. Biomaterials.2009;30:1857-1869.[29] Sun XJ,Wang ZG,Zhu PF,et al.Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2005;21(11):833-837.孙新君,王正国,朱佩芳,等.脱细胞骨基质材料的特性及生物安全性观察[J].中华创伤杂志, 2005,21(11);833-837.[30] Kujawa P,Schmauch G,Viitala T,et al. Construction of viscoelastic biocompatible films via the layer-by-layer assembly of hyaluronan and phosphorylcholine-modified chitosan.Biomacromolecule.2007;8:3169-176.[31] Qiao K,Liu H,Hu N.Layer-by-layer assembly of myoglobin and nonionic poly (ethylene glycol) through iondipole interaction: an electrochemical study. Electrochim Acta.2008;53: 4654-4662.[32] Dobrucki LW,Tsutsumi Y,Kalinowski L,et al. Analysis of angiogenesis induced by local IGF-1 expression after myocardial infarction using microSPECT-CT imaging. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2010;48(6):1071-1079.[33] Kämena A, Streitparth F, Grieser C, et al. Dynamic perfusion CT: Optimizing the temporal resolution for the calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. Eur J Radiol. 2007;64:111-118.[34] Wiest R,von Bredow F,Schindler K,et al.Detection of regional blood perfusion changes in epileptic seizures with dynamic brain perfusion CT—A pilot study. Epilepsy Res.2006;72(2-3): 102-110.[35] Aralasmak A, Karaali K, Akyuz M, et al. MR imaging and CT perfusion findings of an extraventricular neurocytoma. Eur J Radiol Extra.2009;69: e53-e56.[36] Bai K,Huang Y,Jia X, et al. Endothelium oriented differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under chemical and mechanical stimulations. J Biomech.2010;43(6): 1176-1181.[37] Oswald J,Boxberger S,Jorgensen B,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells.2004;22:377-384.[38] Hristov M,Erl W,Weber PC.Endothelial progenitor cells: mobilization, differentiation, and homing.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2003;23(7):1185-1189.[39] Avci-Adali M,Ziemer G,Wendel HP.Induction of EPC homing on biofunctionalized vascular grafts for rapid in vivo self-endothelialization-A review of current strategies. Biotechnol Adv. 2010;28(1):119-129.[40] Grayson WL,Bhumiratana S,Cannizzaro C,et al. Effects of initial seeding density and fluid perfusion rate on formation of tissue-engineered bone. Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(11): 1809-1820.[41] Oest ME,Dupont KM,Kong HJ,et al. Quantitative assessment of scaffold and growth factor-mediated repair of critically sized bone defects. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(7):941-950.[42] Dawson JI,Oreffo RO.Bridging the regeneration gap: Stem cells, biomaterials and clinical translation in bone tissue engineering. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;(473):124-131.[43] Reichert JC,Saifzadeh S,Wullschleger ME,et al.The challenge of establishing preclinical models for segmental bone defect research. Biomaterials.2009;30(12):2149-2163.[44] Pearce AI,Richards RG,Milz S,et al. Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: a review. Eur Cell Mater. 2007;13:1-10.[45] Liu F,Yu SF,Wang ZG,et al. Biomimetic construction of large engineered bone using hemoperfusion and cyto-capture in traumatic bone defect. BioResearch Open Access.2012; 1(5): 247-251.[46] Gugala Z,Lindsey RW,Gogolewski S.New approaches in the treatment of critical size segmental defects in long bones. Macromol Symp.2007;253:147-161. |
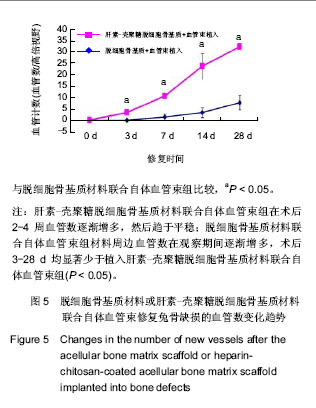
.jpg)