• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
载银磷酸锆可影响293T细胞的生长与增殖
刘 晶1,孙迎春2,曾妃菲2
- 1天津市红桥区口腔医院,天津市 300091 2天津医科大学口腔医院修复科,天津市 300070
Silver-zirconium phosphate impacts the vitality of 293T cells in vitro
Liu Jing1, Sun Ying-chun2, Zeng Fei-fei2
- 1 Stomatology Hospital of Hongqiao District, Tianjin 300091, China
2 Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatology Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
摘要:
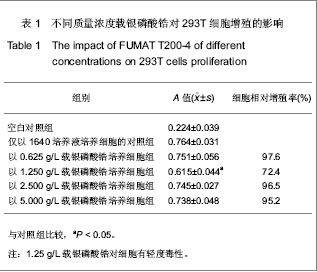
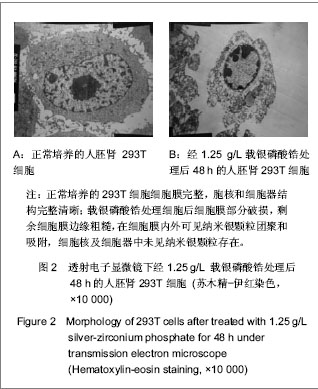
背景:研究表明6种国内外知名品牌口腔抗菌纳米载银无机抗菌剂中载银磷酸锆的杀菌性和安全性最佳。 目的:进一步观察载银磷酸锆对体外培养人胚肾上皮293T细胞生长、超微结构及胰岛素样生长因子1表达与分泌的影响。 方法:采用CCK-8方法检测5,2.5,1.25,0.625 g/L载银磷酸锆稀释液对293T细胞增殖的影响。根据结果选择对细胞增殖影响最大的质量浓度处理293T细胞,光学倒置显微镜观察细胞形态变化,于透射电镜下观察细胞超微结构及代谢变化,RT-PCR检测细胞胰岛素样生长因子1 mRNA的表达,ELISA法检测细胞培养上清液中胰岛素样生长因子1蛋白的水平。 结果与结论:载银磷酸锆作用于293T细胞48 h,1.25 g/L组细胞毒性为Ⅱ级,轻度细胞毒性,其余质量浓度组均为Ⅰ级,无细胞毒性。1.25 g/L载银磷酸锆处理293T细胞24,36,48 h后,细胞形态发生异常,细胞膜破损,出现轻度中毒现象,尤以48 h表现明显。1.25 g/L载银磷酸锆处理48 h后,293T细胞中胰岛素样生长因子1 mRNA的表达及上清液中胰岛素样生长因子1蛋白水平与正常培养细胞差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。表明载银磷酸锆影响293T细胞的生长及增殖,具有一定的细胞毒性,其在牙科材料中的应用还有待于进一步研究。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)