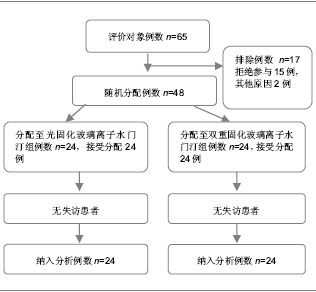
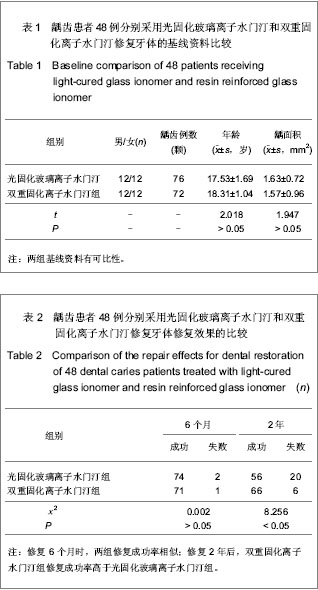
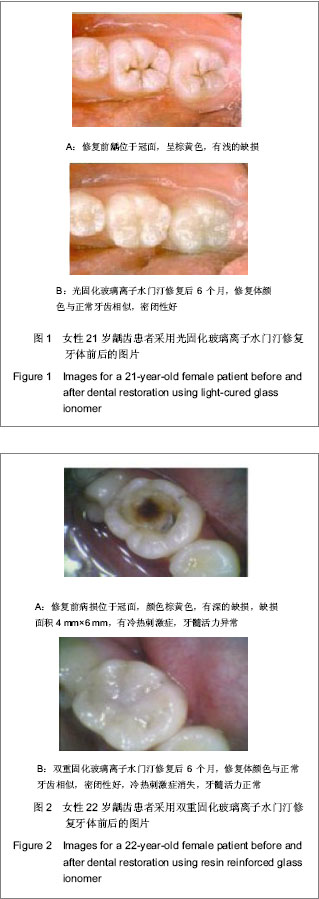
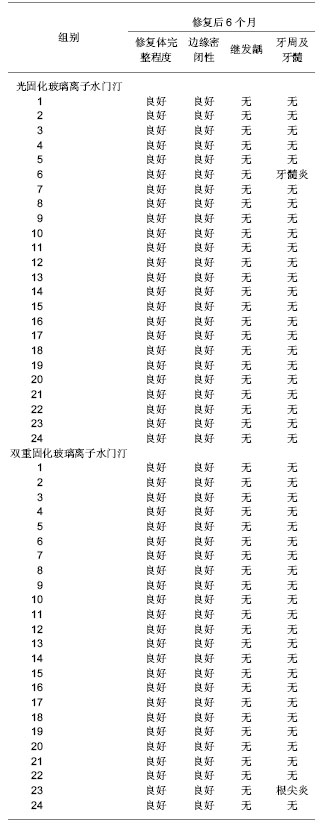
| [1] Li Y,Yang H.Guizhou Yiyao. 2010;34(5):437-438.李燕,杨宏.光固化玻璃离子结合光固化氢氧化钙修复恒磨牙髓底穿孔53例临床观察[J].贵州医药,2010,34(5):437-438. [2] Pan XY.Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Zixun. 2010;2(10):76-77.潘小勇.两种材料充填楔状缺损的疗效比较[J].中国中医药咨讯, 2010,2(10):76-77. [3] Su DH,Zhang XH,Qin J.Zhongguo Zonghe Linchuang. 2007; 23(7):648-649.苏东华,张贤华,秦简.不同充填方法对牙齿楔形缺损美容修复的临床效果比较[J].中国综合临床,2007,23(7):648-649. [4] Ren F,Liu JP,Huang SH,et al.Zhongguo Zuhzi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;15(38):7165-7169.任飞,刘建平,黄少宏,等.玻璃离子与光固化树脂封闭剂封闭乳牙窝沟[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,15(38):7165-7169. [5] Shan LH,Zhang D,Shi YT,et al.Kouqiang Zhengji Yixue. 2002; 9(3):124-126.单丽华,张丁,石彦涛,等.光固化树脂加强型玻璃离子水门汀粘结性能的研究[J].口腔正畸学,2002,9(3):124-126. [6] Yang JG,Pu JX.Yixue Linchuang Yanjiu. 2010;27(12):2349-2350.杨建国,蒲佳欣.玻璃离子、光固化材料充填乳牙龋齿疗效的临床对比观察[J].医学临床研究,2010,27(12):2349-2350. [7] Shen YY,Lu Q,Wei CJ.Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao. 2010; 30(11):1389-1392.沈一吟,陆群,魏本娟.不同充填材料修复对楔状缺损患牙牙周组织健康的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2010,30(11): 1389-1392. [8] Zhang L,Ma X,Zhu XG,et al.Haerbin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2010;45(1):77-79.张蕾,马雪,朱兴国,等.不同充填材料修复楔状缺损的临床疗效评价[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2010,45(1):77-79. [9] Gu HM,Feng Y.Jiangsu Daxue Xuebao. 2010;20(5):451-452.顾红政,冯英.3种不同材料修复楔状缺损3年疗效观察[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2010,20(5):451-452. [10] Liao W,Zhou NG,Hu ZW,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;15(8):1467-1470.廖伟,周年苟,扈祚文,等.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,15(8):1467-1470. [11] Jin JJ,Li YQ,Yu QS,et al.Dangdai Yixue. 2010;16(20):4-5.全君杰,李永青,于青松,等.不同粘结系统对纤维桩粘结强度的对比分析[J].当代医学,2010,16(20):4-5.[12] Jin YW,Liu Y.Zhongguo Shiyong Kouqiangke Zazhi. 2010;3 (11): 689-690.金英武,刘颖.两种黏结剂黏固纤维桩临床效果比较研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(11):689-690. [13] Meng XF,Yao H,Luo XP,et al.Shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2010;26(4):469-472.孟翔峰,姚海,骆小平,等.光照射强度和水储存条件对双重固化树脂机械性能的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(4): 469-472. [14] Meng XF,Liu X,Luo XP,et al.Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2010; 28(1):13-16.孟翔峰,刘晓,骆小平,等.光强度对双重固化树脂陶瓷粘接耐久性的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2010,28(1):13-16. [15] Jiang Y,Yang XD.Shenyang Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010;12(3): 167-169.姜月,杨晓东.两种固化方式对树脂纤维桩粘接强度的影响[J].沈阳医学院学报,2010,12(3):167-169. [16] Su JS,Zhai JB,Zhao Y,et al. Yati Yasui Yazhoubingxue Zazhi. 2006;16(9):515-517.苏俭生,翟建博,赵芸,等.新型高强度玻璃离子水门汀修复漏斗状残根的实验研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2006,16(9): 515-517.[17] Chen H,He J,Zhou SL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(8):1422-1425.陈洪,何静,周劭丽.GC Fuji Ⅸ型及增强型玻璃离子水门汀修复老年楔状缺损活髓牙:材料临床应用可行性1年的随访比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(8):1422-1425.[18] Zhang J,Peng B.Yati Yasui Yazhoubingxue Zazhi. 2008;18(1): 28-30.张军,彭彬.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟离子体外释放的比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(1):28-30. [19] Wu AM,Zhu YJ.Wuhan Daxue Xuebao. 2007;28(6):756-758, 785.伍爱民,朱有家.两种玻璃离子水门汀边缘封闭性的体外比较[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2007,28(6):756-758,785. [20] Hui HW.Shandong Yiyao. 2010;50(51):38-39.回宏伟.玻璃离子水门汀用于口腔正畸效果观察[J].山东医药, 2010,50(51):38-39. [21] Huang Y,Yu LF,Zou DR,et al.Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2011;27(9):546-548.黄艺,俞律峰,邹德荣,等.玻璃离子水门汀牙体充填后边缘封闭性的观察[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011,27(9):546-548.[22] Ji YL,Wang ZG.Zhonghua Shiyong Zhenduan yu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2010;24(2):187-188.吉雅丽,王志刚.Vitapex糊剂与光固化玻璃离子水门汀修补乳磨牙髓室底穿孔疗效观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2010,24 (2): 187-188. [23] Shan LH,Cui ZQ,Shen QH,et al. Zhongguo Zuhzi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(6):1149-1152.单丽华,崔占琴,沈庆华,等.光固化树脂加强型玻璃离子水门汀在正牙学实践中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(6):1149-1152. [24] Lai YZ,Lin S.Yixue Zongshu. 2010;16(1):85-87.赖颖真,林珊.玻璃离子水门汀边缘封闭性的研究[J].医学综述, 2010, 16(1):85-87. [25] Mu H,Jia BJ.Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2008;17(24): 3825-3825.穆宏,贾博军.玻璃离子水门汀粘接带环的效果观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2008,17(24):3825-3825. [26] Liang GX.Yati Yasui Yazhoubingxue Zazhi. 2004;14(8): 450-452.梁桂香.三种方法修复楔形缺损疗效对比[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2004,14(8):450-452. [27] Ding L,Lu Y,Lu Q,et al.Shanghai Dier Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2005;25(7):698-701.丁玲,陆忆,陆群,等.改良型玻璃离子水门汀及复合体Ⅴ类洞型充填的边缘微漏[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2005,25(7):698-701.[28] Liu YT,Bai LW.Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2009;9(1):53-54.刘颖婷,白敛薇.光固化玻璃离子水门汀和复合树脂联合修复楔状缺损疗效分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2009,9(1):53-54. [29] Wei L,Tan JY,Tan DX,et al.Weichuang Yixue. 2010;5(4): 357-358.韦玲,谭俊扬,谭端行,等.应用玻璃离子水门汀粘结正畸托槽的临床研究[J].微创医学,2010,5(4):357-358. |