| [1] An HS, Thonar EJ, Masuda K. Biological repair of intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(15 Suppl):S86-92.[2] Colombini A, Lombardi G, Corsi MM, et al. Pathophysiology of the human intervertebral disc. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008; 40(5):837-842. [3] Schnabel LV, Mohammed HO, Miller BJ, et al. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) enhances anabolic gene expression patterns in flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthop Res. 2007;25 (2):230-240.[4] Whitman DH, Berry RL, Green DM. Platelet gel: an autologous alternative to fibrin glue with applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55(11): 1294-1299.[5] Ma J, Li F, Ren DJ, et al. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun yu Shijian. 2011;17(3):223-225.马健,李放,任大江,等.富含血小板血浆凝胶的超微结构[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(3):223-225.[6] Marx RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(4):489-496.[7] Weibrich G, Kleis WK, Hafner G, et al. Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2002;30(2):97-102.[8] Landesberg R, Roy M, Glickman RS. Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3):297-301.[9] Jeong JH, Lee JH, Jin ES, et al. Regeneration of intervertebral discs in a rat disc degeneration model by implanted adipose-tissue-derived stromal cells. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010;152(10):1771-1777.[10] Ganey T, Hutton WC, Moseley T, et al. Intervertebral disc repair using adipose tissue-derived stem and regenerative cells: experiments in a canine model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(21):2297-2304.[11] Hoogendoorn RJ, Lu ZF, Kroeze RJ, et al. Adipose stem cells for intervertebral disc regeneration: current status and concepts for the future. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6A):2205-2216. [12] Jeong JH, Lee JH, Jin ES, et al. Regeneration of intervertebral discs in a rat disc degeneration model by implanted adipose-tissue-derived stromal cells. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010;152(10):1771-1777. [13] Nagae M, Ikeda T, Mikami Y, et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(1): 147-158.[14] Chen WH, Liu HY, Lo WC, et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration in an ex vivo culture system using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 2009;30(29): 5523-5533. [15] Sell SA, Wolfe PS, Ericksen JJ, et al Incorporating platelet-rich plasma into electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(21-22): 2723-2737. [16] Ma J, Li F, Ren DJ, et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2011; 21(5):353-357.马健,李放,任大江,等.富含血小板血浆凝胶复合脂肪间充质干细胞构建可注射组织工程髓核[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(5): 353-357.[17] Zhang N, Li F, LuoT. Juyi Jinxiu Xueyuan Xuebao. 2012;33(6): 14-18.张宁,李放,罗涛.不同抗凝剂和激活剂组合在自体富血小板血浆凝胶支架促进脂肪间充质干细胞增殖的影响[J].军医进修学院学报,2012,33(6):14-18.[18] Wang SJ, Li CD, Sun HL, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhigongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(9):1957-1600.王诗军,李淳德,孙浩林,等.针刺损伤兔椎间盘退变模型组织病理变化及软骨样细胞的迁移规律[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(9): 1957-1600.[19] Liu G, Shu C, Cui L, et al. Tissue-engineered bone formation with cryopreserved human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cryobiology. 2008;56(3):209-215. [20] Gentile P, Orlandi A, Scioli MG, et al. A comparative translational study: the combined use of enhanced stromal vascular fraction and platelet-rich plasma improves fat grafting maintenance in breast reconstruction. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(4):341-351.[21] Cervelli V, Scioli MG, Gentile P, et al. Platelet-rich plasma greatly potentiates insulin-induced adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells through a serine/threonine kinase Akt-dependent mechanism and promotes clinical fat graft maintenance. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(3):206-220. [22] Hernandez-Fernandez A, Vélez R, Soldado F, et al. Effect of administration of platelet-rich plasma in early phases of distraction osteogenesis: An experimental study in an ovine femur model. Injury. 2012. in press. [23] Mifune Y, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):175-185. [24] Gobbi A, Karnatzikos G, Mahajan V, et al. Platelet-rich plasma treatment in symptomatic patients with knee osteoarthritis: preliminary results in a group of active patients. Sports Health. 2012;4(2):162-172.[25] Hapa O, Cak?c? H, Kükner A, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on tendon-to-bone healing after rotator cuff repair in rats: an in vivo experimental study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(4):301-307. |


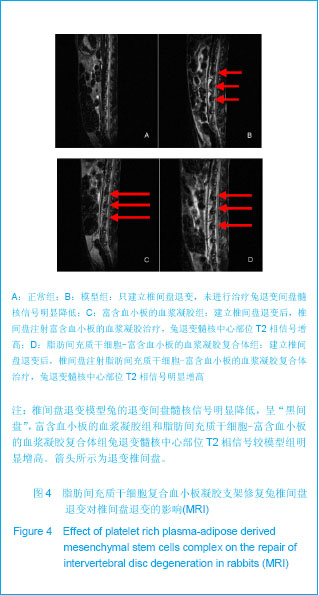
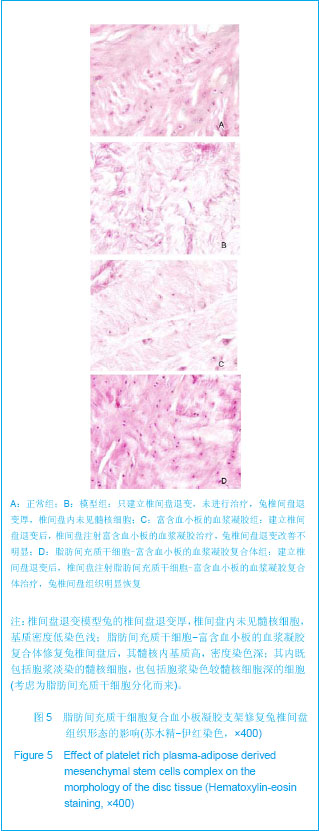

.jpg)
.jpg)