Design
A cellular observation.
Time and setting
The experiment was performed at Institute of Medical Equipment of Academy of Military Medical Sciences from March 2011 to September 2011.
Materials
MC3T3-E1 cells and RAW264.7 cells were provided by Institute of Basic Medicine of Peking Union Medical College. Dulbecco minimum essential medium/F12 and fetal bovine serums were obtained from Hyclone Biotechnology. Toluidine blue and methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide were purchased from Tianjin Huashengyuan Company. The kits of alkaline phosphatase and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Company. 1α, 25(OH)2D3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor were obtained from Peprotech Asia.
Methods
Establishment of co-culture system
MC3T3-E1 cells, a mouse monoclonal pre-osteoblastic cell line, were embedded with 5×104 on the bottom of the transwell plates, and RAW264.7 cells, a mouse pre-osteoclastic cell line, were incubated with 5×104 in the transwell inserts on the top of the MC3T3-E1 cells sheet. The co-culture system was maintained in Dulbecco minimum essential medium/F12 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin-streptomycin, 10-8 mol/L 1α,25(OH)2D3 and 50 ng/mL macrophage colony-stimulating factor in 5% CO2 at 37 ℃. Simultaneously, MC3T3-E1 and RAW264.7 cells were cultured alone respectively for control. After co-cultured for 6 days, the sequential experiments were performed.
Cell viability assay for osteoblasts
Cell viability of osteoblasts was determined by methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide assay. Briefly, the methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide solution was added into each well of plates and then the cells were incubated in 5% CO2 at 37 ℃ for 4 hours. Subsequently, the medium in each well was replaced with dimethyl sulfoxide to dissolve the methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide formazan. Finally, 20 μL solute per well was added to 96-well plates and quantified by the absorbance at 490 nm using an enzyme-labeled meter.
Alkaline phosphatase activity analysis for osteoblasts
Briefly, alkaline phosphatase activity in the cultured supernatant was determined on the base of the enzyme conversion of alkaline phosphatase. The activity of alkaline phosphatase was quantified by the absorbance at 520 nm according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
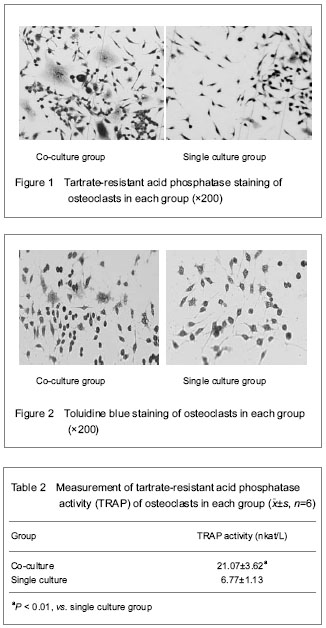
Toluidine blue staining for osteoclasts
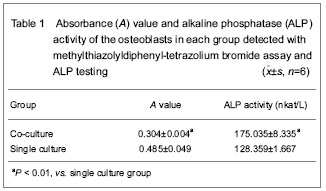
After fixed with 95% alcohol, the osteoclast-like cells on coverslips were stained in the 0.5% solution of toluidine blue at 56 ℃ for 20 minutes, and washed with distilled water. After dehydrate, clear and mount, multinuclear cells with the characteristics of abundant cytoplasm and vacuolation were observed as mature osteoclasts under a light microscope.
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining for osteoclasts
After fixed with 95% alcohol, the osteoclast-like cells on coverslips were incubated in the solution of naphthol AS-BI phosphate and tartrate at 37 ℃ for 60 minutes, followed by counterstaining with the haematoxylin solution. After dehydrate, clear and mount, the coverslips were observed and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinuclear cells were regarded as mature osteoclasts.
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase activity analysis for osteoclasts
Briefly, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase activity in the cultured supernatant was detected by spectrophotometer on the base of the enzyme conversion of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. The activity of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase was assayed by the absorbance at 530 nm according to the protocol.
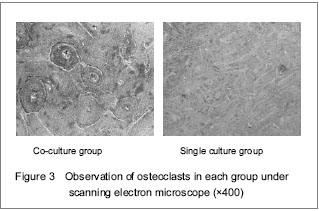
Morphology of resorption lacunae observed under scanning electron microscope
First, the osteoclastic cells were wiped off the bone slices by ultrasonication with 0.25% ammonium hydroxide for 15 minutes. After rinsing in phosphate buffered solution, the bone slices were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde and further in 1% osmium tetroxide solution. After dehydrated, air-dried and gold coated slices were examined in a scanning electron microscope for resorption pit.
Main outcome measures
Cell viability and alkaline phosphatase activity of osteoblasts, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase/TB staining and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase activity of osteoclasts, as well as bone resorption lacunae were determined.
Statistical analysis
All data were presented as means±standard deviation. Statistical differences were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance using SPSS 13.0 software and P < 0.05 was considered as significant.