| [1] Seo BM,Miura M,Gronthos S,et al.Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament.Lancet. 2004;364(9429):149-155.[2] Grove JE,Bmseia E,Krause DS.Plasticity of bone marrow-derived stem cells.Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):487-500. [3] Kémoun P, Gronthos S, Snead ML, Rue J,et al. The role of cell surface markers and enamel matrix derivatives on human periodontal ligament mesenchymal progenitor responses in vitro. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30):7375-7388. [4] Molinelli A, Bonsignore A, Cicconi M, et al.IGF-1 abuse in sport:clinical and medico-legal aspects.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2010;50(4):530-535.[5] Shen F, Sun B, Kreutz JE, et al. Multiplexed quantification of nucleic acids with large dynamic range using multivolume digital RT-PCR on a rotational SlipChip tested with HIV and hepatitis C viral load. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(44):17705- 17712. [6] Nuñez J, Sanz-Blasco S, Vignoletti F,et al.Periodontal regeneration following implantation of cementum and periodontal ligament-derived cells.J Periodontal Res. 2012; 47(1):33-44. [7] Kerkis I, Caplan AI.Stem cells in dental pulp of deciduous teeth.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2012;18(2):129-138. [8] Yamamoto S, Masuda H, Shibukawa Y, et al.Combination of bovine-derived xenografts and enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects in dogs. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2007;27(5):471-479.[9] Dangaria SJ, Ito Y, Luan X, et al. Successful periodontal ligament regeneration by periodontal progenitor preseeding on natural tooth root surfaces. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(10): 1659-1668. [10] Friedman AA, Tucker G, Singh R, et al. Proteomic and functional genomic landscape of receptor tyrosine kinase and ras to extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling. Sci Signal. 2011;4(196):rs10.[11] De Luca A, Gallo M, Aldinucci D, et al. Role of the EGFR ligand/receptor system in the secretion of angiogenic factors in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Physiol. 2011;226(8): 2131-2138. [12] Kowanetz M, Valcourt U, Bergström R, et al. Id2 and Id3 Define the Potency of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation Responses to Transforming Growth Factor β and Bone Morphogenetic Protein. Mol Cell Biol.2004; 24(10):4241- 4254. [13] Gittens RA, McLachlan T, Olivares-Navarrete R, et al. The effects of combined micron-/submicron-scale surface roughness and nanoscale features on cell proliferation and differentiation. Biomaterials. 2011;32(13):3395-3403.[14] Kurtoglu S,Kondolot M,Mazicioglu MM,et al.Growth hormone,insulin like growth factor-1,and insulin- like growth factor-binding protein-3 levels in the neonatal period:a preliminary study.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010;23(9): 885-889.[15] Ali A, Hashim R, Khan FA, et al.Evaluation of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulinlike growth factor binding protein-3 in diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency in short-stature children. Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2009;21(3): 40-45.[16] Rosenfeld RG, Buckway C, Selva K, et al.Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) parameters and tools for efficacy: the IGF-I generation test in children. Horm Res. 2004;62 (1):37-43.[17] Varkey M, Kucharski C,Haque T,et al . In vitro osteogenic response of rat bone marrow cells to bFGF and BMP-2 treatments. Clin Or Thop Relat Res. 2006;443(2):113-123.[18] Li Q, Liu T, Zhang L, et al. The role of bFGF in down-regulating α-SMA expression of chondrogenically induced BMSCs and preventing the shrinkage of BMSC engineered cartilage. Biomaterials. 2011;32(21):4773-4781. [19] Zhang X, Sobue T, Hurley MM. FGF-2 increases colony formation,PTH receptor,and IGF-1 mRNA in mouse marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290(1): 526-531.[20] Dupree MA, Pollack SR, Levine EM, et al . Fibroblast growth factor-2 induced proliferation in osteoblasts and bone marrow stromal cells: a whole cell model. Biophys J. 2006;91(8): 3097-3112.[21] Harris MT, Butler DL, Boivin GP, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells used for rabbit tendon repair can form ectopic bone and express alkaline phosphatase activity in constructs. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(5):998-1003.[22] Salamon A, Toldy E.Use of mesenchymal stem cells from adult bone marrow for injured tissue repair. Orv Hetil. 2009; 150(27):1259-1265.[23] Vilquin JT, Rosset P. Mesenchymal stem cells in bone and cartilage repair: current status. Regen Med.2006;1(4): 589-604. |
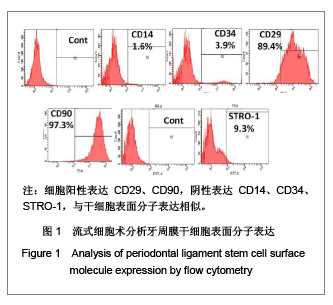
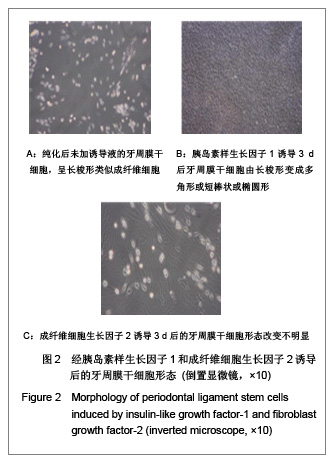

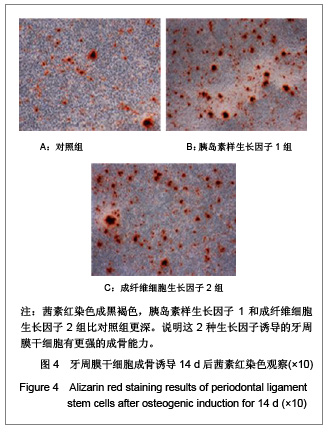
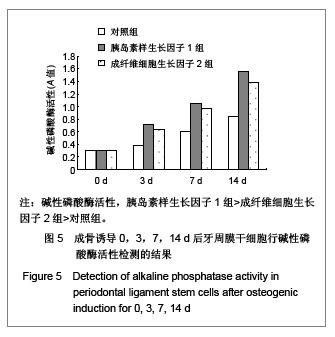
.jpg)
.jpg)