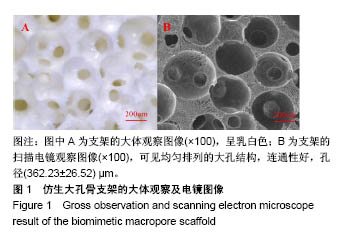
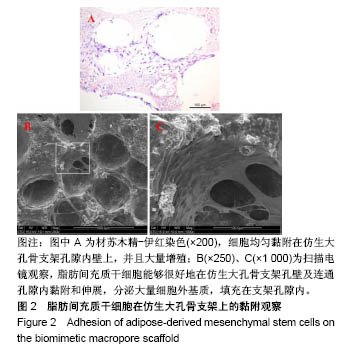
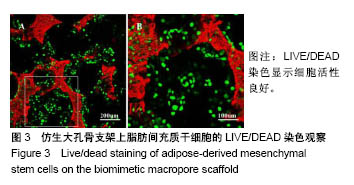
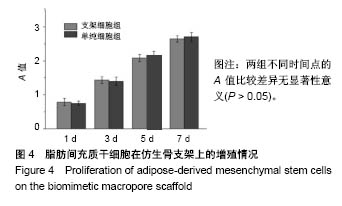
| [1] Kim HD,Amirthalingam S,Kim SL,et al.Biomimetic Materials and Fabrication Approaches for Bone Tissue Engineering.Adv Healthc Mater.2017;6(23). doi:10.1002/adhm.201700612. Epub 2017 Nov 24.[2] 张屹,陈建常,史振满.组织工程支架在修复骨缺损中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(16): 1617-1619.[3] 张淦,程迅生.骨组织工程的研究进展[J].安徽医学, 2016,37(8): 1057-1061.[4] Su P,Tian Y,Yang C,et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration during Bone Formation and Bone Diseases Therapy.Int J Mol Sci.2018; 19(8):E2343.[5] Noori A,Ashrafi SJ,Vaez-Ghaemi R,et al.A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12(12):4937-4961.[6] Kim HJ,Kim UJ,Kim HS,et al. Bone tissue engineering with premineralized silk scaffolds. Bone. 2008;42(6):1226-1234.[7] 徐桂文,乌日开西•艾依提,滕勇.复合型组织工程化人工骨支架:应用进展与未来方向[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(14):2245-2250.[8] 葛振,邹刚,刘毅,等.组织工程支架材料:特征及在组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(26):4222-4228.[9] 陈海霞,谢志刚.骨组织工程支架材料:脱矿骨基质[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(3):426-431.[10] Zheng Z,Ning M,Li D.Silicification of silk fibroin and their application in bone tissue engineering.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2018;35(4):643-646.[11] 高欣欣,许燕,周建平,等.丝素蛋白-聚乙烯醇复合凝胶对骨组织工程支架性能的影响[J].燕山大学学报,2017,41(2):127-132.[12] Mandal BB, Park SH, Gil ES, et al. Multilayered silk scaffolds for meniscus tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32(2):639-651.[13] 陆史俊,左保齐,刘洪臣.丝素蛋白生物支架材料在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(10):1307-1310.[14] Meinel L,Karageorgiou V,Hofmann S,et al.Engineering bone-like tissue in vitro using human bone marrow stem cells and silk scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A.2004;71(1):25-34. [15] 余文,孟昊业,孙逊,等.3D打印生物陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(14): 1306-1310.[16] 赵呈智,张悠,付睿捷,等.骨组织工程中纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料现状、评价及展望[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(17):4-5.[17] Bhumiratana S,Grayson WL,Castaneda A,et al.Nucleation and growth of mineralized bone matrix on silk-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds. Biomaterials.2011;32(11):2812-2820.[18] 赵呈智,张悠,付睿捷,等.骨组织工程中纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料现状、评价及展望[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(17):4-5.[19] Jo YY,Kim S,Kwon K,et al.Silk Fibroin-Alginate-Hydroxyapatite Composite Particles in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci.2017;18(4):E858.[20] Zhou J,Xu C,Wu G,et al.In vitro generation of osteochondral differentiation of human marrow mesenchymal stem cells in novel collagen- hydroxyapatite layered scaffolds.Acta Biomater.2011;7(11): 3999-4006.[21] Lee CM,Yang SW,Jung SC,et al.Oxygen Plasma Treatment on 3D-Printed Chitosan/Gelatin/Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2017;17(4):2747-2750.[22] Zeng C,Yang Q,Zhu M,et al.Silk fibroin porous scaffolds for nucleus pulposus tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;37:232-240.[23] 杨强,丁晓明,徐宝山,等.取向性丝素蛋白仿生软骨支架的制备及其生物相容性评估[J].天津医药,2015, 43(7):709-712,834.[24] Bunnell BA,Flaat M,Gagliardi C,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, expansion and differentiation.Methods. 2008;45(2):115-120.[25] Liew LJ,Ong HT,Dilley RJ.Isolation and Culture of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells from Subcutaneous Fat. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1627: 193-203.[26] Shafieian R,Matin MM,Rahpeyma A,et al.Effects of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma on Healing Response of Canine Alveolar Surgical Bone Defects.Arch Bone J Surg. 2017;5(6):406-418.[27] Angele P,Kujat R,Nerlich M,et al.Engineering of osteochondral tissue with bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells in a derivatized hyaluronan-gelatin composite sponge.Tissue Eng. 1999;5(6): 545-554.[28] Moriguchi Y,Mojica-Santiago J,Grunert P,et al.Total disc replacement using tissue-engineered intervertebral discs in the canine cervical spine. PLoS One.2017;12(10):e0185716. [29] Mohan N,Dormer NH,Caldwell KL,et al.The Tissue-Engineered Tendon-Bone Interface: In Vitro and In Vivo Synergistic Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel.Plast Reconstr Surg.2017;140(6): 1169-1184. [30] Wang Y,Wang K,Li X,et al.3D fabrication and characterization of phosphoric acid scaffold with a HA/β-TCP weight ratio of 60:40 for bone tissue engineering applications.PLoS One 2017;12(4): e0174870. [31] Campbell GM,Ominsky MS,Boyd SK.Bone quality is partially recovered after the discontinuation of RANKL administration in rats by increased bone mass on existing trabeculae: an in vivo micro-CT study.Osteoporos Int.2011;22(3):931-942. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)