2.1 自体骨和同种异体骨 自体骨移植融合率可高达95%以上,在骨缺损重建中一直是骨移植“金标准”,目前亦运用最为广泛。虽然自体骨移植后局部骨融合较为理想,但其来源极为有限,常无法完全满足充分植骨量需求;自体髂骨取骨会使额外增加手术时间,部分患者会残留供区局部疼痛,增加感染概率,甚至会引发患者心理问题,导致手术费用增加;更重要的是,自体骨如植入量有限,有被组织吸收而导致骨不连风险。有研究表明,同种异体冻干松质骨在融合时间及融合率方面与自体骨基本相当
[5]。使用同种异体冻干松质骨,其主要优点有:①不存在供区并发症:局部疼痛、感染等;②手术中可对局部骨缺损区进行精细的修补裁剪;③可避免疲劳性骨折。但在临床实践中,其亦有一定使用缺点,主要有:①诱导新骨生成能力相对低于自体骨;②存在传染疾病风险,部分患者可发生局部宿主炎性、免疫性反应或排斥反应;③来源受到一定限制,极为有限。Shi等
[6]对30例下颈椎结核患者采取了前路病灶清除+植骨内固定术治疗,按植骨材料分为2组:同种异体骨组(A组,15例)和自体髂骨(B组,15例),术后发现两组病例融合时间无明显差异(
P > 0.05),分别为(7.6±2.1)个月和(4.2±1.1)个月,两组术后6个月及末次随访Cobb角较术前均有明显改善,且两组之间无明显差异(
P > 0.05)。
2.2 合成人工骨材料 合成人工骨材料主要包括合成人工珊瑚骨、医用硫酸钙骨等,因其能解决自体骨和同种异体骨来源受限的问题,同时具备骨诱导活性,逐渐为临床所接受。董健等[7]运用人工合成医用硫酸钙骨替代物Osteoset治疗骨缺损患者及脊柱手术患者共30例,获得了满意的临床疗效。张闻力等[8]采用一期前路病灶清除+Osteoset人工骨加部分自体骨植骨内固定术治疗胸腰椎结核患者24例,术后3个月随访融合率为95.8%;术后6个月随访所有患者均骨性融合,内固定位置形态正常;无复发病例;Cobb角平均矫正(15.2±6.7)°。但结核病灶是否会被病灶内合成人工骨材料再次激活,甚至使感染扩散;人工骨材料是否能与结核杆菌(M.tuberculosis)长期安全友好共存,是否会成为一种新的感染源,导致远期骨关节结核复发或复燃等安全性问题,均尚未完全解决,目前极度缺乏关于人工合成骨材料与M.tuberculosis相互影响的相关研究。
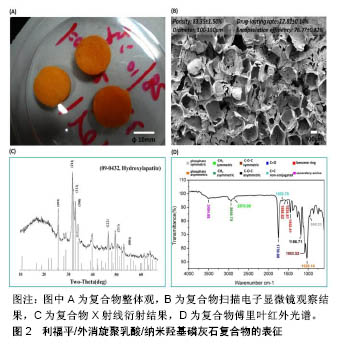
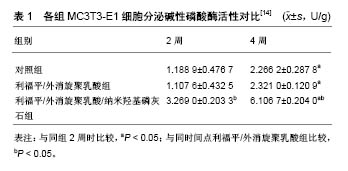
纳米羟基磷灰石和外消旋聚乳酸是21世纪最具前途的药物转运系统载体材料、组织工程支架材料和骨修复材料,被广泛应用于生物医药学、材料学等热门领域。研究表明,成骨细胞活性与骨组织工程支架成分、比例、三维立体结构密切相关。局部微环境会因为外消旋聚乳酸的酸性降解产物(CO2)呈弱酸性,不利于成骨细胞的分化与生长。纳米羟基磷灰石具有骨传导性和骨诱导性,亦可中和外消旋聚乳酸的酸性抑制效应,常与外消旋聚乳酸联用以改进支架的骨修复能力[9-10]。Ronca 等[11]运用激光快速成型技术成功制作出一种先进的新型三维多孔外消旋聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架,该材料通过引入纳米羟基磷灰石明显改善了力学性能,且纳米羟基磷灰石引入对支架三维立体结构并未产生任何明显负面影响;将其与人骨髓间充质干细胞体外共培养3周,发现加入纳米羟基磷灰石后支架材料的骨诱导潜能亦得到显著提高。近年来,外消旋聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料亦可作为功能性涂层,与钛金属合用用于骨缺损的修复[12]。Jensen等[13]将含涂层的2种多孔钛植入体植入绵羊肱骨近端,一种质量比为50/50的外消旋聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石复合涂层,对照组为含纯外消旋聚乳酸涂层;12周时,2种涂层的降解率分别为79.7%和80.2%,复合涂层中新骨形成率为39.3%,而对照组几乎全部为纤维组织未见新骨形成。外消旋聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料在骨缺损修复方面已展示出巨大的应用潜能,但其在骨关节结核治疗方面的相关研究极为缺乏。作者曾于2014年尝试利用外消旋聚乳酸和纳米羟基磷灰石作为原料[14],成功制备出搭载利福平多孔复合物(利福平/外消旋聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合物),见图2,并对其理化性能进行了初步探讨。结果显示,利福平/外消旋聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合物复合物具备良好的降解性能和缓释特性,与MC3T3-E1细胞共培养能显著促进细胞分泌碱性磷酸酶活性,见表1,展示出一定运用潜能,但机械性能明显不足,尚待进一步研究改善。
2.3 人工椎体 人工椎体为恢复脊柱生理曲度、矫正脊柱畸形提供了新的解决方案。部分学者对人工椎体的运用,做了很多尝试。Farage等
[15]发现在脊柱结核治疗中运用人工椎体重建时,人工椎体与自体骨的骨融合时间基本相同,6-8个月后逐渐开始出现界面模糊、界面融合,显示出其在脊柱结核方面具有良好的应用前景。王永清等
[16]亦报道框架式人工椎体融合率高、安全有效,可用于骨质破坏较重的胸腰椎结核治疗。纳米羟基磷灰石复合人工椎体费用低廉、使用便利,具备骨传导性和骨诱导性,融合率高,亦开始被用于骨关节结核治疗。王群波
[17]对19例脊柱结核患者采用纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合人工椎体治疗,随访9个月,融合率为85%,无内固定失败病例。但人工椎体适应证较窄,禁忌证较多,心、肝、肺、肾等重要器官功能不良、术前未经规范化抗痨治疗、活动期结核、血沉较高病灶破坏持续进展且合并大量脓液形成、严重脊柱后凸畸形、局部病灶已骨性融合、持续发热、合并明显椎体骨质疏松等均不适宜选用人工椎体重建。尽管人工椎体可作为脊柱结核重建的一种选择,但总体报道运用较少,更缺乏中长期随访资料,其安全性和有效性均有待深入研究。
2.4 钛网 钛是一种生物惰性材料,并不会引发感染扩散或在局部形成结核病灶,将其运用于骨关节结核治疗安全可行[18]。目前在脊柱结核外科手术中,已广泛运用钛网+自体骨移植修复骨缺损。钛网可重建脊柱即刻稳定性,有利于局部结核控制,促进骨性融合。细菌与材料的黏附是与内固定有关骨关节感染发生的始动因素,内植入物表面生物膜形成则会导致感染迁延不愈。M.tuberculosis对不锈钢和钛的黏附能力较弱;内植入物表面M.tuberculosis黏附量与界面光滑程度密切相关,光滑表面细菌黏附数量显著少于粗糙内表面[19]。周劲松等[20]亦证实钛金属表面M.tuberculosis黏附数量较少,且在M.tuberculosis周围未检测出鞭毛、荚膜、菌毛、黏附配体等生长。这一重要发现被视为脊柱结核术中可运用钛网的重要安全性支持之一。与传统髂骨相比,运用钛网加植骨方式重建更符合脊柱三柱生物力学理论,其在修复骨缺损重建脊柱序列同时,能更加有效维持脊柱畸形的矫正角度。钛网可通过自身的机械刚度对抗来自相应方向的压应力、剪切力、扭转力等,可分散脊柱后路椎弓根钉棒系统所承受的部分载荷,避免内固定装置因应力过度集中导致的金属疲劳、折断而致内固定失败;钛网与植骨床接触面越大,对移植骨的应力遮挡越小,椎间融合效果越理想[21]。但术后钛网头尾端沉降率亦可分别高达38%和35%[22-24],以及后凸矫正Cobb角再丢失等问题亦应引起重视。近年来一种可膨胀式新型钛网被引入脊柱外科,总体疗效满意[25-26],不少学者进行了尝试,将其应用在脊柱结核缺损重建。Bhatia等[27]采用前后路联合手术治疗了1例因T6椎体结核而导致严重后凸畸形(Cobb角为60°)的70岁老年男性患者,术中尝试使用了一种可膨胀式新型钛网重建,疗效满意。然而对于此类新型重建材料目前认识较为肤浅,尚需更多中远期随访资料。
对于钛网重建,有观点认为病灶清除理论上并不能完全清除局部病灶内M.tuberculosis。将钛网直接放置于感染性病灶,可能为脊柱结核治疗失败或中远期复发的重要原因之一[28]。钛网特殊的网状三维立体结构可为局部M.tuberculosis提供较大且粗糙的接触面,导致M.tuberculosis黏附量增加,同时其可降低抗结核药物的渗透,有利于M.tuberculosis的繁殖生长。脊柱结核翻修患者取出钛网时,有研究发现钛网内所植骨质中含大量脓液,为抗结核治疗死角[28]。因此,其建议术中尽可能缩小骨质切除范围,一期重建脊柱序列钛网不宜作为首选,对钛网的选择应当持谨慎态度。
2.5 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥在关节置换中运用极为广泛,近年来其亦被尝试用于脊柱结核骨缺损的修复重建。周长民等[29]对32例胸椎结核患者采用椎体成形术治疗,未发生聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎管内渗漏,术后平均随访3年发现Cobb角平均矫正12°,均无明显丢失,优良率为100%,总体疗效满意。Jan等[30]通过利用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥包埋抗结核药物治疗1例T10、T11椎体结核患者,获得了满意临床疗效,为治疗脊柱结核提供了新思路。但在使用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯过程中,固化期会释放大量热源,导致局部温度较高,极易灼伤周围重要组织及器官,特别对于胸椎结核前路手术中运用时,风险较大,极易发生严重并发症;聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯单体能抑制巨噬细胞对局部细菌的吞噬和杀灭作用,有一定细胞毒性;聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯有诱发心脏骤停风险[31],可能与一过性血压下降或上升导致心率骤然变化有关;术中亦可因骨水泥渗漏而压迫脊髓或神经根导致医源性截瘫,特别是对于胸椎结核患者更应引起重视;聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯是一种不可降解的有机多聚物,尚缺乏将其直接应用于结核感染病灶内的更权威理论依据、生物安全性评测及中长期临床随访资料。
2.6 抗结核活性材料 因骨关节结核局部的一些特殊病理变化,通过常规口服结核药物方式常难以在局部结核病灶内维持有效药物浓度。因此,不少学者将局部药物缓释技术的应用到骨关节结核治疗中来。Witsø等[32]将利福平灌注到人冻干松质骨空隙内,通过体内外缓释实验发现该复合材料的体内外释放曲线基本相近,7 d时均仍高于100倍最低抑菌浓度。张泽华[33]将同种异体骨复合纤维蛋白后再搭载利福平,其发现该复合物不仅能成功修复山羊椎间和髂骨缺损,其亦可在局部维持利福平有效抑菌浓度达42 d以上。作者制备的利福平/外消旋聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合物亦展示出良好药物缓释性能[14]。
钙磷基人工合成骨材料来源广泛,无免疫原性且具备骨诱导性,是目前最具前途的药物传递系统载体材料之一。孙建英等[34]成功制备出利福平/磷酸八钙骨水泥,发现将利福平添加于磷酸八钙中并不会影响最终磷酸八钙的产物物相;对于搭载不同药物浓度的磷酸八钙骨水泥,载体孔隙率与药物含量呈正相关,而载体强度与药物含量呈负相关;利福平含量为60 mg/g与40 mg/g的2种骨水泥释放过程,均符合 Higuchi扩散释放模型,但高浓度者展示出更好相关性。王德平等[35]将磷酸钙为主体的多孔微晶玻璃搭载利福平后,发现玻璃基药物载体亦可通过缓释效应,缓慢长期释放高浓度利福平,且其药物释放速率与载体孔隙率密切相关。乙胺丁醇-磷酸钙骨水泥可能是一种治疗骨关节结核的有效植入式缓释剂。钱志松等[36]发现乙胺丁醇-磷酸钙骨水泥复合体在兔臀肌和股骨中均能持续缓释乙胺丁醇。硫酸钙亦为一种搭载利福平非常理想的药物传递系统载体材料。有学者制备的利福平-硫酸钙植入剂展示出良好生物相容性、持续骨诱导能力和药物缓释特性,该材料在局部植入时,全身浓度较低,局部缓释可持续45 d以上[37-38]。
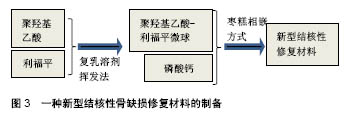
很多学者在制备新型抗结核活性材料制备方法上亦进行了大量改进与尝试。叶向阳等
[39]先采用复乳溶剂挥发法制备出粒径为(80.0±9.4)µm、载药量为(33.18± 1.36)%、包封率为(54.79±1.13)%的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物利福平微球,再通过“枣糕相嵌”方式与磷酸钙骨水泥复合制备出一种新型骨缺损修复材料,研究表明通过材料的降解可达到缓释效果,可维持局部利福平浓度在最低抑菌浓度之上长达8周,维持利福平杀菌浓度长达4周,可用于防止局部结核复发
[40],见
图3。伍卫刚
等
[41]利用三维打印技术按特定顺序将利福平和异烟肼由内到外加载制备出孔隙率为(61.76±2.53)%的多层同心圆柱体结构载药人工骨,2种药可通过依次序贯释放方式实现药物联合治疗,同时具备良好细胞相容性,可适用于体内植入修复结核性骨缺损。近日出现一种中空疏松的搭载利福平和异烟肼2种药物的介孔二氧化硅纳米粒复合药物缓释材料,利福平和异烟肼装载量分别为3.77 mg/g和37.89 mg/g,释放实验显示其在体内外均可持续缓释维持有效药物浓度达42 d以上,且成功修复兔桡骨骨缺损
[42]。
骨关节结核即使临床治愈后,局部仍可能长期潜伏结核病灶,其为术后或长期愈合后再次复发的主要原因之一。脊柱结核多在术后二三年内复发,复发率可高达13%-26%。患者全身健康状况不良、术中局部病灶是否清除彻底、是否存在遗漏隐匿病灶、是否有效重建脊柱稳定性、局部是否达到骨性融合、术后不规律化疗及耐药菌株的产生等都可能导致复发,其中不规律化疗是术后复发最主要原因之一[43]。因此,即使彻底清除病灶后,仍应合理、规范的使用抗结核药物治疗,以有效防止局部病灶复发。目前推荐手术前使用抗结核药物治疗至少4-6周,手术后应不少于9个月[44]。但长期服用抗结核药物会导致肝、肾损害及其他并发症,同时抗结核药物很难到达骨关节结核病灶周围,局部常无法达到有效药物浓度,导致耐药结核菌产生。因此,开发既具备抗结核药物缓释功能又具备骨修复能力的新型重建材料,将意义非凡[45]。但尽管抗结核活性材料的研究进步迅速,但目前均处于实验研究阶段;如何提高材料载药量、调控降解速率与新骨生成相匹配、有效增加机械性能、提高材料骨修复能力、材料生物安全性评定、局部运用新型抗结核生物材料后的全身化疗方案制定、安全局部有效药物浓度的确定、局部使用抗结核药是否会诱导耐药结核菌株出现等问题都亟需解决[46]。
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)