| [1] Andersson H, van den Berg A.Microfabrication and microfluidics for tissue engineering: state of the art and future opportunities. Lab Chip. 2004;4(2):98-103 [2] Beauchamp MJ, Nordin GP, Woolley AT. Moving from millifluidic to truly microfluidic sub-100-μm cross-section 3D printed devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017; 409(18):4311-4319.[3] Sun X, Nunes SS. Maturation of Human Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes in Biowires Using Electrical Stimulation. J Vis Exp. 2017;(123). [4] Yeon JH, Na D, Choi K,et al. Reliable permeability assay system in a microfluidic device mimicking cerebral vasculatures. Biomed. Microdevices. Biomed Microdevices. 2012;14(6): 1141-1148.[5] Griep LM, Wolbers F, de Wagenaar B,et al.BBB on chip: microfluidic platform to mechanically and biochemically modulate blood-brain barrier function. Biomed Microdevices. 2013;15(1):145-150.[6] Kim JA, Kim HN, Im SK, Chung S,et al.Collagen-based brain microvasculature model in vitro using three-dimensional printed template. Biomicrofluidics. 2015;9(2):024115.[7] Brown JA, Pensabene V, Markov DA, et al. Recreating blood-brain barrier physiology and structure on chip: A novel neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor.Biomicrofluidics. 2015; 9(5):054124.[8] Herland A, van der Meer AD, FitzGerald EA, et al.Distinct Contributions of Astrocytes and Pericytes to Neuroinflammation Identified in a 3D Human Blood-Brain Barrier on a Chip. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150360.[9] Fox EL,Bowers RW,Foss ML.The physiological basis for exercise and sport.1993.[10] Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, et al. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension.Nature. Nature. 1997;389(6654):990-994.[11] Jacot JG, McCulloch AD, Omens JH. Substrate stiffness affects the functional maturation of neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Biophys. J. Biophys J. 2008;95(7):3479-3487.[12] Grosberg A, Nesmith AP, Goss JA, et al.Muscle on a chip: in vitro contractility assays for smooth and striated muscle. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2012 ;65(3):126-135.[13] Ma Z, Liu Q, Liu H, et al. Laser-patterned stem-cell bridges in a cardiac muscle model for on-chip electrical conductivity analyses. Lab Chip. 2012;12(3):566-573.[14] Zhang D, Shadrin IY, Lam J, et al. Tissue-engineered cardiac patch for advanced functional maturation of human ESC-derived cardiomyocytes. Biomaterials. 2013;34(23): 5813-5820.[15] Juhas M, Engelmayr GC Jr, Fontanella AN, et al.Biomimetic engineered muscle with capacity for vascular integration and functional maturation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(15):5508-5513.[16] Zhang YS, Arneri A, Bersini S, et al.Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials. 2016;110:45-59.[17] Huh D, Matthews BD, Mammoto A, et al.Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 2010;328(5986): 1662-1668.[18] Stucki AO, Stucki JD, Hall SR, et al.A lung-on-a-chip array with an integrated bio-inspired respiration mechanism. Lab Chip. 2015;15(5):1302-1310.[19] Blume C, Reale R, Held M, et al.Temporal Monitoring of Differentiated Human Airway Epithelial Cells Using Microfluidics. PLoS One.2015 ;10(10):e0139872.[20] Schilders KA, Eenjes E, van Riet S, et al.Regeneration of the lung: Lung stem cells and the development of lung mimicking devices. Respir Res.2016;17:44. [21] Kniazeva T, Hsiao JC, Charest JL,et al.A microfluidic respiratory assist device with high gas permeance for artificial lung applications. Biomed Microdevices. 2011;13(2):315-323. [22] Hoganson DM, Pryor HI 2nd, Bassett EK, et al.Lung assist device technology with physiologic blood flow developed on a tissue engineered scaffold platform. Lab Chip.2011;11(4): 700-777. [23] Rochow N, Manan A, Wu WI, et al.An integrated array of microfluidic oxygenators as a neonatal lung assist device: in vitro characterization and in vivo demonstration.Artif Organs. 2014;38(10):856-866.[24] Jang KJ, Suh KY. A multi-layer microfluidic device for efficient culture and analysis of renal tubular cells. Lab Chip. 2010; 10(1):36-42.[25] Jang KJ, Mehr AP, Hamilton GA,et al.Human kidney proximal tubule-on-a-chip for drug transport and nephrotoxicity assessment. Integr Biol (Camb). 2013;5(9):1119-1129. [26] Maschmeyer I, Lorenz AK, Schimek K, et al.A four-organ-chip for interconnected long-term co-culture of human intestine, liver, skin and kidney equivalents. Lab Chip. 2015;15(12):2688-2699.[27] Zhou M, Zhang X, Wen X, et al.Development of a Functional Glomerulus at the Organ Level on a Chip to Mimic Hypertensive Nephropathy. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31771.[28] Kane BJ, Zinner MJ, Yarmush ML, et al.Liver-Specific Functional Studies in a Microfluidic Array of Primary Mammalian Hepatocytes. Anal Chem. 2006;78(13):4291-4298.[29] Lee PJ, Hung PJ, Lee LP et al.An artificial liver sinusoid with a microfluidic endothelial-like barrier for primary hepatocyte culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007;97(5):1340-1346.[30] Lee SA, No da Y, Kang E, et al.Spheroid-based three-dimensional liver-on-a-chip to investigate hepatocyte- hepatic stellate cell interactions and flow effects. Lab Chip. 2013;13(18):3529-3537. [31] Bhise NS, Manoharan V, Massa S,et al.A liver-on-a-chip platform with bioprinted hepatic spheroids. Biofabrication. 2016;8(1):014101. [32] Ong LJY, Chong LH, Jin L, et al.A pump-free microfluidic 3D perfusion platform for the efficient differentiation of human hepatocyte-like cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017;114(10): 2360-2370. [33] Banaeiyan AA, Theobald J, Paukštyte J,et al.Design and fabrication of a scalable liver-lobule-on-a-chip microphysiological platform. Biofabrication. 2017 ;9(1):015014.[34] O'Neill AT, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Walker GM,et al.Characterization of microfluidic human epidermal keratinocyte culture. Cytotechnology. 2008;56(3):197-207. [35] Ataç B, Wagner I, Horland R, et al.Skin and hair on-a-chip: in vitro skin models versus ex vivo tissue maintenance with dynamic perfusion. Lab Chip. 2013;13(18):3555-3561. [36] Ilka Wagner, Beren Atac, Gerd Lindner ,et al.Skin and hair-on-a-chip: Hair and skin assembly versus native skin maintenance in a chip-based perfusion system. BMC Proc. 2013;7:P93.[37] Abaci HE,Gledhill K,Guo Z,AM,et al.Pumpless microfluidic platform for drug testing on human skin equivalents. Lab Chip.2015;15(3):882-888. [38] Wufuer M,Lee G,Hur W,et al.Skin-on-a-chip model simulating inflammation, edema and drug-based treatment.Sci Rep.2016; 6:37471. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
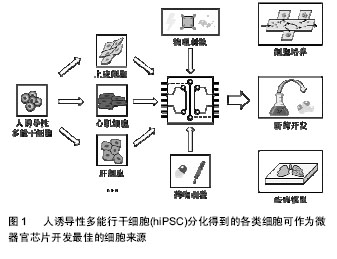
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。
文题释义:
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。.jpg) 文题释义:
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。
文题释义:
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。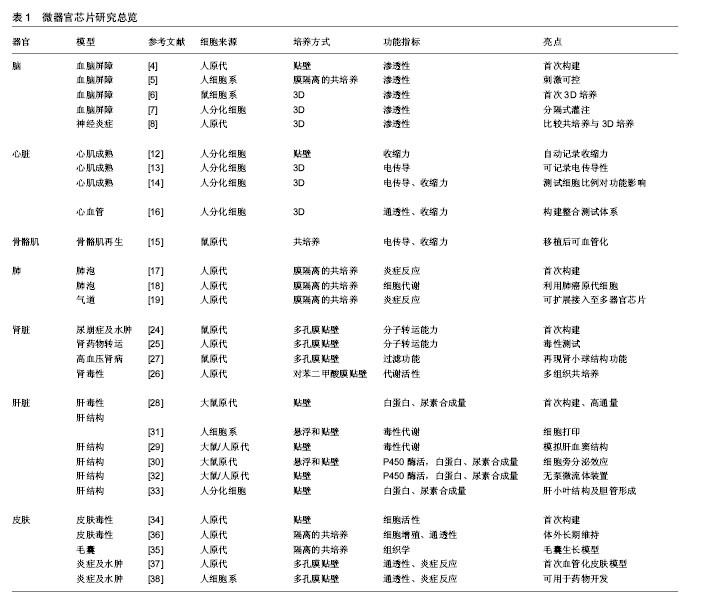
.jpg) 文题释义:
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。
文题释义:
微器官组织芯片:通过微流控或组织工程技术,将同种组织的不同细胞按照一定的排列和组织形式集成在有限的培养空间上,形成具有一定组织结构和生理功能的活细胞结构单元,就是微器官组织芯片。
微流控组件:它是指利用微流控将目的细胞送达指定位置的组件,也包括在培养过程中培养液的输入,以及废液的排出系统。通常,该组件具有小型化、集成化和自动化的特点。