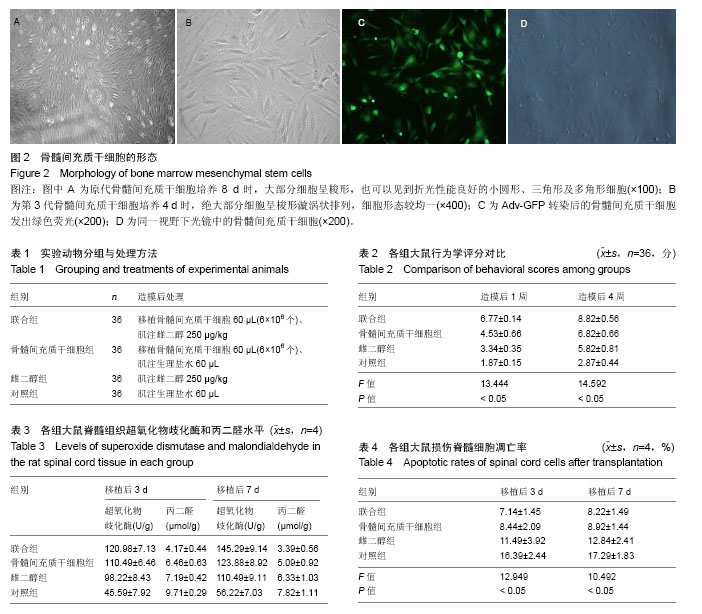
| [1] Deng C, Gu YJ, Zhang H, et al. Estrogen affects neuropathic pain through upregulating N-methyl-D-aspartate acid receptor 1 expression in the dorsal root ganglion of rats. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(3):464-469.[2] Colón JM, Miranda JD. Tamoxifen: an FDA approved drug with neuroprotective effects for spinal cord injury recovery. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(8):1208-1211.[3] Samantaray S, Das A, Matzelle DC, et al. Administration of low dose estrogen attenuates persistent inflammation, promotes angiogenesis, and improves locomotor function following chronic spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem. 2016;137(4):604-617.[4] Yeng CH, Chen PJ, Chang HK, et al. Attenuating spinal cord injury by conditioned medium from human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34? cells in rats. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;55(1):85-93.[5] Lin CW, Chen B, Huang KL, et al. Inhibition of Autophagy by Estradiol Promotes Locomotor Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neurosci Bull. 2016;32(2):137-144.[6] Melcangi RC, Giatti S, Garcia-Segura LM. Levels and actions of neuroactive steroids in the nervous system under physiological and pathological conditions: Sex-specific features. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;67:25-40.[7] Letaif OB, Cristante AF, Barros Filho TE, et al. Effects of estrogen on functional and neurological recovery after spinal cord injury: An experimental study with rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015;70(10):700-705. [8] Na W, Lee JY, Kim WS, et al. 17β-Estradiol Ameliorates Tight Junction Disruption via Repression of MMP Transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 2015;29(9):1347-1361.[9] Cox A, Varma A, Barry J, et al. Nanoparticle Estrogen in Rat Spinal Cord Injury Elicits Rapid Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Plasma, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Tissue. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(18):1413-1421.[10] Lee JY, Choi HY, Na WH, et al. 17β-estradiol inhibits MMP-9 and SUR1/TrpM4 expression and activation and thereby attenuates BSCB disruption/hemorrhage after spinal cord injury in male rats. Endocrinology. 2015;156(5):1838-1850.[11] Lu Y, Gao H, Zhang M, et al. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Transfected Placenta-Derived Versus Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Cells for Treating Spinal Cord Injury. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1800-1811.[12] Wang YH, Chen J, Zhou J, et al. Reduced inflammatory cell recruitment and tissue damage in spinal cord injury by acellular spinal cord scaffold seeded with mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(1):203-207. [13] Sun BW, Shen HM, Liu BC, et al. Research on the effect and mechanism of the CXCR-4-overexpressing BMSCs combined with SDF-1α for the cure of acute SCI in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(1):167-174. [14] Wang GD, Liu YX, Wang X, et al. The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis promotes recovery after spinal cord injury by mediating bone marrow-derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(7):11629-11640. [15] Hoellig M, Westhauser F, Kornienko K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from reaming material possess high osteogenic potential and react sensitively to bone morphogenetic protein 7. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2017;15(1):e54-e62.[16] Okuda A, Horii-Hayashi N, Sasagawa T, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell sheets may promote axonal regeneration and functional recovery with suppression of glial scar formation after spinal cord transection injury in rats. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;26(3):388-395.[17] Gu C, Li H, Wang C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decrease CHOP expression and neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2017;636:282-289. [18] Ide C, Nakano N, Kanekiyo K. Cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury - bone marrow stromal cells and choroid plexus epithelial cells. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(9):1385-1388.[19] Shi Y, Hu Y, Lv C, et al. Effects of Reactive Oxygen Species on Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Ann Transplant. 2016;21:695-700.[20] Wang Y, Jia H, Li WY, et al. Molecular examination of bone marrow stromal cells and chondroitinase ABC-assisted acellular nerve allograft for peripheral nerve regeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(4):1980-1992.[21] Ide C, Kanekiyo K. Points regarding cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2016; 11(7):1046-1049.[22] 刘兴, 虞乐华. 雌激素神经保护作用及其机制的研究进展[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2016, 32(11):1679-1682.[23] Xiong LL, Li Y, Shang FF, et al. Chondroitinase administration and pcDNA3.1-BDNF-BMSC transplantation promote motor functional recovery associated with NGF expression in spinal cord-transected rat. Spinal Cord. 2016;54(12):1088-1095. [24] Wang C, Shi D, Song X, et al. Calpain inhibitor attenuates ER stress-induced apoptosis in injured spinal cord after bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation. Neurochem Int. 2016;97:15-25.[25] Han S, Wang B, Li X, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture promote neuronal regeneration by neurotrophic protection and immunomodulation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(7): 1759-1769.[26] 刘莉, 叶鹏. 绝经后激素治疗和脑卒中的风险:雌激素给药途径及孕激素类型的影响[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2016(7):684-684.[27] Yang W, Yang Y, Yang JY, et al. Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(4):1075-1082.[28] Wang Z, Fang B, Tan Z, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning increases the protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):1953-1960.[29] Chen M, Chen S, Lin D. Carvedilol protects bone marrow stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death via PI3K-AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:257-263. [30] Chen J, Hu R, Ge H, et al. G-protein-coupled receptor 30-mediated antiapoptotic effect of estrogen on spinal motor neurons following injury and its underlying mechanisms. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2):1733-1740.[31] Xiong LL, Liu F, Lu BT, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem-Cell Transplantation Promotes Functional Improvement Associated with CNTF-STAT3 Activation after Hemi-Sectioned Spinal Cord Injury in Tree Shrews. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:172.[32] Peng RJ, Jiang B, Ding XP, et al. Effect of TNF-α Inhibition on Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Neurological Function Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury via the Wnt Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):743-752. [33] 康聪,孟宪勇,杨新明,等. 小剂量雌激素肌肉注射联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(25):4022-4027.[34] Fan X, Wang JZ, Lin XM, et al. Stem cell transplantation for spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis of treatment effectiveness and safety. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(5):815-825.[35] Li J, Guo W, Xiong M, et al. Erythropoietin facilitates the recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to sites of spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):1806-1812.[36] Shende P, Subedi M. Pathophysiology, mechanisms and applications of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:693-706.[37] Matyas JJ, Stewart AN, Goldsmith A, et al. Effects of bone-marrow-derived MSC transplantation on functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord injury: comparisons of transplant locations and cell concentrations.Cell Transplant. 2017 Apr 26. [Epub ahead of print][38] 杨新明,胡长波,成垚昱. 脊髓损伤机制及骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗机制的研究[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2016, 13(6):68-71.[39] 黄华, Raynald, 安沂华,等. 移植人骨髓间充质干细胞促进大鼠脊髓损伤后的神经功能恢复[J]. 武警后勤学院学报(医学版), 2016(11):865-868.[40] 陈志,申才良. 间充质干细胞与神经干细胞序贯移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤的作用研究[J]. 医学信息, 2017, 30(20):38-42. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)