| [1] Smith JS, Lafage V, Ryan DJ, et al. Association of myelopathy scores with cervical sagittal balance and normalized spinal cord volume: analysis of 56 preoperative cases from the AOSpine North America Myelopathy study. Spine. 2013;38(1):161-70.[2] Cho JH, Ha JK, Kim DG, et al. Does preoperative T1 slope affect radiological and functional outcomes following cervical laminoplasty? Spine. 2014;39(26):E1575.[3] Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, et al. Relationship between T1 slope and cervical alignment following multilevel posterior cervical fusion surgery: impact of T1 slope minus cervical lordosis. Spine. 2016;41(7):E396.[4] Kim TH, Lee SY, Kim YC, et al. T1 slope as a predictor of kyphotic alignment change after laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy. Spine. 2013;38(16):E992.[5] Angevine PD, Arons RR, Mccormick PC. National and regional rates and variation of cervical discectomy with and without anterior fusion, 1990-1999. Spine. 2003;28(9):931-939.[6] Wen ZQ, Du JY, Ling ZH, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: systematic review and a meta-analysis. Ther Clini Risk Manag. 2015;11(3):161-70.[7] Liu T, Yang HL, Xu YZ, et al. ACDF with the PCB cage-plate system versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Spine Surg. 2011;24(24):213-220.[8] Carrier CS, Bono CM, Lebl DR. Evidence-based analysis of adjacent segment degeneration and disease after ACDF: a systematic review. Spine J. 2013;13(10):1370-1378.[9] Roguski M, Benzel EC, Curran JN, et al. Postoperative cervical sagittal imbalance negatively affects outcomes after surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine. 2014;39(25):2070-2077.[10] Weng C, Wang J, Tuchman A, et al. The influence of T1 slope on the cervical sagittal balance in degenerative cervical spine: an analysis using kinematic MRI. Spine. 2015;41(3):185.[11] Ames CP, Smith JS, Scheer JK, et al. Impact of spinopelvic alignment on decision making in deformity surgery in adults: a review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(6):547.[12] Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(3):662.[13] Jr NJ, Sherk HH. Biomechanical evaluation of the extensor musculature of the cervical spine. Spine. 1988;13(1):9-11.[14] Katsuura A, Hukuda S, Saruhashi Y, et al. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Euro Spine J. 2001;10(4):320.[15] Knott PT, Mardjetko SM, Techy F. The use of the T1 sagittal angle in predicting overall sagittal balance of the spine. Spine J. 2010;10(11): 994-998.[16] Ono A, Tonosaki Y, Numasawa T, et al. The relationship between the anatomy of the nuchal ligament and postoperative axial pain after cervical laminoplasty: cadaver and clinical study. Spine. 2012;37(26): 1607-1613.[17] Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, et al. Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine. 2010;35(25):2224.[18] Lee SH, Kim KT, Seo EM, et al. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):E41.[19] Jun HS, Kim JH, Ahn JH, et al. T1 slope and degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2015;40(4):220-226.[20] Villavicencio AT, Babuska JM, Ashton A, et al. Prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical study evaluating the correlation of clinical outcomes and cervical sagittal alignment. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(5):1309-1316.[21] Lee CK, Shin DA, Yi S, et al. Correlation between cervical spine sagittal alignment and clinical outcome after cervical laminoplasty for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(1):100-107.[22] Taemin O, Scheer JK, Robert E, et al. Cervical compensatory alignment changes following correction of adult thoracic deformity: a multicenter experience in 57 patients with a 2-year follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(6):658-665.[23] Denaro V, Longo UG, Berton A, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: the relevance of the spinal cord back shift after posterior multilevel decompression. A systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2015;7(7):832-841.[24] Mummaneni PV, Kaiser MG, Matz PG, et al. Cervical surgical techniques for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(2):130.[25] Gaffney CJ, Spiker WR. Treating multilevel (three or four level) cervical myelopathy with ACDF or ACCF. Semin Spine Surg. 2014;26(3):122-127.[26] Barsa P, Suchomel P. Factors affecting sagittal malalignment due to cage subsidence in standalone cage assisted anterior cervical fusion. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9):1395.[27] Tomé-Bermejo F, Morales-Valencia JA, Moreno-Pérez J, et al. Long-term changes in sagittal alignment and its clinical implications after cervical interbody fusion cage subsidence for degenerative cervical disc disease. A prospective study with standalone lordotic tantalum cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;30(5):E648.[28] 张伟,陈德玉,杨立利,等.两种颈椎前路减压融合术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的临床疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3):181-183.[29] Sakai K, Yoshii T, Hirai T, et al. Impact of the surgical treatment for degenerative cervical myelopathy on the preoperative cervical sagittal balance: a review of prospective comparative cohort between anterior decompression with fusion and laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(1): 104-112.[30] Oh MC, Zhang HY, Park JY, et al. Two-level anterior cervical discectomy versus one-level corpectomy in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine. 2009;34(7):692-696. |
.jpg)
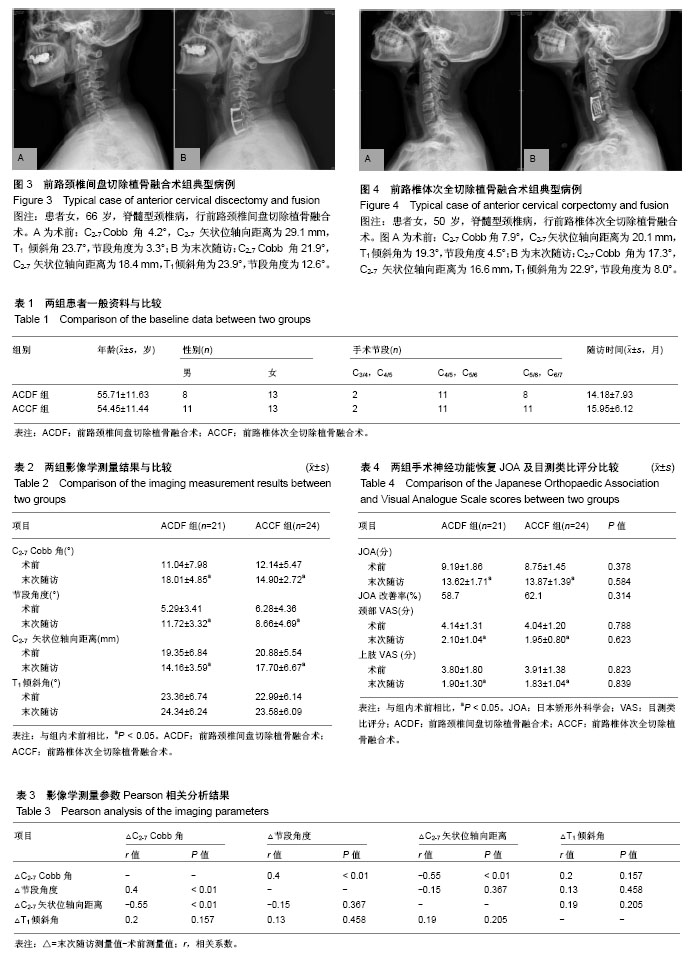
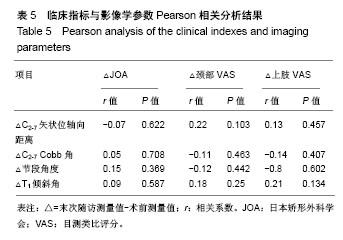
.jpg)
.jpg)