中国组织工程研究 ›› 2010, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (39): 7246-7250.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2010.39.007
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
锁骨内力分布特征的空间曲梁简化分析法
杨 予1,沈进稳2,徐定华3
- 浙江理工大学, 1建工学院土木系,3理学院,浙江省杭州市 310018;2浙江省中医院骨伤科,浙江省杭州市 310000
Curved beam simplified analysis of clavicle internal force distribution
Yang Yu1, Shen Jin-wen2, Xu Ding-hua3
- 1 Civil Engineering Department, Zhejiang Sci-tech University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; 2 Department of Orthopedics, Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China; 3 College of Science, Zhejiang Sci-tech University, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
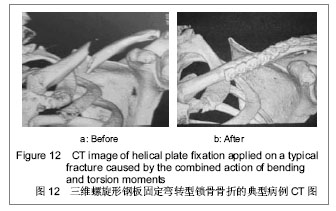
背景:锁骨的内力分布特征对于确定适当的骨折钢板固定方案具有重要参考价值,但目前常用的三维有限元方法由于受到单元形状、加载方式、边界条件等方面限制,尚无法对锁骨的宏观内力分布特征进行讨论。 目的:根据锁骨的生理特点,利用相对简单直观的力学分析方法分析锁骨的内力分布规律。 方法:通过截取特定横截面,将锁骨简化为空间曲梁模型而将肌肉的作用简化为作用在梁端的主矢和主矩,并根据静力平衡条件得出锁骨形心线上任意位置的内力解答,最后通过对锁骨实例的内力分析,探讨锁骨各内力的变化趋势。 结果与结论:计算结果与临床经验及有限元分析结果相吻合。此外通过对弯转比的分析显示多数情况下,锁骨中部区域为弯矩和转矩的组合变形区,在考虑骨折部位固定方案时,必须综合考虑抗弯和抗转能力。
中图分类号:
.jpg) 锁骨力学分析的常见方法为有限元法,例如杨志勇等[23]利用有限元软件Ansys,根据CT扫描资料将一男性患者锁骨离散为40 878个空间四面体单元,按各向同性弹性材料假定进行了受压状态下的应力分析;桂斌捷等[24]则进一步按横观各向同性材料假定,用Mimics和Ansys等软件对一女性患者锁骨进行了类似分析。然而通过上述文献可见,有限元法在以下方面尚存在不足:①人体骨骼外形复杂,软件直接生成的三维有限元模型往往与真实外形匹配欠佳[24] ,而且如何恰当地为三维实体单元确定边界条件也是个较困难的问题,设置不当的边界条件往往会导致虚假的应力集中现象,干扰了分析结果的正确判断和解读。②锁骨有限元模型往往难以处理复杂的加载条件,因而文献[23]和文献[24]中均只讨论了最简单的轴向压力情况,而锁骨实际受力情况要远为复杂,拉、压、弯、剪、扭均有可能。③有限元模型对锁骨的宏观内力分布规律掌握不足,由前述研究可见,多数有限元模型只能给出具体某个位置的应力矢量而无法对内力沿着长度方向的宏观变化趋势作出合理分析,而这一点却又恰恰是临床手术中的重要依据。
锁骨力学分析的常见方法为有限元法,例如杨志勇等[23]利用有限元软件Ansys,根据CT扫描资料将一男性患者锁骨离散为40 878个空间四面体单元,按各向同性弹性材料假定进行了受压状态下的应力分析;桂斌捷等[24]则进一步按横观各向同性材料假定,用Mimics和Ansys等软件对一女性患者锁骨进行了类似分析。然而通过上述文献可见,有限元法在以下方面尚存在不足:①人体骨骼外形复杂,软件直接生成的三维有限元模型往往与真实外形匹配欠佳[24] ,而且如何恰当地为三维实体单元确定边界条件也是个较困难的问题,设置不当的边界条件往往会导致虚假的应力集中现象,干扰了分析结果的正确判断和解读。②锁骨有限元模型往往难以处理复杂的加载条件,因而文献[23]和文献[24]中均只讨论了最简单的轴向压力情况,而锁骨实际受力情况要远为复杂,拉、压、弯、剪、扭均有可能。③有限元模型对锁骨的宏观内力分布规律掌握不足,由前述研究可见,多数有限元模型只能给出具体某个位置的应力矢量而无法对内力沿着长度方向的宏观变化趋势作出合理分析,而这一点却又恰恰是临床手术中的重要依据。