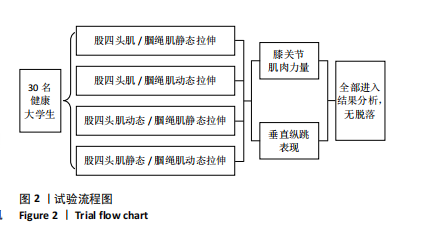
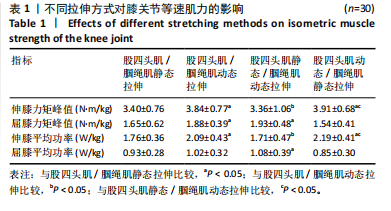
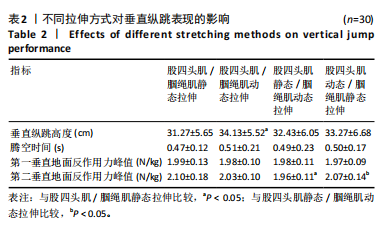
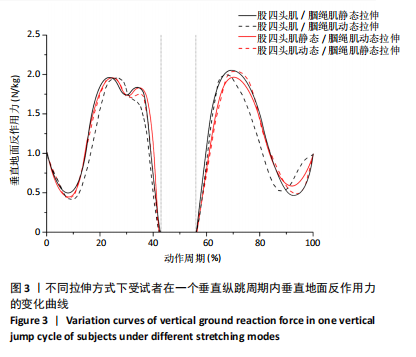
[1] ASGARI M, ALIZADEH MH, SHAHRBANIAN S, et al. Effects of the FIFA 11+ and a modified warm-up programme on injury prevention and performance improvement among youth male football players. PLoS One. 2022;17(10):745-755.
[2] ARNTZ F, MARKOV A, BEHM D G, et al. Chronic effects of static stretching exercises on muscle strength and power in healthy individuals across the lifespan: A systematic review with multi-level meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023;53(3):723-745.
[3] CHAABENE H, BEHM DG, NEGRA Y, et al. Acute effects of static stretching on muscle strength and power: an attempt to clarify previous caveats. Front Physiol. 2019;10(1):1468-1476.
[4] OPPLERT J, GENTY JB, BABAULT N. Do stretch durations affect muscle mechanical and neurophysiological properties? Int J Sports Med. 2016; 37(9):673-679.
[5] KHORASANI M, KELLIS E. Acute effects of different agonist and antagonist stretching arrangements on static and dynamic range of motion. Asian J Sports Med. 2015;6(4):244-268.
[6] SIMIC L, SARABON N, MARKOVIC G. Does pre-exercise static stretching inhibit maximal muscular performance? A meta-analytical review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(2):131-148.
[7] SEKIR U, ARABACI R, AKOVA B, et al. Acute effects of static and dynamic stretching on leg flexor and extensor isokinetic strength in elite women athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(2):268-281.
[8] SU H, CHANG NJ, WU WL, et al. Acute effects of foam rolling, static stretching, and dynamic stretching during warm-ups on muscular flexibility and strength in young adults. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(6): 469-477.
[9] PAPPAS PT, PARADISIS GP, EXELL TA, et al. Acute effects of stretching on leg and vertical stiffness during treadmill running. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(12):3417-3424.
[10] MALEK NFA, NADZALAN AM, TAN K, et al. The acute effect of dynamic vs. proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching on sprint and jump performance. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2024;9(1):1-8.
[11] PINCIVERO DM, POLEN RR, BYRD BN. Contraction mode and intensity effects on elbow antagonist muscle co-activation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2019;44(2):101-107.
[12] LATASH ML. Muscle coactivation: definitions, mechanisms, and functions. J Neurophysiol. 2018;120(1):88-104.
[13] SANDBERG JB, WAGNER DR, WILLARDSON JM, et al. Acute effects of antagonist stretching on jump height, torque, and electromyography of agonist musculature. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(5):1249-1256.
[14] MIRANDA H, MAIA MDE F, PAZ GA, et al. Acute effects of antagonist static stretching in the inter-set rest period on repetition performance and muscle activation. Res Sports Med. 2015;23(1):37-50.
[15] SEREFOGLU A, SEKIR U, GÜR H, et al. Effects of static and dynamic stretching on the Isokinetic peak torques and electromyographic activities of the antagonist muscles. J Sports Sci Med. 2017;16(1):6-13.
[16] GAO Z, SONG Y, YU PM, et al. Acute effects of different stretching techniques on lower limb kinematics, kinetics and muscle activities during vertical jump. J Biom Biomater Biomed Eng. 2019;40(2):1-15.
[17] BEHM DG, CHAOUACHI A. A review of the acute effects of static and dynamic stretching on performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(11): 2633-2651.
[18] MACIEL DG, DANTAS GAF, CERQUEIRA MS, et al. Peak torque angle, acceleration time and time to peak torque as additional parameters extracted from isokinetic test in professional soccer players: a cross-sectional study. Sports Biomech. 2020;16(6):1-12.
[19] ARAUJO JB, RODRIGUES R, AZEVEDO R, et al. Inter-machine reliability of the biodex and cybex isokinetic dynamometers for knee flexor/extensor isometric, concentric and eccentric tests. Phys Ther Sport. 2015;16(1): 59-65.
[20] PANOUTSAKOPOULOS V, KOTZAMANIDOU MC, PAPAIAKOVOU G, et al. The ankle joint range of motion and its effect on squat jump performance with and without arm swing in adolescent female volleyball players. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2021;6(1):14.
[21] WANG M, SONG Y, QIN H. Experimental study on the influence of exercise intervention on the physical and mental health of contemporary college students. J Boletin Tecnico. 2017;55(15):456-461.
[22] SAMSON M, BUTTON DC, CHAOUACHI A, et al. Effects of dynamic and static stretching within general and activity specific warm-up protocols. J Sports Sci Med. 2012;11(2):279-285.
[23] MAREK SM, CRAMER JT, FINCHER AL, et al. Acute effects of static and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching on muscle strength and power output. J Athl Train. 2005;40(2):94-103.
[24] BRANDENBURG JP. Duration of stretch does not influence the degree of force loss following static stretching. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2006; 46(4):526-534.
[25] BEHM DG, BLAZEVICH AJ, KAY AD, et al. Acute effects of muscle stretching on physical performance, range of motion, and injury incidence in healthy active individuals: a systematic review. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(1):1-11.
[26] MCGOWAN CJ, PYNE DB, THOMPSON KG, et al. Warm-Up strategies for sport and exercise: mechanisms and applications. Sports Med. 2015; 45(11):1523-1546.
[27] GUILLERON C, MAKTOUF W, BEAUNE B, et al. Coactivation pattern in leg muscles during treadmill walking in patients suffering from intermittent claudication. Gait Posture. 2021;84(6):245-253.
[28] XIONG QL, WU XY, XIAO N, et al. Antagonist muscle co-activation of limbs in human infant crawling: A pilot study. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015;15(6):2115-2118.
[29] HIGGINSON JS, ZAJAC FE, NEPTUNE RR, et al. Muscle contributions to support during gait in an individual with post-stroke hemiparesis. J Biomech. 2006;39(10):1769-1777.
[30] WAKEFIELD CB, COTTRELL GT. Changes in hip flexor passive compliance do not account for improvement in vertical jump performance after hip flexor static stretching. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(6):1601-1608.
[31] SUBATHRA P, ELANGO M, SUBRAMANI A. Effect of parcourse training on leg explosive power and shoulder strength among volleyball players. Int J Anal Exp Modal Anal. 2021;13(1):704-707.
[32] EWING KA, BEGG RK, GALEA MP, et al. Effects of prophylactic knee Bracing on lower limb kinematics, kinetics, and energetics during double-leg drop landing at 2 heights. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7): 1753-1761.
[33] YOUNG WB, BEHM DG. Effects of running, static stretching and practice jumps on explosive force production and jumping performance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2003;43(1):21-27.
[34] LEMPKE L, WILKINSON R, MURRAY C, et al. The effectiveness of PNF versus static stretching on Increasing hip-flexion range of motion. J Sport Rehabil. 2018;27(3):289-294.
[35] ÁLVAREZ-YATES T, GARCÍA-GARCÍA O. Effect of a Hamstring Flexibility Program Performed Concurrently During an Elite Canoeist Competition Season. J Strength Cond Res. 2020;34(3):838-846.
[36] CALDWELL SL, BILODEAU RLS, COX MJ, et al. Cross Education Training Effects are Evident with Twice Daily, Self-Administered Band Stretch Training. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(3):544-551.
[37] WARNEKE K, LOHMANN LH, PLÖSCHBERGER G, et al. Critical evaluation and recalculation of current systematic reviews with meta-analysis on the effects of acute and chronic stretching on passive properties and passive peak torque. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05564-6.
[38] SHEA A, BAHRAMI M, SARDROODIAN M, et al. The Effects of Static Stretching 2-Hours Prior to a Traditional Warm-Up on Performance. J Sports Sci Med. 2024 Sep 1;23(1):663-671.
[39] VANRENTERGHEM J, LEES A, LENOIR M, et al. Performing the vertical jump: movement adaptations for submaximal jumping. Hum Mov Sci. 2004;22(6):713-727.
[40] FONG CM, BLACKBURN JT, NORCROSS MF, et al. Ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion and landing biomechanics. J Athl Train. 2011;46(1): 5-10.
|