[1] YANG Y, RAO C, YIN T, et al. Application and underlying mechanism of acupuncture for the nerve repair after peripheral nerve injury: Remodeling of nerve system. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1253438.
[2] WAN T, ZHANG FS, QIN MY, et al. Growth factors: Bioactive macromolecular drugs for peripheral nerve injury treatment - molecular mechanisms and delivery platforms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;170: 116024.
[3] ZHOU W, RAHMAN MSU, SUN C, et al. Perspectives on the novel multifunctional nerve guidance conduits: From specific regenerative procedures to motor function rebuilding. Adv Mater. 2024;36(14): e2307805.
[4] REN J, TANG X, WANG T, et al. A dual-modal magnetic resonance/photoacoustic imaging tracer for long-term high-precision tracking and facilitating repair of peripheral nerve injuries. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13):e2200183.
[5] BEHTAJ S, EKBERG JAK, ST JOHN JA. Advances in electrospun nerve guidance conduits for engineering neural regeneration. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(2):219.
[6] BITTNER GD, BUSHMAN JS, GHERGHEREHCHI CL, et al. Typical and atypical properties of peripheral nerve allografts enable novel strategies to repair segmental-loss injuries. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):60.
[7] MANKAVI F, IBRAHIM R, WANG H. Advances in biomimetic nerve guidance conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023;13(18):2528.
[8] SUN J, CAO W, PAN S, et al. Porous organic materials in tissue engineering: Recent advances and applications for severed facial nerve injury repair. Molecules. 2024;29(3):566.
[9] 曹银利,傅锴锴,陈文,等.可生物降解的聚氨酯体内应用进展[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2023,52(1):111-116.
[10] JIA B, HUANG H, DONG Z, et al. Degradable biomedical elastomers: Paving the future of tissue repair and regenerative medicine. Chem Soc Rev. 2024;53(8):4086-4153.
[11] PEDERSEN DD, KIM S, WAGNER WR. Biodegradable polyurethane scaffolds in regenerative medicine: Clinical translation review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(8):1460-1487.
[12] GU D, XIA Y, DING Z, et al. Inflammation in the peripheral nervous system after injury. Biomedicines. 2024;12(6):1256.
[13] MIN Q, PARKINSON DB, DUN XP. Migrating schwann cells direct axon regeneration within the peripheral nerve bridge. Glia. 2021;69(2): 235-254.
[14] QIAN Y, LIN H, YAN Z, et al. Functional nanomaterials in peripheral nerve regeneration: Scaffold design, chemical principles and microenvironmental remodeling. Mater Today. 2021;51:165-187.
[15] ZHANG CY, FU CP, LI XY, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for tissue engineering. Molecules. 2022;27(11):3442.
[16] BROWN M, LI J, MORAES C, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix: New promising and challenging biomaterials for regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. 2022;289:121786.
[17] WANG Y, LIN J, CHEN J, et al. Biodegradable polyurethane-incorporating decellularized spinal cord matrix scaffolds enhance schwann cell reprogramming to promote peripheral nerve repair. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(10):2115-2128.
[18] CHEN YW, CHEN CC, NG HY, et al. Additive manufacturing of nerve decellularized extracellular matrix-contained polyurethane conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Polymers. 2019;11(10):1612.
[19] MORELLI S, PISCIONERI A, MESSINA A, et al. Neuronal growth and differentiation on biodegradable membranes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(2):106-117.
[20] MAULIDA HN, QULUB F, ROSDIANI AF, et al. Hollowfiber polyurethane-collagen coating chitosan as nerve graft for therapy of peripheral nerve injury in extreme paralysis. J Biomim Biomater Biomed Eng. 2016;28:78-84.
[21] XU W, ZHANG Z, LU H, et al. Biocompatible polyurethane conduit grafted with vascular endothelial growth factor-loaded hydrogel repairs the peripheral nerve defect in rats. Macromol Biosci. 2022; 22(3):e2100397.
[22] NASAB ST, ROODBARI NH, GOODARZI V, et al. Nanobioglass enhanced polyurethane/collagen conduit in sciatic nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(5):1093-1102.
[23] WANG Y, LI D, WANG G, et al. The effect of co-transplantation of nerve fibroblasts and schwann cells on peripheral nerve repair. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(12):1507-1519.
[24] CHEN ZX, LU HB, JIN XL, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived cells repair peripheral nerve defects in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(1): 152-161.
[25] FILIPPI M, GARELLO F, YASA O, et al. Engineered magnetic nanocomposites to modulate cellular function. Small. 2022;18(9): e2104079.
[26] DENG P, CHEN F, ZHANG H, et al. Multifunctional double-layer composite hydrogel conduit based on chitosan for peripheral nerve repairing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13):e2200115.
[27] NIU Y, CHEN KC, HE T, et al. Scaffolds from block polyurethanes based on poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (pcl) and poly(ethylene glycol) (peg) for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(14):4266-4277.
[28] HSU SH, CHANG WC, YEN CT. Novel flexible nerve conduits made of water-based biodegradable polyurethane for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(5):1383-1392.
[29] LIN W, LAN W, WU Y, et al. Aligned 3d porous polyurethane scaffolds for biological anisotropic tissue regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2020; 7(1):19-27.
[30] TRAN RT, CHOY WM, CAO H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of biomimetic multichanneled crosslinked-urethane-doped polyester tissue engineered nerve guides. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(8): 2793-2804.
[31] DONG X, LIU S, YANG Y, et al. Aligned microfiber-induced macrophage polarization to guide schwann-cell-enabled peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;272:120767.
[32] SALA MR, SKALLI O, LEVENTIS N, et al. Nerve response to superelastic shape memory polyurethane aerogels. Polymers (Basel). 2020; 12(12):2995.
[33] NIU Y, GALLUZZI M. A biodegradable block polyurethane nerve-guidance scaffold enhancing rapid vascularization and promoting reconstruction of transected sciatic nerve in sprague-dawley rats. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(48):11063-11073.
[34] WANG Y, LIANG R, LIN J, et al. Biodegradable polyurethane nerve guide conduits with different moduli influence axon regeneration in transected peripheral nerve injury. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(38): 7979-7990.
[35] ZHOU K, WEI W, YANG D, et al. Dual electrical stimulation at spinal-muscular interface reconstructs spinal sensorimotor circuits after spinal cord injury.Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):619.
[36] LI L, LI D, WANG Y, et al. Implantable zinc-oxygen battery for in situ electrical stimulation-promoted neural regeneration. Adv Mater. 2023;35(32):e2302997.
[37] WU Y, WANG L, GUO B, et al. Electroactive biodegradable polyurethane significantly enhanced schwann cells myelin gene expression and neurotrophin secretion for peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2016;87:18-31.
[38] SHAHROUSVAND M, HOSEINIAN MS, GHOLLASI M, et al. Flexible magnetic polyurethane/Fe2O3 nanoparticles as organic-inorganic nanocomposites for biomedical applications: Properties and cell behavior. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;74:556-567.
[39] HOSEINIAN MS, POORMOGHADAM D, KHEIROLLAHZADEH F, et al.
Improved neural differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cell(hipscs) on a novel polyurethane-based scaffold containing iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3 nps). Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;18(7): 993-1000.
[40] LEE TH, YEN CT, HSU SH. Preparation of polyurethane-graphene nanocomposite and evaluation of neurovascular regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):597-609.
[41] ZHANG Q, CHEN J, FENG Y, et al. Electroactive scaffolds of biodegradable polyurethane/polydopamine-functionalized graphene oxide regulating the inflammatory response and revitalizing the axonal growth cone for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(27):6308-6318.
[42] RIOS MU, BUCKSOT JE, RAHEBI KC, et al. Protocol for construction of rat nerve stimulation cuff electrodes. Methods Protoc. 2019;2(1):19.
[43] HUANG Z, GUO Z, SUN M, et al. A study on graphene composites for peripheral nerve injury repair under electrical stimulation. RSC Adv. 2019;9(49):28627-28635.
[44] CHOI YS, HSUEH YY, KOO J, et al. Stretchable, dynamic covalent polymers for soft, long-lived bioresorbable electronic stimulators designed to facilitate neuromuscular regeneration. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5990.
[45] SALEHI M, NASERI-NOSAR M, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, et al. Polyurethane/gelatin nanofibrils neural guidance conduit containing platelet-rich plasma and melatonin for transplantation of schwann cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(3):703-713.
[46] CHEN SH, CHOU PY, CHEN ZY, et al. An electrospun nerve wrap comprising bletilla striata polysaccharide with dual function for nerve regeneration and scar prevention. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;250:116981.
[47] CHEN Y, LONG X, LIN W, et al. Bioactive 3d porous cobalt-doped alginate/waterborne polyurethane scaffolds with a coral reef-like rough surface for nerve tissue engineering application. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(2):322-335.
[48] YANG H, LI Q, LI L, et al. Gastrodin modified polyurethane conduit promotes nerve repair via optimizing schwann cells function. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:355-367.
[49] SINGH A, SHIEKH PA, QAYOOM I, et al. Evaluation of polymeric aligned ngcs and exosomes in nerve injury models in diabetic peripheral neuropathy condition. Eur polym J. 2021;146:110256.
[50] SINGH A, SHIEKH PA, DAS M, et al. Aligned chitosan-gelatin cryogel-filled polyurethane nerve guidance channel for neural tissue engineering: Fabrication, characterization, and in vitro evaluation. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(2):662-673.
[51] KIM JI, HWANG TI, AGUILAR LE, et al. A controlled design of aligned and random nanofibers for 3d bi-functionalized nerve conduits fabricated via a novel electrospinning set-up. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23761.
[52] VINZONS LU, DONG GC, LIN SP. Hierarchically patterned polyurethane microgrooves featuring nanopillars or nanoholes for neurite elongation and alignment. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2023;14:1157-1168.
[53] THAMPI S, THEKKUVEETTIL A, MUTHUVIJAYAN V, et al. Accelerated outgrowth of neurites on graphene oxide-based hybrid electrospun fibro-porous polymeric substrates. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(4): 2160-2169.
[54] KAI D, TAN MJ, PRABHAKARAN MP, et al. Biocompatible electrically conductive nanofibers from inorganic-organic shape memory polymers. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;148:557-565.
[55] NABIPOUR M, MELLATI A, ABASI M, et al. Preparation of bilayer tissue-engineered polyurethane/poly-l-lactic acid nerve conduits and their in vitro characterization for use in peripheral nerve regeneration. J Biol Eng. 2024;18(1):16.
[56] WU Y, WANG L, HU T, et al. Conductive micropatterned polyurethane films as tissue engineering scaffolds for schwann cells and pc12 cells. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;518:252-262.
[57] ZHAO Y, LIANG Y, DING S, et al. Application of conductive ppy/sf composite scaffold and electrical stimulation for neural tissue engineering . Biomaterials. 2020;255:120164.
[58] SUN Y, ZHANG Y, GUO Y, et al. Electrical aligned polyurethane nerve guidance conduit modulates macrophage polarization and facilitates immunoregulatory peripheral nerve regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):244.
[59] SHRESTHA S, SHRESTHA BK, LEE J, et al. A conducting neural interface of polyurethane/silk-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes with enhanced mechanical strength for neuroregeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:511-523.
[60] DEMIR US, SHAHBAZI R, CALAMAK S, et al. Gold nano-decorated aligned polyurethane nanofibers for enhancement of neurite outgrowth and elongation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(6):1604-1613.
[61] SHAN Y, XU L, CUI X, et al. A responsive cascade drug delivery scaffold adapted to the therapeutic time window for peripheral nerve injury repair. Mater Horiz. 2024;11(4):1032-1045.
|

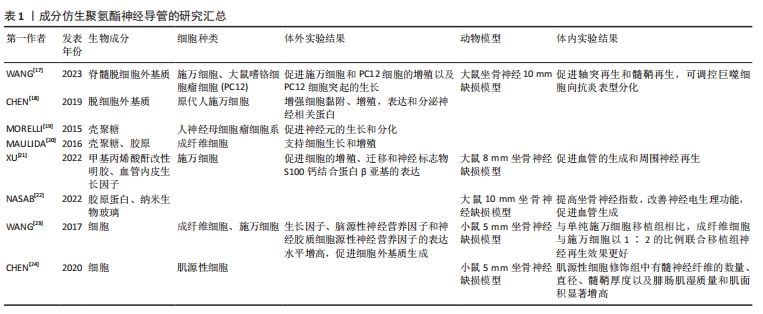

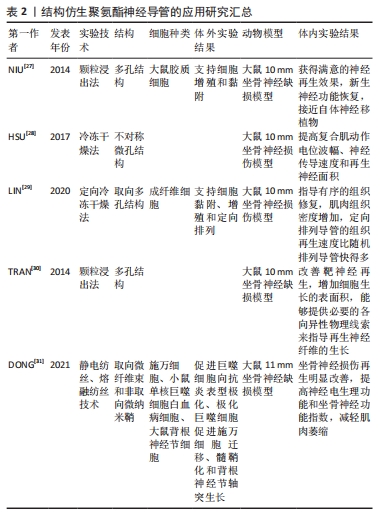

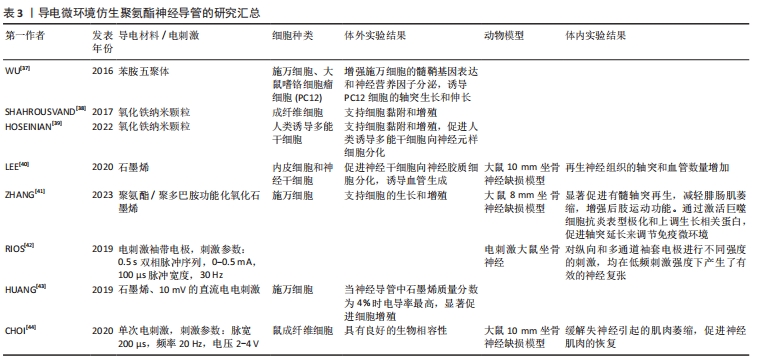



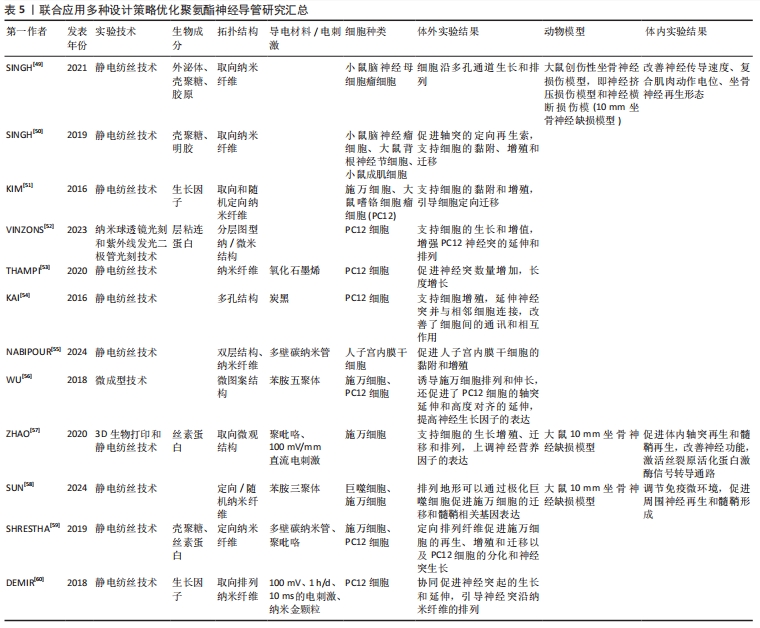
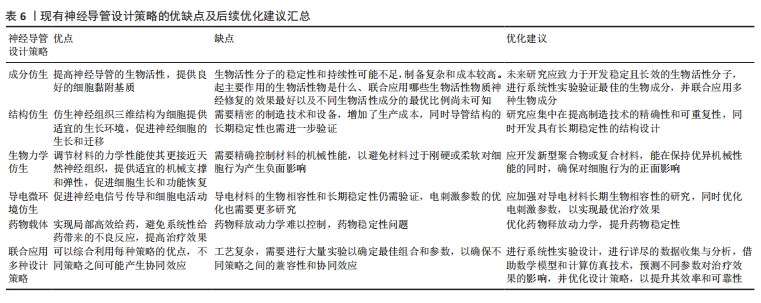




 基于以往研究人员的贡献,目前聚氨酯材料领域已经积累了相对完整的知识储备,周围神经损伤修复研究也取得了显著进展。尽管聚氨酯神经导管在神经组织工程中展现出巨大潜力,但其修复效果尚不及自体神经移植。与国外相比,国内聚氨酯神经导管的临床应用方案相对较少,主要处于基础研究阶段。因此,亟需开发对标国际顶尖的医用聚氨酯神经导管。现有研究未充分考虑神经再生过程中复杂的病理生理机制和微环境变化,也未充分探讨如何通过新型仿生策略优化神经导管以适应这些变化;此外,目前研究较少深入探讨聚氨酯材料在神经修复中的关键通路和具体作用机制。
基于以往研究人员的贡献,目前聚氨酯材料领域已经积累了相对完整的知识储备,周围神经损伤修复研究也取得了显著进展。尽管聚氨酯神经导管在神经组织工程中展现出巨大潜力,但其修复效果尚不及自体神经移植。与国外相比,国内聚氨酯神经导管的临床应用方案相对较少,主要处于基础研究阶段。因此,亟需开发对标国际顶尖的医用聚氨酯神经导管。现有研究未充分考虑神经再生过程中复杂的病理生理机制和微环境变化,也未充分探讨如何通过新型仿生策略优化神经导管以适应这些变化;此外,目前研究较少深入探讨聚氨酯材料在神经修复中的关键通路和具体作用机制。