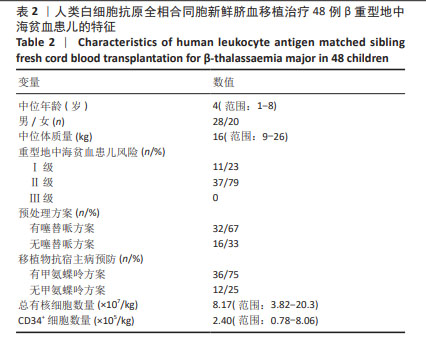
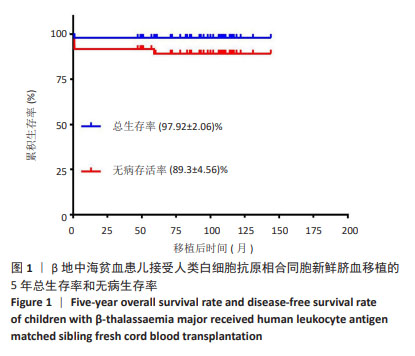
[1] KATTAMIS A, KWIATKOWSKI JL, AYDINOK Y. Thalassaemia. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2310-2324.
[2] LOCATELLI F, KABBARA N, RUGGERI A, et al. Outcome of patients with hemoglobinopathies given either cord blood or bone marrow transplantation from an HLAidentical sibling. Blood. 2013;122(6): 1072-1078.
[3] 陆婧媛,林进宗,陈凌非,等.非冻存同胞脐血干细胞移植治疗儿童重型地中海贫血症9例[J].中华器官移植杂志,2022,43(3): 151-155.
[4] WEN J, HAQUE Q, PEI F, et al. Transplant outcomes in beta-thalassemia major patients receiving combined granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-primed bone marrow and cord blood graft compared to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-primed bone marrow alone. Acta Haematol. 2018;140(1):20-29.
[5] TANG X, FANG J, YU J, et al. Clinical outcomes of unrelated cord blood transplantation in children with malignant and non-malignant diseases: multicenter experience in China. Pediatr Transplant. 2018;22(1): e13090.
[6] ZHU X, TANG B, SUN Z. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: Still growing and improving. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;Suppl 2(Suppl 2): S62-S74.
[7] CHEN G, YUE A, RUAN Z, et al. Comparison of the effects of different cryoprotectants on stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1396783.
[8] MCMANUS MP, WANG L, CALDER C, et al. Comparison of pre-cryopreserved and post-thaw-and-wash-nucleated cell count on major outcomes following unrelated cord blood transplant in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16(5):438-442.
[9] GALAMBRUN C, PONDARRÉ C, BERTRAND Y, et al. French multicenter 22- year experience in stem cell transplantation for beta-thalassemia major: lessons and future directions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(1):62-68.
[10] 康栋梁,谭永红,陈亚玫,等.不同年龄段地中海贫血患儿接受异基因造血干细胞移植后疗效的比较[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2022,30(2):539-542.
[11] LI C, WU X, FENG X, et al. A novel conditioning regimen improves outcomes in β-thalassemia major patients using unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(19): 3875-3881.
[12] HE Y, JIANG H, LI C, et al. Long-term results of the NF-08-TM protocol in stem cell transplant for patients with thalassemia major: A multi-center large-sample study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(11):E297-E299.
[13] SODANI P, GAZIEV D, POLCHI P, et al. New approach for bone marrow transplantation in patients with class 3 thalassemia aged younger than 17 years. Blood. 2004;104(4):1201-1203.
[14] PRZEPIORKA D, WEISDORF D, MARTIN P, et al. 1994Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15(6):825-828.
[15] SHAMSHAD GU, AHMED S, BHATTI FA, et al. Mixed donor chimerism in non-malignant haematological diseases after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22(12):765-768.
[16] FOUZIA NA, EDISON ES, LAKSHMI KM, et al. Long-term outcome of mixed chimerism after stem cell transplantation for thalassemia major conditioned with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(2):169-174.
[17] LI XY, SUN X, CHEN J, et al. Hematopoietie stem cell transplantation for children with beta-thalassemia major:muhicenter experience in China. World J Pediatr. 2018;14(1):92-99.
[18] SUN Z, YAO B, XIE H, et al. Clinical Progress and Preclinical Insights Into Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Improvement. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(9):912-926.
[19] 孙自敏.非血缘脐血移植的展望[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2016, 39(6):461-465.
[20] MAYANI H, WAGNER JE, BROXMEYER HE. Cord blood research, banking, and transplantation: achievements, challenges, and perspectives. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(1):48-61.
[21] RUGGERI A, EAPEN M, SCARAVADOU A, et al. Umbilical cord blood transplantation for children with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(9):1375-1382.
[22] FENG J, LEE V, LEUNG AWK, et al. Double-unit unrelated cord blood transplantation for thalassemia major: Comparison with HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2021;25(3): e13901.
[23] MATZA LS, PARAMORE LC, STEWART KD, et al. Health state utilities associated with treatment for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. Eur J Health Econ. 2020;21(3):397-407.
[24] IINO M, SATO T, SAKAMOTO Y. Minimum-Dose, Short-Term Methotrexate With Tacrolimus for Graft-vs-Host Disease Prophylaxis Following Unrelated Cord Blood Transplantation in Adults: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Institution. Transplant Proc. 2021; 53(1):396-404.
[25] PONCE DM, POLITIKOS I, ALOUSI A, et al. Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Graft-versus-Host Disease after Cord Blood Transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(7):540-544.
[26] LERTKOVIT O, ANURATHAPAN U, HONGENG S, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in children and adolescents with thalassemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2021; 113(4):556-565.
[27] ANDREANI M, NESCI S, LUCARELLI G, et al. Long-term survival of ex-thalassemic patients with persistent mixed chimerism after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;25(4):401-404.
[28] ANDREANI M, TESTI M, LUCARELLI G. Mixed chimerism in haemoglobinopathies: from risk of graft rejection to immune tolerance. Tissue Antigens. 2014;83(3):137-146.
[29] MCCANN S, PASSWEG J, BACIGALUPO A, et al. The influence of cyclosporin alone, or cyclosporin and methotrexate, on the incidence of mixed haematopoietic chimaerism following allogeneic sibling bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;39(2):109-114.
[30] KAKO S, KANDA Y, ONIZUKA M, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for aplastic anemia with pre-transplant conditioning using fludarabine, reduced-dose cyclophosphamide, and low-dose thymoglobulin: A KSGCT prospective study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(3):251-257.
[31] LISINI D, ZECCA M, GIORGIANI G, et al. Donor/recipient mixed chimerism does not predict graft failure in children with beta-thalassemia given an allogeneic cord blood transplant from an HLA-identical sibling. Haematologica. 2008;93(12):1859- 1867.
[32] BRUCKNER M, KATHERIA AC, SCHMÖLZER GM. Delayed cord clamping in healthy term infants: More harm or good? Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;26(2):101221. |