[1] CUI D, LI H, WAN M, et al. The Origin and Identification of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Teeth: from Odontogenic to Non-odontogenic. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(1):39-45.
[2] SCHMALZ G, WIDBILLER M, GALLER KM. Clinical Perspectives of Pulp Regeneration. J Endod. 2020;46(9S):S161-S174.
[3] KıLıÇ Y, KARATAŞLıOĞLU E, KAVAL ME. The Effect of Root Canal Preparation Size and Taper of Middle Mesial Canals on Fracture Resistance of the Mandibular Molar Teeth: An In Vitro Study. J Endod. 2021;47(9):1467-1471.
[4] SISMANOGLU S, ERCAL P. Dentin-Pulp Tissue Regeneration Approaches in Dentistry: An Overview and Current Trends. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1298: 79-103.
[5] SUGIAMAN VK, DJUANDA R, PRANATA N, et al. Tissue Engineering with Stem Cell from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth (SHED) and Collagen Matrix, Regulated by Growth Factor in Regenerating the Dental Pulp. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(18):3712.
[6] YUAN SM, YANG XT, ZHANG SY, et al. Therapeutic potential of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives: Insights from basic research toward clinical applications. World J Stem Cells. 2022;14(7):435-452.
[7] YOSHIDA S, TOMOKIYO A, HASEGAWA D, et al. Insight into the Role of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(7):160.
[8] 张浩,高淑君,武沐洋,等.低氧浓度促进人牙髓干细胞增殖及神经分化[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2022,31(2):133-138.
[9] XIE Z, SHEN Z, ZHAN P, et al. Functional Dental Pulp Regeneration: Basic Research and Clinical Translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8991.
[10] LIU P, ZHANG Y, MA Y, et al. Application of dental pulp stem cells in oral maxillofacial tissue engineering. Int J Med Sci. 2022;19(2):310-320.
[11] FERNANDES TL, CORTEZ DE SANTANNA JP, FRISENE I, et al. Systematic Review of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Cartilage Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(1):1-12.
[12] DAS M, SLOAN AJ. Stem cell sources from human biological waste material: a role for the umbilical cord and dental pulp stem cells for regenerative medicine. Hum Cell. 2023;36(4):1312-1325.
[13] 赵阳鹏,陈佳楠,朱强.组织工程技术在牙髓再生中的研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2023,39(10):634-637.
[14] CHANSORIA P, ASIF S, POLKOFF K, et al. Characterizing the Effects of Synergistic Thermal and Photo-Cross-Linking during Biofabrication on the Structural and Functional Properties of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(11):5175-5188.
[15] SUN M, SUN X, WANG Z, et al. Synthesis and Properties of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels and Their Recent Applications in Load-Bearing Tissue. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(11):1290.
[16] PEPELANOVA I, KRUPPA K, SCHEPER T, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels with Defined Degree of Functionalization as a Versatile Toolkit for 3D Cell Culture and Extrusion Bioprinting. Bioengineering (Basel). 2018;5(3):55.
[17] ZHANG X, ZHOU S, ZHAN Y, et al. Molecular insights into the proteomic composition of porcine treated dentin matrix. Mater Today Bio. 2024;25: 100990.
[18] LI R, GUO W, YANG B, et al. Human treated dentin matrix as a natural scaffold for complete human dentin tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(20):4525-4538.
[19] ZHU T, GUO WH. Dentin matrix in tissue regeneration: a progress report. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;37(1):92-96.
[20] BI F, ZHANG Z, GUO W. Treated Dentin Matrix in Tissue Regeneration: Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):91.
[21] YANG B, CHEN G, LI J, et al. Tooth root regeneration using dental follicle cell sheets in combination with a dentin matrix - based scaffold. Biomaterials. 2012;33(8):2449-2461.
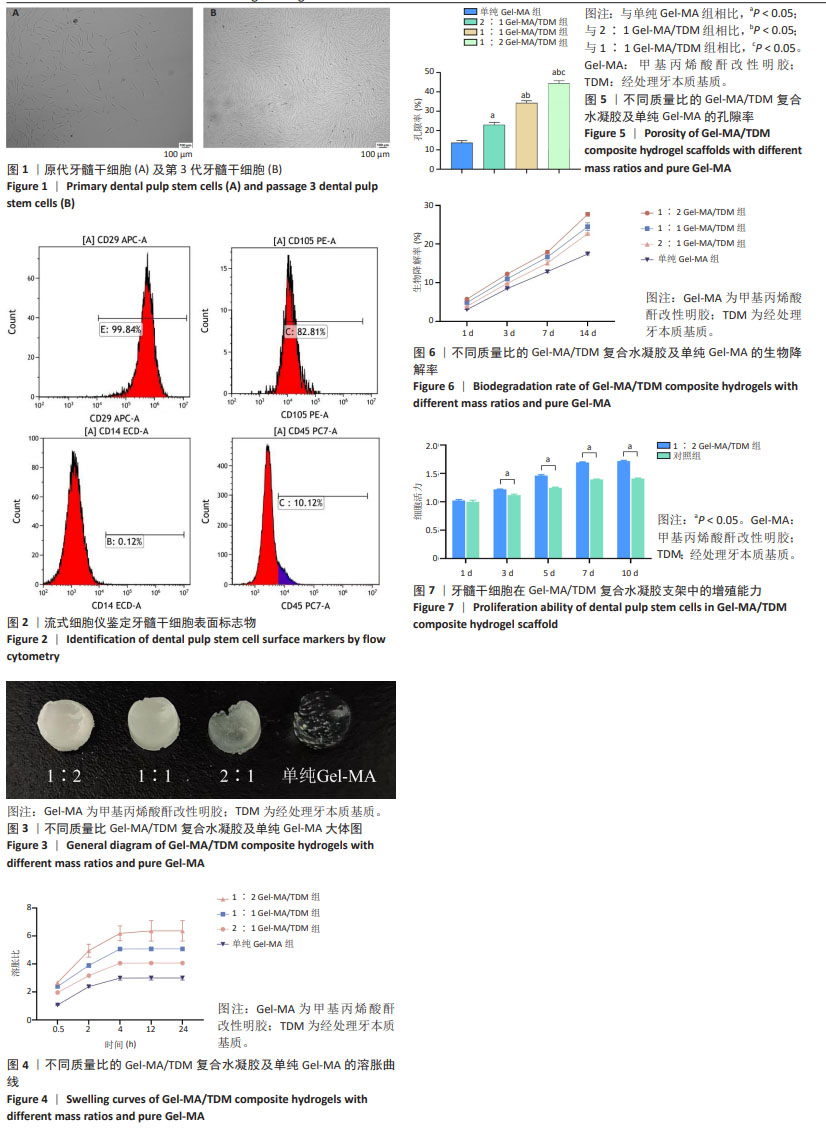
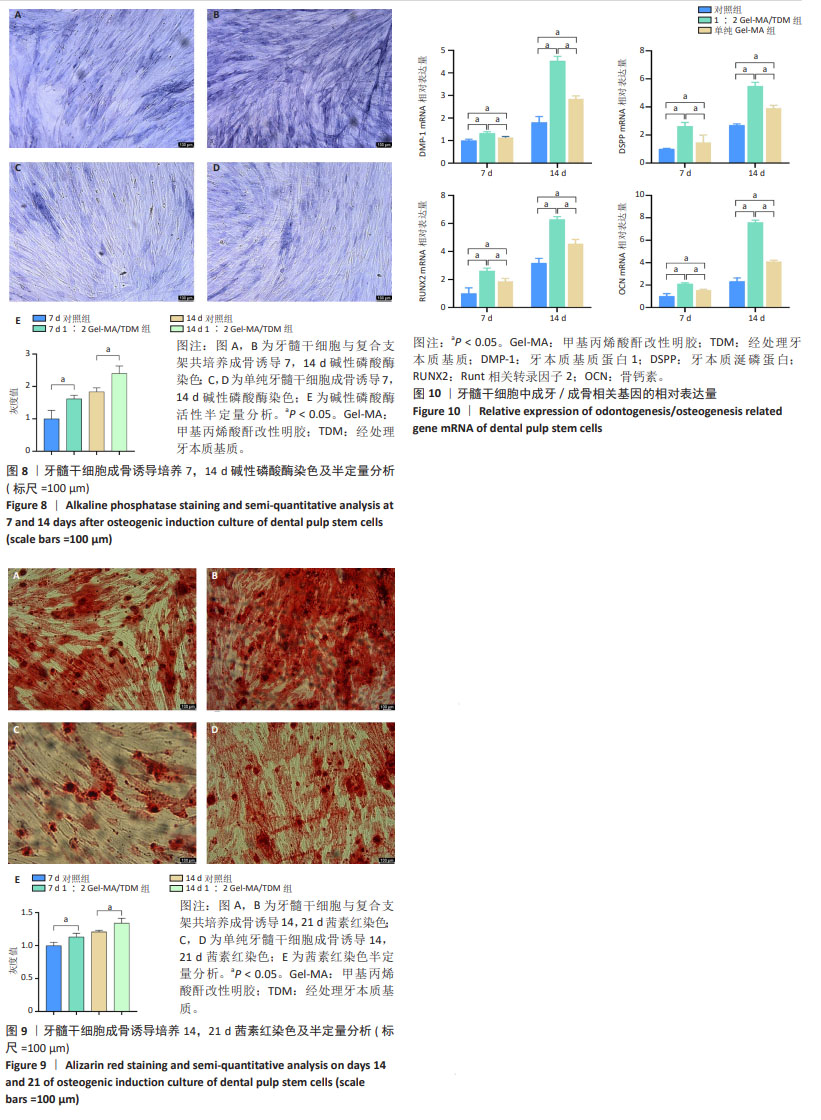
[22] 程梦可,杨杜娟,刘佳.甲基丙烯酸酐改性明胶/经处理牙本质基质生物活性支架的制备及性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(22): 3555-3560.
[23] 刘源,惠以宁,姜冰,等.LED红光上调MAPK信号促进炎性环境中人牙髓干细胞成骨/成牙本质分化[J].口腔疾病防治,2023,31(10):701-711.
[24] MOUSSA DG, APARICIO C. Present and future of tissue engineering scaffolds for dentin-pulp complex regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(1):58-75.
[25] 黄波,陈明学,彭礼庆,等.可注射性甲基丙烯酸酐改性明胶/软骨源性基质微粒复合水凝胶支架的制备及生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2480-2486.
[26] KLOTZ BJ, GAWLITTA D, ROSENBERG AJWP, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):394-407.
[27] DUBEY N, RIBEIRO JS, ZHANG Z, et al. Gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel as an injectable scaffold with multi-therapeutic effects to promote antimicrobial disinfection and angiogenesis for regenerative endodontics. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(17):3823-3835.
[28] CELIKKIN N, MASTROGIACOMO S, JAROSZEWICZ J, et al. Gelatin methacrylate scaffold for bone tissue engineering: The influence of polymer concentration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(1):201-209.
[29] KHAYAT A, MONTEIRO N, SMITH EE, et al. GelMA-Encapsulated hDPSCs and HUVECs for Dental Pulp Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2017;96(2):192-199.
[30] HOLIEL AA, MUSTAFA HM, SEDEK EM. Biodegradation of an injectable treated dentin matrix hydrogel as a novel pulp capping agent for dentin regeneration. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):126.
[31] GRAWISH ME, GRAWISH LM, GRAWISH HM, et al. Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental and Alveolar Bone Tissues Regeneration: An Innovative Scope Review. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(4):687-701.
[32] TRAPHAGEN SB, FOURLIGAS N, XYLAS JF, et al. Characterization of natural, decellularized and reseeded porcine tooth bud matrices. Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5287-5296.
[33] JIAO L, XIE L, YANG B, et al. Cryopreserved dentin matrix as a scaffold material for dentin-pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(18): 4929-4939.
[34] LIU S, SUN J, YUAN S, et al. Treated dentin matrix induces odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:85-97.
[35] 李鹏,杨秀.基于铜离子交联改善壳聚糖水凝胶力学性能和抗菌性能的研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2024,43(1):88-93.
[36] FATHIL MAM, KATAS H. Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Pro-Migratory Effects of Double Layered Hydrogels Packaged with Lactoferrin-DsiRNA-Silver Nanoparticles for Chronic Wound Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):991.
[37] LI L, YU F, ZHENG L, et al. Natural hydrogels for cartilage regeneration: Modification, preparation and application. J Orthop Translat. 2018;17:26-41.
[38] ZHOU Z, CUI J, WU S, et al. Silk fibroin-based biomaterials for cartilage/osteochondral repair. Theranostics. 2022;12(11):5103-5124.
[39] SEDEK EM, KAMOUN EA, EL-DEEB NM, et al. Photocrosslinkable gelatin-treated dentin matrix hydrogel as a novel pulp capping agent for dentin regeneration: I. synthesis, characterizations and grafting optimization. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):536.
[40] LIU Y, LI T, SUN M, et al. ZIF-8 modified multifunctional injectable photopolymerizable GelMA hydrogel for the treatment of periodontitis. Acta Biomater. 2022;146:37-48. |