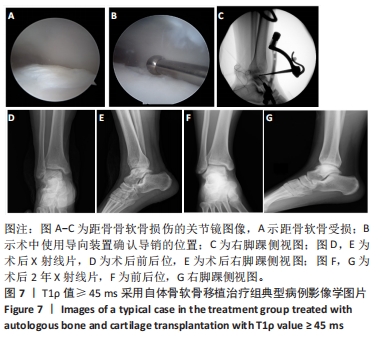
[1] BRUNS J, HABERMANN C, WERNER M. Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: A Review on Talus Osteochondral Injuries, Including Osteochondritis Dissecans. Cartilage. 2021;13(1):1380-1401.
[2] BURGER D, FEUCHT M, MUENCH LN, et al. Good clinical outcomes after patellar cartilage repair with no evidence for inferior results in complex cases with the need for additional patellofemoral realignment procedures: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(5):1752-1768.
[3] SHAFFER JJ JR, MANI M, SCHMITZ SL, et al. Proton Exchange Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Current and Future Applications in Psychiatric Research. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:532606.
[4] SHAFSHAK TS, ELNEMR R. The Visual Analogue Scale Versus Numerical Rating Scale in Measuring Pain Severity and Predicting Disability in Low Back Pain. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27(7):282-285.
[5] BALAJI G, BHUKYA S, NEMA S, et al. Predictors of Functional Outcome in Unstable Ankle Fractures Treated Surgically - A Prospective Cohort Study. Malays Orthop J. 2021;15(1):85-92.
[6] 申成春, 黄雷, 张峰, 等. 踝关节镜下微骨折术联合富血小板血浆治疗滑轨样距骨骨软骨损伤疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2022,37(6):652-653.
[7] PFLÜGER P, ZYSKOWSKI M, WEBER A, et al. Patient reported outcome of 33 operatively treated talar fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):698.
[8] HU W, CHEN Y, DOU C, et al. Microenvironment in subchondral bone: predominant regulator for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(4):413-422.
[9] ROUGEREAU G, NOAILLES T, KHOURY GE, et al. Is lateral ankle sprain of the child and adolescent a myth or a reality? A systematic review of the literature. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;28(3):294-299.
[10] 赵振拴, 李军, 于晓光, 等. 骨软骨移植术对距骨骨软骨损伤术后凝血功能步态参数下肢力线的影响[J]. 河北医学,2023,29(2):323-328.
[11] ANASTASIO AT, BAGHERI K, PEAIRS EM, et al. Juvenile Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: Current Concepts Review and an Update on the Literature. Children (Basel). 2023;10(5):884.
[12] 邱元洲, 高彦军, 王士波, 等. 关节镜下微骨折联合自体富血小板血浆治疗Hepple Ⅲ-Ⅳ型距骨骨软骨损伤[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2020,26(2):182-184.
[13] 高丽香, 袁慧书. T1ρ技术定量评估踝关节距骨骨软骨损伤[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2020,36(3):444-447.
[14] YANG Z, XIE C, OU S, et al. Cutoff points of T1 rho/T2 mapping relaxation times distinguishing early-stage and advanced osteoarthritis. Arch Med Sci. 2021;18(4):1004-1015.
[15] 保超宇, 潘斯学, 何光雄, 等. MRI测量正常成人距骨关节面软骨的厚度[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(5):140-143.
[16] 丰凡翔, 王勇, 张鑫, 等. 踝关节富血小板血浆注射结合冲击波治疗距骨软骨损伤微骨折术后患者的疗效及对踝关节功能恢复的影响[J]. 中国临床医生杂志,2023,51(6):715-719.
[17] BUERKE M, SHERIFF A, GARLICHS CD. CRP-Apherese bei akutem Myokardinfarkt bzw. COVID-19 CRP apheresis in acute myocardial infarction and COVID-19. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2022; 117(3):191-199.
[18] LODYGA M, HINZ B. TGF-β1 - A truly transforming growth factor in fibrosis and immunity. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020;101(1):123-139.
[19] LU L, ZHANG H, DAUPHARS DJ, et al. A Potential Role of Interleukin 10 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2021;42(1):3-5.
[20] YE Z, HU Y. TGF‑β1: Gentlemanly orchestrator in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):132.
[21] 王梅, 张晓东. 化学交换饱和转移成像技术在肌肉骨骼系统的研究进展[J]. 磁共振成像,2021,12(9):116-120.
[22] MARQUEZ-LARA A, STUBBS AJ. Editorial Commentary: Microfracture Remains a Foundational Tool for Cartilage Restoration During Hip-Preservation Procedures: Defying the Odds. Arthroscopy. 2023;39(5): 1195-1197.
[23] DI MARTINO A, SILVA S, ANDRIOLO L, et al. Osteochondral autograft transplantation versus autologous bone-cartilage paste grafting for the treatment of knee osteochondritis dissecans. Int Orthop. 2021;45(2):453-461.
[24] BAJURI MY, SABRI S, MAZLI N, et al. Osteochondral Injury of the Talus Treated With Cell-Free Hyaluronic Acid-Based Scaffold (Hyalofast®) - A Reliable Solution. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e17928.
[25] CHOI SW, LEE GW, LEE KB. Arthroscopic Microfracture for Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: Functional Outcomes at a Mean of 6.7 Years in 165 Consecutive Ankles. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(1): 153-158.
[26] DILLEY JE, EVERHART JS, KLITZMAN RG. Hyaluronic acid as an adjunct to microfracture in the treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):313.
[27] BERNSTEIN EM, KELSEY TJ, COCHRAN GK, et al. Femoral Neck Stress Fractures: An Updated Review. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(7): 302-311.
[28] HIGEUCHI M, NAMAKI S, FURUKAWA A, et al. Radiological and histochemical study of bone regeneration using the costal cartilage in rats. J Oral Sci. 2023;65(2):90-95.
[29] PASHA S, RAJAPASKE CR, REDDY R, et al. Quantitative imaging of the spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: shifting the paradigm from diagnostic to comprehensive prognostic evaluation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021;31(7):1273-1285.
[30] YEUNG KH, MAN GCW, LAM TP, et al. Accuracy on the preoperative assessment of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using biplanar low-dose stereoradiography: a comparison with computed tomography. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):558.
[31] SHARAFI A, BABOLI R, CHANG G, et al. 3D-T1ρ prepared zero echo time-based PETRA sequence for in vivo biexponential relaxation mapping of semisolid short-T2 tissues at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;50(4):1207-1218.
|