[1] SCHERRER D, BARKER L, HARRY J. Influence of Takeoff and Landing Displacement Strategies on Standing Long Jump Performance. Strength Cond J. 2022;2(1):1-9.
[2] DUCHARME SW, WU WFW, LIM K, et al. Standing Long Jump Performance With an External Focus of Attention Is Improved as a result of a More Effective Projection Angle. Strength Cond J. 2016; 30(1):276-281.
[3] HUANG XJ, QIAN YX, LIN Y, et al. Numerical Investigation of Injury Mechanism on the Human Knee of Long-jumpers. Manuf. 2019;35: 1297-1302.
[4] ONG JH, SIMIC M, EISENHUTH J, et al. Normative Reference Values for Knee Extensor Muscle Rate of Torque Development and Torque Steadiness in Adolescents and Adults. J Clin Rheumatol. 2022;28(3): 155-161.
[5] JANETJAVET M, FRÖHLICH S, BRUHIN B, et al. Swiss-Ski Power Test Results in Youth Competitive Alpine Skiers Are Associated With Biological Maturation and Skiing Performance. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2022;17(6):961-968.
[6] ASHBY BM, HEEGAARD JH. Role of arm motion in the standing long jump. J Biomech. 2003;35(12):1631-1637.
[7] HARMAN EA, ROSENSTEIN MT, FRYKMAN PN, et al. The effects of arms and countermovement on vertical jumping. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1990;22(6):825-830.
[8] GROSPRÊTRE S, EL KHATTABI S. Training habits and lower limb injury prevention in parkour practitioners. Mov Sports Sci. 2022;(115):43-55.
[9] HRVATSKIRASKI M, LARGER M. The Relationship between Age and Selected Kinematic Parameters of Standing Long Jump Test. Am Anthropol. 2016;24(1):237-242.
[10] ÖZALTAŞ HN, SERIN E. The Effect of Caffeine use at Different Times on Vertical Jump and Long Jump Performance in Elite Male Athletes. Pak J Med Health Sci. 2022;16(2):648-648.
[11] ASHBY BM, DELP SL. Optimal control simulations reveal mechanisms by which arm movement improves standing long jump performance. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1726-1734.
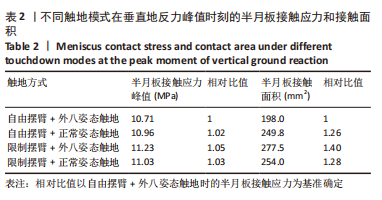
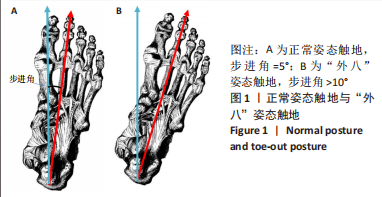
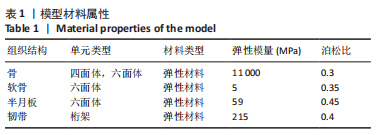
[12] 潘正晔,马勇,耿治中,等.预期条件下不同侧切角度膝关节应力状态的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(5):762-768.
[13] YOON J, HA S, LEE S, et al. Analysis of Contact Pressure at Knee Cartilage during Gait concerning Foot Progression Angle. Int J Precis Eng. 2018;19(5):761-766.
[14] OKUBO Y, KANEOKA K, SHIINA I, et al. Abdominal Muscle Activity During a Standing Long Jump. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43(8):577-582.
[15] HILL CE, HEALES LJ, STANTON R, et al. Effects of multidirectional elastic tape on forearm muscle activity and wrist extension during submaximal gripping in individuals with lateral elbow tendinopathy: A randomised crossover trial. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2022;100:105810.
[16] GONZÁLEZ FJQ, SCULCO PK, KAHLENBERG CA, et al. Undersizing the tibial baseplate in cementless total knee arthroplasty has only a small impact on bone-implant interaction: A Finite Element Biomechanical Study. Arthroplasty. 2022;S0883-5403(22)00969-X. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.10.032.
[17] DENG Z, WANG K, WANG H, et al. A finite element study of traditional Chinese cervical manipulation. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(7):2308-2317.
[18] FANELLI GC, EDSON C, REINHEIMER KN, et al. Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterolateral Corner Reconstruction. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2009;15(4):168-175.
[19] DONAHUE TL, FISHER MB, MAHER SA. Meniscus mechanics and mechanobiology. J Biomech. 2015;48(8):1341-1342.
[20] WALLER C, HAYES D, BLOCK JE, et al. Unload it: the key to the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19(11):1823-1829.
[21] GROOD ES, SUNTAY WJ. A Joint Coordinate System for the Clinical Description of Three-Dimensional Motions: Application to the Knee. J Biomech Eng. 1983;105(2):136-144.
[22] CHECA S, TAYLOR M, NEW A. Influence of an interposition spacer on the behaviour of the tibiofemoral joint: A finite element study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2008;23(8):1044-1052.
[23] NAGURA T, DYRBY CO, ALEXANDER EJ, et al. Mechanical loads at the knee joint during deep flexion. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(4):881-886.
[24] REN S, SHI H, LIU Z, et al. Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Validation of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Implications for the Injury Mechanism. Bioengineering. 2022;9(10):590.
[25] KUROSAWA H, KOBAYASHI T, NAKAJIMA H. Load-Bearing Mode of the Knee Joint: Physical Behavior of the Knee Joint with or Without Menisci. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;149(149):283-290.
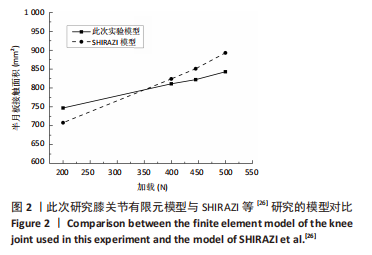
[26] SHIRAZI R, SHIRAZI-ADL A, HURTIG M. Role of cartilage collagen fibrils networks in knee joint biomechanics under compression. J Biomech. 2008;41(16):3340-3348.
[27] KIMURA A, YOKOZAWA T, OZAKI H. Clarifying the biomechanical concept of coordination through comparison with coordination in motor control. Front Sport Act Living. 2021;3:753062.
[28] JIN X, DONG Y, WANG F, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of lower extremity musculoskeletal disorders among manufacturing workers: a cross-sectional study in China. BMJ Open. 2022;12(2): e054969.
[29] KOSHINO Y, ISHIDA T, YAMANAKA M, et al. Toe-in landing increases the ankle inversion angle and moment during single-leg landing: implications in the prevention of lateral ankle sprains. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(6):530-535.
[30] FONG CM, BLACKBURN JT, NORCROSS MF, et al. Ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion and landing biomechanics. J Athl Train. 2011;46(1): 5-10.
[31] MASON-MACKAY AR, WHATMAN C, REID D. The effect of reduced ankle dorsiflexion on lower extremity mechanics during landing: A systematic review. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(5):451-458.
[32] PEEL SA, WEINHANDL JT. Task but not arm restriction influences lower extremity joint mechanics during bilateral landings. Sport Biomech. 2022;21(5):637-653.
[33] TAIT DB, NEWMAN P, BALL NB, et al. What did the ankle say to the knee? Estimating knee dynamics during landing—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2022;25(2):183-191.
[34] SELF BP, PAINE D. Ankle biomechanics during four landing techniques. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(8):1338-1344.
[35] LIM BO, KIM J, KIM SH, et al. The effects of taekwondo shoes on anterior cruciate ligament injury risk factors during jump whip kicks. Sci Sport. 2022;37(1):51-57.
[36] TOMTOMIN M, KMETTY Á. 217 Development of wrestling mat materials to achieve better mechanical properties and improve the safety of the athletes. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(Suppl 1):A85-A85.
|