中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4507-4512.doi: 10.12307/2023.538
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
补肾壮骨方干预去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠骨代谢及骨密度的变化
苏 辉1,闫炳翰1,王若冲2,薛海鹏3,谭国庆3,徐展望1,3
- 1山东中医药大学,山东省济南市 250355;2北京中医药大学,北京市 100000;3山东中医药大学附属医院,山东省济南市 250014
Effect of Bushen Zhuanggu Fang on bone metabolism and bone mineral density in rats with ovariectomized osteoporosis
Su Hui1, Yan Binghan1, Wang Ruochong2, Xue Haipeng3, Tan Guoqing3, Xu Zhanwang1, 3
- 1Shandong University of Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100000, China; 3Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Chinese Medicine, Shandong 250014, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨质疏松症:是一种以骨量减低、骨组织微结构损坏,导致骨脆性增加、易发生骨折为特征的全身性骨病。补肾壮骨方:全国名老中医药专家曹贻训老先生在多年的骨科临床工作中应用补肾壮骨方为院内协定方治疗骨质疏松症,并取得了良好的临床效果,但其治疗骨质疏松症具体机制尚不明确。
背景:中医药以其良好的治疗效果及安全性越来越多的应用于骨质疏松症的治疗中,补肾壮骨方目前作为山东中医药大学附属医院协定方被广泛应用于临床中,获得了极好的治疗效果。
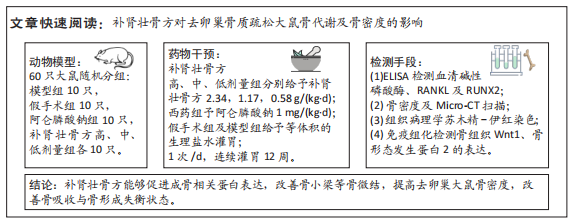
目的:评价补肾壮骨方对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢及骨密度的影响。
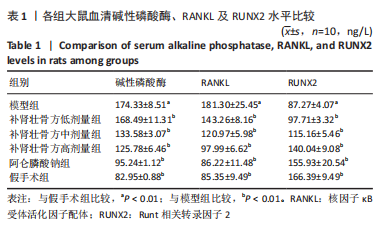
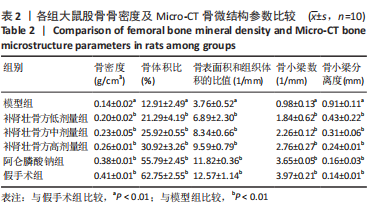
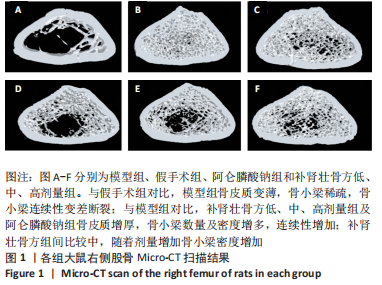
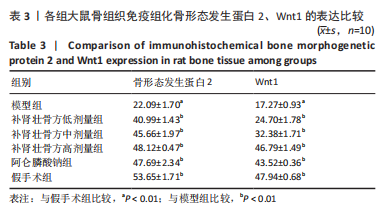
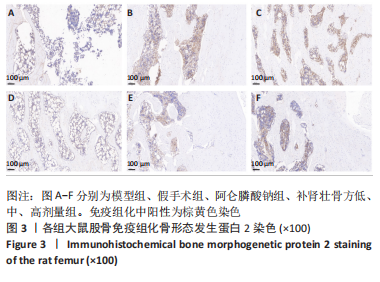
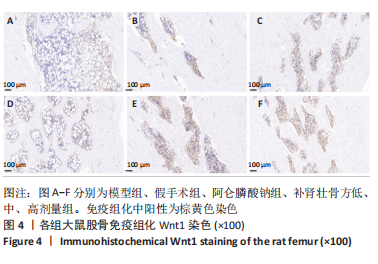
方法:60 只SD大鼠随机分为6组,分别为假手术组、模型组、阿仑膦酸钠组、补肾壮骨方高、中、低剂量组,每组10只,后5组制备去卵巢骨质疏松症模型,假手术组只切除卵巢周围脂肪组织。造模8周后,补肾壮骨方高、中、低剂量组分别予以2.34,1.17,0.58 g/(kg·d)补肾壮骨方,阿仑膦酸钠组予阿仑膦酸钠 1 mg/(kg·d),假手术组及模型组给予等体积的生理盐水,1次/d灌胃。连续灌胃12周后检测各组大鼠血清碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2及核因子κB受体活化因子配体水平;取右侧股骨观察骨密度及骨微结构;苏木精-伊红染色观察组织病理改变;免疫组化法检测骨组织 Wnt1、骨形态发生蛋白2蛋白表达。
结果与结论:①造模8周后,与假手术组对比,模型组大鼠骨密度、骨小梁数明显降低(P < 0.05),提示造模成功;②与模型组大鼠对比,补肾壮骨方低、中、高剂量组及阿仑膦酸钠组骨密度、大鼠骨体积比、骨表面积/组织体积的比值、骨小梁数明显增加(P < 0.01),骨小梁分离度显著降低(P < 0.01),其中阿仑膦酸钠组的改善作用优于补肾壮骨方组;苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,与模型组大鼠相比,补肾壮骨方低、中、高剂量组与阿仑膦酸钠组骨小梁数量增多,连续性增加,说明补肾壮骨方在去卵巢大鼠骨微结构上可明显改善骨骼状态;③补肾壮骨方低、中、高剂量组大鼠血清中 Runt相关转录因子2水平高于模型组(P < 0.01),碱性磷酸酶、核因子κB受体活化因子配体水平低于模型组(P < 0.01),其中阿仑膦酸钠组的改善作用优于补肾壮骨方组;免疫组化结果显示,补肾壮骨方低、中、高剂量组与阿仑膦酸钠组大鼠股骨中Wnt1、骨形态发生蛋白2相对表达量均显著增加;④提示补肾壮骨方能够改善大鼠骨代谢失衡部分指标,提高骨形成相关因子水平,从而改善骨吸收与骨形成失衡状态。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4458-0193(苏辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: