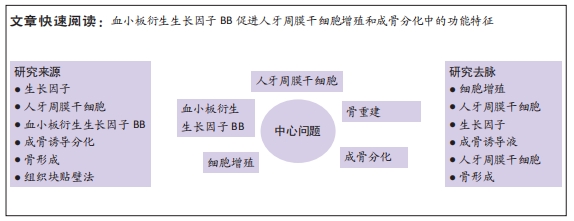
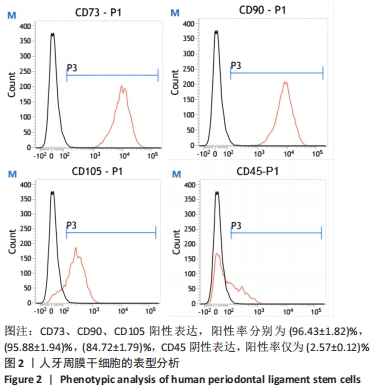
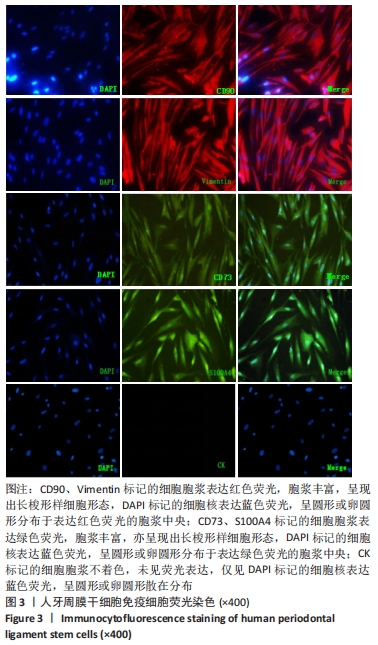
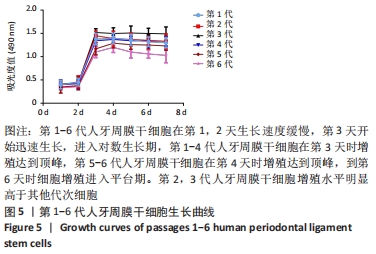
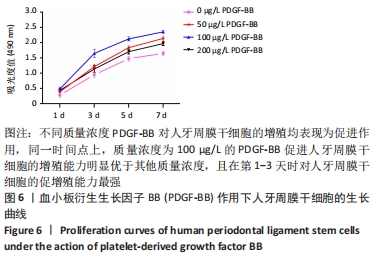
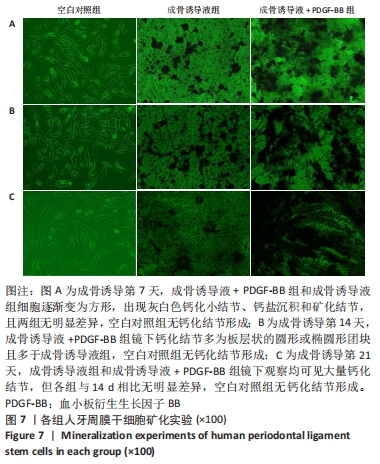
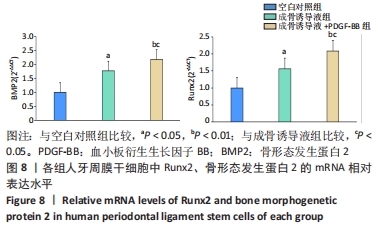
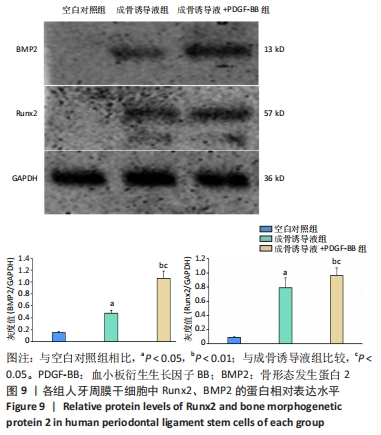
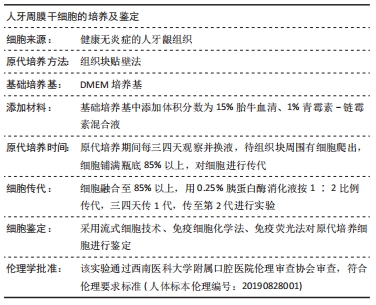
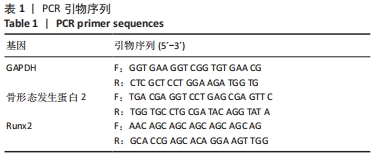
[1] IWASAKI K, AKAZAWA K, NAGATA M, et al. The fate of transplanted periodontal ligament stem cells in surgically created periodontal defects in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(1):192.
[2] PIZZICANNELLA J, GUGLIANDOLO A, ORSINI T, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles from human periodontal-ligament stem cells increase VEGF/VEGFR2 expression during bone regeneration. Front Physiol. 2019;10:512.
[3] DIOMEDE F, D’AURORA M, GUGLIANDOLO A, et al. A novel role in skeletal segment regeneration of extracellular vesicles released from periodontal-ligament stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:3805-3825.
[4] ZHAO Q, LI G, WANG T, et al. Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Transplanted with Nanohydroxyapatite/Chitosan/Gelatin 3D Porous Scaffolds Promote Jaw Bone Regeneration in Swine. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(10):548-559.
[5] MA C, WEI Q, CAO B, et al. A multifunctional bioactive material that stimulates osteogenesis and promotes the vascularization bone marrow stem cells and their resistance to bacterial infection. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(3):e0172499.
[6] QIN Z, YIN L, WANG K, et al. Effects of Icariin promotion on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;33(4):370-376.
[7] ZHANG N, LO CW, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. PDGF-BB and IL-4 co-overexpression is a potential strategy to enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):40.
[8] SANTHANAM L, LIU G, JANDU S, et al. Skeleton-secreted PDGF-BB mediates arterial stiffening. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(20):e147116.
[9] PERRAULT R, MOLNAR P, POOLE J, et al. PDGF-BB-mediated activation of CREB in vascular smooth muscle cells alters cell cycling via Rb, FoxO1 and p27kip1. Exp Cell Res. 2021;404(1):112612.
[10] SU F, SHI M, ZHANG J, et al. MiR-223/NFAT5 signaling suppresses arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and motility in vitro. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):26188-26198.
[11] ENDO K, HORIUCHI K, KATANO H, et al. Intra-articular Injection of PDGF-BB Explored in a Novel in Vitro Model Mobilizes Mesenchymal Stem Cells From the Synovium Into Synovial Fluid in Rats. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(5):1768-1779.
[12] ZHANG Z, LI Z, WANG Y, et al. PDGF-BB/SA/Dex injectable hydrogels accelerate BMSC-mediated functional full thickness skin wound repair by promoting angiogenesis. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(31):6176-6189.
[13] GAO SY, LIN RB, HUANG SH, et al. PDGF-BB exhibited therapeutic effects on rat model of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bone. 2021;144:115117.
[14] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[15] GUO J, HU Z, YAN F, et al. Angelica dahurica promoted angiogenesis and accelerated wound healing in db/db mice via the HIF-1α/PDGF-β signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:447-457.
[16] ZHANG Y, WU D, ZHAO X, et al. Stem Cell-Friendly Scaffold Biomaterials: Applications for Bone Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:598607.
[17] YOUNESI SOLTANI F, JAVANSHIR S, DOWLATI G, et al. Differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward tenocyte by platelet-derived growth factor-BB and growth differentiation factor-6. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022;23(2):237-246.
[18] CHEN H, TENG Y, CHEN X, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB protects dopaminergic neurons via activation of Akt/ERK/CREB pathways to upregulate tyrosine hydroxylase. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021; 27(11):1300-1312.
[19] WAN WF, ZHANG X, HUANG CR, et al. miR-34c inhibits PDGF-BB-induced HAVSMCs phenotypic transformation and proliferation via PDGFR-β/SIRT1 pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(5):4137-4151.
[20] YANG Y, MAO W, WANG L, et al. Circular RNA circLMF1 regulates PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of human aortic smooth muscle cells by regulating the miR-125a-3p/VEGFA or FGF1 axis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2022;80(2):167-183.
[21] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155.
[22] REN XS, TONG Y, QIU Y, et al. MiR155-5p in adventitial fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;9(1):1698795.
[23] ZHANG Z, SHUAI Y, ZHOU F, et al. PDLSCs regulate angiogenesis of periodontal ligaments via VEGF transferred by exosomes in periodontitis. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(5):558-567.
[24] ZHAO M, DAI W, WANG H, et al. Periodontal ligament fibroblasts regulate osteoblasts by exosome secretion induced by inflammatory stimuli. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;105:27-34.
[25] LIU T, HU W, ZOU X, et al. Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Bone Regeneration by Altering MicroRNA Profiles. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8852307.
[26] XIE HX, CAO L, YE LL, et al. Autogenous bone particles combined with platelet-rich plasma can stimulate bone regeneration in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):279.
[27] NIU W, LIM TC, ALSHIHRI A, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Stimulated Migration of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into an Injectable Gelatin-Hydroxyphenyl Propionic Acid Matrix. Biomedicines. 2021;9(2):203.
[28] CHOPRA H, LIAO C, ZHANG CF, et al. Lapine periodontal ligament stem cells for musculoskeletal research in preclinical animal trials. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):174.
[29] 李殿奇. PDGF-BB调节成、破骨细胞的作用机制及促进骨愈合的实验研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2016.
[30] WANG Q, LIN H, RAN J, et al. miR-200a-3p represses osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting ZEB2 and activating the NF-κB pathway. Acta Odontol Scand. 2022;80(2):140-149.
[31] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175.
|