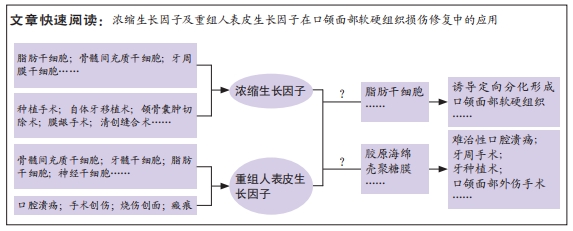
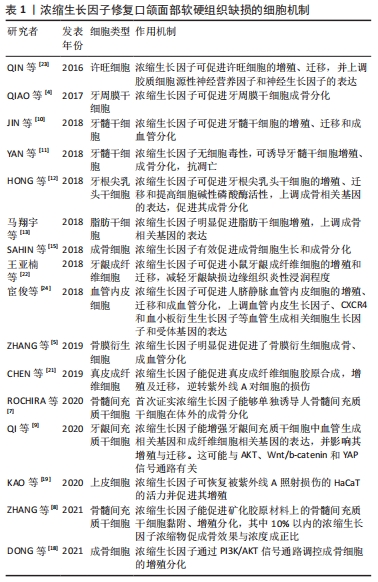
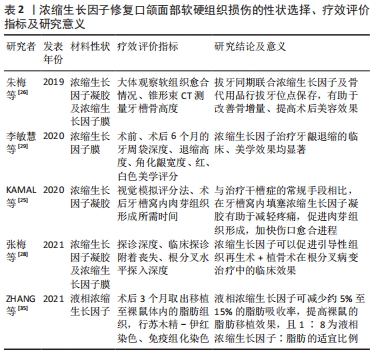
[1] RODELLA LF, FAVERO G, BONINSEGNA R, et al. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(8):772-777.
[2] HU Y, JIANG Y, WANG M, et al. Concentrated growth factor enhanced fat graft survival: a comparative study. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44(7):976-984.
[3] BRISSETT AE, HOM DB. The effects of tissue sealants, platelet gels, and growth factors on wound healing. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11(4):245-250.
[4] QIAO J, AN N. Effect of concentrated growth factors on function and Wnt3a expression of human periodontal ligament cells in vitro. Platelets. 2017;28(3):281-286.
[5] ZHANG L, AI H. Concentrated growth factor promotes proliferation, osteogenic differentiation, and angiogenic potential of rabbit periosteum-derived cells in vitro. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):146.
[6] CHEN X, WANG J, YU L, et al. Effect of concentrated growth factor (CGF) on the promotion of osteogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) in vivo. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5876.
[7] ROCHIRA A, SICULELLA L, DAMIANO F, et al. Concentrated growth factors (CGF) induce osteogenic differentiation in human bone marrow stem cells. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(11):370.
[8] ZHANG Y, LIU K, YAN M, et al. Effect of concentrated growth factor combined with mineralized collagen material on the adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and the osteogenic effect in vivo. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(3):295-302.
[9] QI L, LIU L, HU Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor promotes gingival regeneration through the AKT/Wnt/β-catenin and YAP signaling pathways. Artif Cell Nanomed B. 2020;48(1):920-993.
[10] JIN R, SONG G, CHAI J, et al. Effects of concentrated growth factor onproliferation, migration, and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9:2041731418817505.
[11] YAN QF, DOU L, HUAN J, et al. The effect of concentrate growth factors on the survival, proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban). 2018;49(5):716-719.
[12] HONG S, CHEN W, JIANG B. A comparative evaluation of concentrated growth factor and platelet-rich fibrin on the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human stem cells of the apical papilla. J Endod. 2018;44(6):977-983.
[13] 马翔宇,丁俐丹,唐世俊,等.自体浓缩生长因子对比格犬脂肪干细胞体外增殖及成骨向分化的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2018,43(1):1-6.
[14] HU T, ZHANG H, YU W, et al. The combination of concentrated growth factor and adipose-derived stem cell sheet repairs skull defects in rats. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(5):905-913.
[15] SAHIN IO, GOKMENOGLU C, KARA C. Effect of concentrated growth factor on osteoblast cell response. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;119(6):477-481.
[16] 李欣,姜志红,柳忠豪.浓缩生长因子提取液对钛片表面MC3T3-E1细胞增殖分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,33(1):84-87.
[17] BORSANI E, BONAZZA V, BUFFOLI B, et al. Beneficial Effects of Concentrated Growth Factors and Resveratrol on Human Osteoblasts In Vitro Treated with Bisphosphonates. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018: 4597321.
[18] DONG K, ZHOU WJ, LIU ZH, et al. The extract of concentrated growth factor enhances osteogenic activity of osteoblast through PI3K/AKT pathway and promotes bone regeneration in vivo. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):70.
[19] KAO CH. Use of concentrate growth factors gel or membrane in chronic wound healing: description of 18 cases. Int Wound J. 2020;17(1):158-166.
[20] YUE H, ZHOU L, ZOU R, et al. Promotion of skin fibroblasts collagen synthesis by polydioxanone mats combined with concentrated growth factor extracts. J Biomater Appl. 2019;34(4):487-497.
[21] CHEN J, JIAO D, ZHANG M, et al. Concentrated growth factors can inhibit photoaging damage induced by ultraviolet A (UVA) on the human dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:3739-3749.
[22] 王亚楠,王佐林.浓缩生长因子促进牙龈软组织缺损修复的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2018,28(3):121-126.
[23] QIN J, WANG L, SUN Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor increases Schwann cell proliferation and neurotrophic factor secretion and promotes functional nerve recovery in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(2): 493-500.
[24] 宦俊,窦磊,严崎方,等.浓缩生长因子促人脐静脉血管内皮细胞成血管化作用研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(3):247-251.
[25] KAMAL A, SALMAN B, ABDUL RAZAK NH, et al. The efficacy of concentrated growth factor in the healing of alveolar osteitis: a clinical study. Int J Dent. 2020;2020:9038629.
[26] 朱梅,孙强,邓佳蕴,等.浓缩生长因子联合骨代用品在美学区拔牙位点保存中的临床应用[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(11):100-103.
[27] 赵军伟,汪涌,韩爽.脱矿冻干骨联合浓缩生长因子治疗牙周骨下袋的临床效果评价[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2021,14(2):166-170.
[28] 张梅,邹高峰,常靓,等.下颌磨牙牙体严重缺损伴Ⅱ度根分叉病变的综合治疗[J].北京口腔医学,2021,29(1):27-31.
[29] 李敏慧,江烨,杨雪超.浓缩生长因子纤维蛋白治疗牙龈退缩疗效评价及对牙龈成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].中国美容医学,2020, 29(12):106-108.
[30] 于文凤,于兰,吕敏敏,等.血小板浓缩生长因子联合冠向复位瓣修复对牙龈退缩患者根面覆盖效果及美学评价的影响[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(10):117-120.
[31] KORKMAZ B, BALLI U. Clinical evaluation of the treatment of multiple gingival recessions with connective tissue graft or concentrated growth factor using tunnel technique: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(11):6347-6356.
[32] BARBU HM, IANCU SA, RAPANI A, et al. Guided bone regeneration with concentrated growth factor enriched bone graft matrix (sticky bone) vs. bone-shell technique in horizontal ridge augmentation: a retrospective study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(17):3953.
[33] 任静,郑佳俊,黄杰,等.浓缩生长因子在上颌前牙美学区种植中的临床应用[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2019,24(3):114-117,138.
[34] SUN W, LI T, YAO H, et al. Effects of concentrated growth factor and nanofat on aging skin of nude mice induced by D-galactose. Physiol Res. 2021;70(3):425-435.
[35] ZHANG T, DAI J, XU Y, et al. Liquid phase concentrated growth factor improves autologous fat graft survival in vivo in nude mice. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45(5):2417-2422.
[36] 付丽,孙悦,翟婧捷,等.3D打印及浓缩生长因子在双侧下牙槽神经移位同期牙种植术中的应用[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(10): 1003-1005.
[37] 王昕,陈小平,赵启明,等.浓缩生长因子注射改善眶周皱纹的临床观察[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2018,29(7):402-405.
[38] 许军旗,高立坤,王艳华.浓缩生长因子联合Biooss引导骨再生在炎症期即刻种植中的价值[J].临床研究,2018,26(11):43-44.
[39] 周海兰,陈漫娟,林臻彦,等.预成型钛网及浓缩生长因子在骨增量中的应用1例[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2021,37(6):372-374.
[40] KERANMU D, AINIWAER A, NUERMUHANMODE N, et al. Application of concentrated growth factor to autotransplantation with inflammation in recipient area. BMC oral health. 2021;21(1):556.
[41] 李勇,程如玉,彭学生,等.富自体浓缩生长因子联合Bio-Oss骨粉在颌骨囊肿中的疗效研究[J].中华全科医学,2018,16(7):1113-1115.
[42] YÜCE MO, ADALI E, IŞIK G. The effect of concentrated growth factor (CGF) in the surgical treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) in osteoporosis patients: a randomized controlled study. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(7):4529-4541.
[43] MASUKI H, OKUDERA T, WATANEBE T, et al. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF),advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2016;2(1):19.
[44] ISLER SC, SOYSAL F, CEYHANLı T, et al. Regenerative surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using either a collagen membrane or concentrated growth factor: a 12-month randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(5):703-712.
[45] TALAAT WM, GHONEIM MM, SALAH O, et al. Autologous bone marrow concentrates and concentrated growth factors accelerate bone regeneration after enucleation of mandibular pathologic lesions. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):992-997.
[46] XU Y, QIU J, SUN Q, et al. One-year results evaluating the effects of concentrated growth factors on the healing of intrabony defects treated with or without bone substitute in chronic periodontitis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4384-4389.
[47] SURESHBABU NM, RANGANATH A, JACOB B. Concentrated growth factor - surgical management of large periapical lesion using a novel platelet concentrate in combination with bone graft. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2020;10(1):246-250.
[48] KOZER N, CLAYTON AHA. In-cell structural dynamics of an EGF receptor during ligand-induced dimer-oligomer transition. Eur Biophys J. 2020; 49(1):21-37.
[49] CHENG B, LI C, ZHAO Y, et al. The impact of postoperative EGFR-TKIs treatment on residual GGO lesions after resection for lung cancer. Signal Transduct Tar. 2021;6(1):73
[50] 石鹏程,纪晓俊.酵母系统表达人表皮生长因子研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2021,41(1):72-79.
[51] FORTINO VR, CHEN RS, PELAEZ D, et al. Neurogenesis of neural crest-derived periodontal ligament stem cells by EGF and bFGF. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(4):479-488.
[52] 胡亚暖,姚永明,张泽敏,等.不同浓度EGF对兔ADSCs体外诱导分化为表皮细胞的实验研究[J].中国美容医学,2016,25(7):47-50.
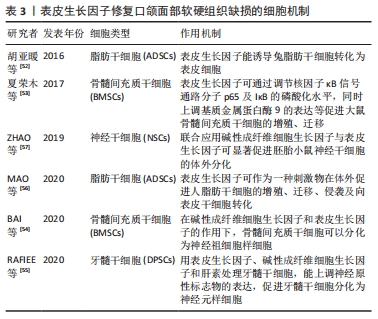
[53] 夏荣木,江其昌,杨龙,等.表皮生长因子影响大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和迁移的信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(29): 4635-4641.
[54] BAI W, ZHANG Y, XU W, et al. Isolation and characterization of neural progenitor cells from bone marrow in cell replacement therapy of brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:49.
[55] RAFIEE F, POURTEYMOURFARD-TABRIZI Z, MAHMOUDIAN-SANI MR, et al. Differentiation of dental pulp stem cells into neuron-like cells. Int J Neurosci. 2020;130(2):107-116.
[56] MAO Y, MA J, XIA Y, et al. The overexpression of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in HaCaT cells promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and transdifferentiation to epidermal stem cell immunophenotyping of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs). Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(1):93-103.
[57] ZHAO H, ZUO X, REN L, et al. Combined use of bFGF/EGF and all-trans-retinoic acid cooperatively promotes neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth in neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett. 2019;690:61-68.
[58] ESQUIROL-CAUSSA J, HERRERO-VILA E. Human recombinant epidermal growth factor in skin lesions: 77 cases in EPItelizando project. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019;30(1):96-101.
[59] 郭磊,吴韫慧,高瑞.重组人表皮生长因子外用溶液联合半导体激光治疗复发性口腔溃疡的临床观察[J].医药论坛杂志,2018,39(9): 95-96.
[60] VISWANATHAN V, JUTTADA U, BABU M. Efficacy of recombinant human epidermal growth factor (regen-D 150) in healing diabetic foot ulcers: a hospital-based randomized controlled trial. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2020;19(2):158-164.
[61] ALAMOUDI NM, EL ASHIRY EA, FARSI NM, et al. Treatment of oral ulcers in dogs using adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2014;38(3):215-222.
[62] 文超举,刘春影,裴婷婷,等.3种不同压膜方法对浓缩生长因子膜细胞因子释放及降解的影响[J].口腔医学,2019,39(10):889-894.
[63] KIM J, LEE KM, HAN SH, et al. Development of stabilized dual growth factor-loaded hyaluronate collagen dressing matrix. J Tissue Eng. 2021; 12:2041731421999750.
|