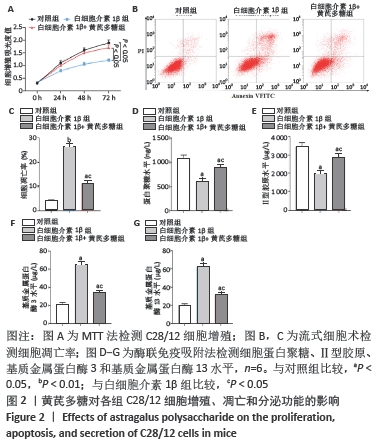
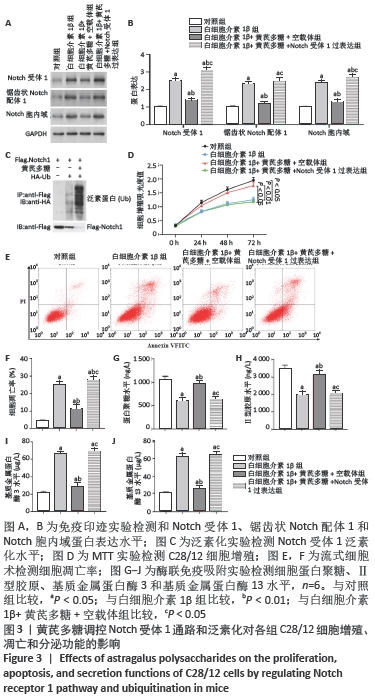
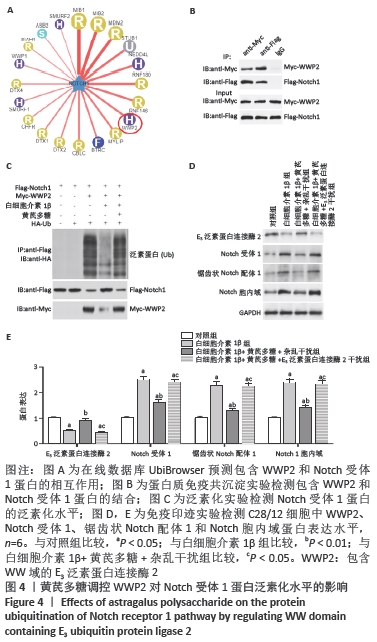
[1] LOESER R. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;64:1697-1707.
[2] O’Neill TW, McCabe PS, McBeth J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326.
[3] Kang D, Shin J, Cho Y, et al. Stress-activated miR-204 governs senescent phenotypes of chondrocytes to promote osteoarthritis development. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(486):eaar6659.
[4] JIE S, ABU-AMER Y, O’KEEFE R, et al. Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):49-63.
[5] EDITH C, CÉLINE D, FEDERICA C, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[6] 肖剑伟, 周唯践, 蔡旭, 等. 黄芪多糖抑制氧化应激致大鼠软骨细胞损伤及凋亡的作用机制分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(10):1040-1044.
[7] LAN L, JIANG Y, ZHANG W, et al. Expression of Notch signaling pathway during osteoarthritis in the temporomandibular joint. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;45(8):1338-1348.
[8] LIN NY, DISTLER A, BEYER C, et al. Inhibition of Notch1 promotes hedgehog signalling in a HES1-dependent manner in chondrocytes and exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(11): 2037.
[9] CHENG HJ, HSU WT, CHEN CN, et al. Activation of NOTCH1 by Shear Force Elicits Immediate Cytokine Expression in Human Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4958.
[10] ZHENG L, CONNER SD. PI5P4Kγ functions in DTX1-mediated Notch signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2018;115(9):E1983-E1990.
[11] ROTIN D, KUMAR S. Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(6):398-409.
[12] MOKUDA S, NAKAMICHI R, MATSUZAKI T, et al. Wwp2 maintains cartilage homeostasis through regulation of Adamts5. Nature Commun. 2019;10(1):2429.
[13] GENG Z, WEI L, ZHANG C, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide, a component of traditional Chinese medicine, inhibits muscle cell atrophy (cachexia) in an in vivo and in vitro rat model of chronic renal failure by activating the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):91-96.
[14] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18 Suppl 3:S17-23.
[15] MATSUZAKI T, MATSUSHITA T, TAKAYAMA K, et al. Disruption of Sirt1 in chondrocytes causes accelerated progression of osteoarthritis under mechanical stress and during ageing in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1397-1404.
[16] SUN X, ZHEN X, HU X, et al. Osteoarthritis in the Middle-Aged and Elderly in China: Prevalence and Influencing Factors. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(23):4701.
[17] O’BRIEN MS, MCDOUGALL JJ. Age and frailty as risk factors for the development of osteoarthritis. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019;180:21-28.
[18] AICHER WK, ROLAUFFS B. The spatial organisation of joint surface chondrocytes: review of its potential roles in tissue functioning, disease and early, preclinical diagnosis of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73(4):645-653.
[19] LYNDIN M, GLUSCHENKO N, SIKORA V, et al. Morphofunctional features of articular cartilage structure. Folia medica Cracoviensia. 2019;59(3): 81-93.
[20] WAEL BA, MOUNA B, MERIEM M, et al. A cross sectional study of bone and cartilage biomarkers: correlation with structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Libyan J Med. 2018;13(1):1512330.
[21] LI H, WANG D, YUAN Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):248.
[22] TANG LP, DING JB, LIU ZH, et al. LncRNA TUG1 promotes osteoarthritis-induced degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-195/MMP-13 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22(24):8574-8581.
[23] HANG F, HUANG L, WELCH I, et al. Early Changes of Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone in The DMM Mouse Model of Osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2855.
[24] LIAO J, LI C, HUANG J, et al. Structure Characterization of Honey-Processed Astragalus Polysaccharides and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity In Vitro. Molecules. 2018;23(1):168.
[25] DONG N, LI X, XUE C, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates LPS‐induced inflammation via the NF‐κB/MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(7-8):5525-5540.
[26] MENG Q, DU X, WANG H, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits cell growth and pro-inflammatory response in IL-1 beta-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes by enhancement of autophagy via PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibition. Apoptosis. 2017;22(9):1138-1146.
[27] FAN L, LI M, CAO FY, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cell injury in ATDC5 cells via miR-92a/KLF4 mediation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109180.
[28] SIEBEL C, LENDAHL U. Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1235-1294.
[29] HENRIQUE D, SCHWEISGUTH F. Mechanisms of Notch signaling: a simple logic deployed in time and space. Development. 2019;146(3): dev172148.
[30] GUAN YJ, LI J, YANG X, et al. Evidence that miR-146a attenuates aging- and trauma-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting Notch1, IL-6, and IL-1 mediated catabolism. Aging Cell. 2018;17(3):e12752.
[31] LIU W, TANG X, QI X, et al. The Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme: An Important Ubiquitin Transfer Platform in Ubiquitin-Proteasome System. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(8):2894.
[32] COLLINS GA, GOLDBERG AL. The Logic of the 26S Proteasome. Cell. 2017;169(5):792.
[33] LU L, HUANG YF, CHEN DX, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides decrease muscle wasting through Akt/mTOR, ubiquitin proteasome and autophagy signalling in 5/6 nephrectomised rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;186:125-135.
[34] WANG Y, YANG BP, CHI YG, et al. Effect of Deltex-1 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into smooth muscle cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(12):3627.
|