中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1722-1727.doi: 10.12307/2022.1021
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
柚皮苷调控成骨细胞成骨分化的机制
吴晶晶1,林海雄2,3,孙伟鹏1,李紫阁1,姜自伟4
- 1广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510405;2宁夏回族自治区中医医院暨中医研究所,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750000;3香港中文大学组织工程与再生医学研究所,香港特别行政区 999077;4广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405
Mechanism by which naringin regulates osteogenic differentiation in osteoblasts
Wu Jingjing1, Lin Haixiong2,3, Sun Weipeng1, Li Zige1, Jiang Ziwei4
- 1The First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405; 2Ningxia Chinese Medicine Research Center, Yinchuan 750000; 3Institute of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin 999077, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China; 4The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405
摘要:
文题释义:
柚皮苷:是一种由葡萄糖、鼠李糖等构成的天然黄酮化合物。作为骨碎补总黄酮的主要有效成分之一,在临床应用时,柚皮苷对促进骨折愈合、抗骨质疏松、抗炎、抗氧化应激等具有良好的疗效。
MiR-206:作为在生物体中广泛存在的一类小分子单链编码RNA,microRNAs已被公认与细胞的增殖、分化和凋亡等过程密切相关,也在骨组织生长、发育、重塑的过程中发挥着重要作用。其中miR-206最早在骨骼肌细胞中被发现,而后发现成骨细胞也能表达miR-206,进一步研究发现miR-206与骨损伤修复密切相关。
背景:研究发现,柚皮苷主要通过Wnt、转化生长因子β、MAPK信号通路、破骨细胞信号通路等直接影响骨代谢,通过P13K-Akt、血管内皮生长因子信号通路等间接调节骨代谢,具有促进骨损伤修复、减缓骨质疏松的作用。
目的:探讨柚皮苷通过下调miR-206表达靶向激活缝隙连接蛋白43/ERK1信号通路对成骨细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响。
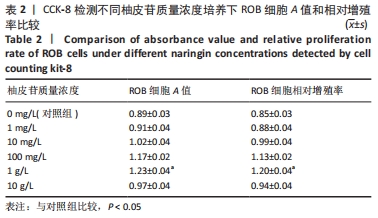
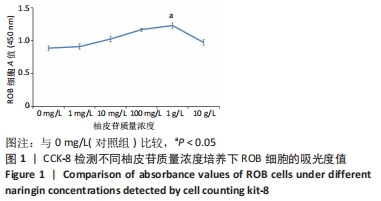
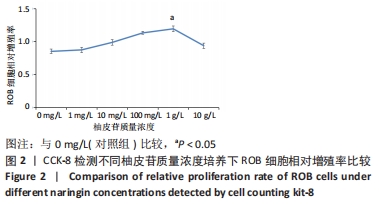
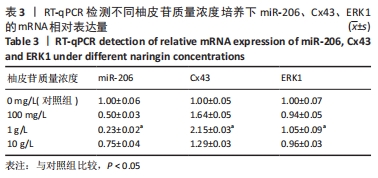
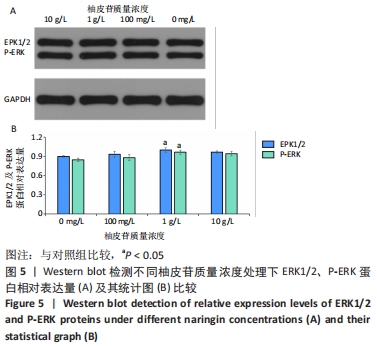
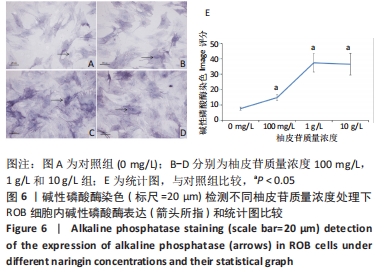
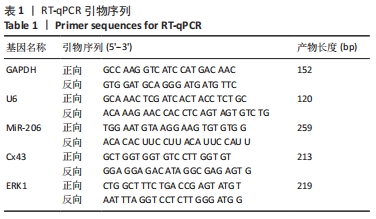
方法:将大鼠成骨细胞(ROB细胞)经不同质量浓度柚皮苷(1,10,100 mg/L及1,10 g/L)处理培养,并进行CCK-8实验检测细胞增殖情况,筛选出柚皮苷质量浓度100 mg/L及1,10 g/L用于后续实验,并以未给药培养做对照组。RT-qPCR检测ROB细胞中miR-206、缝隙连接蛋白43 及ERK1 mRNA相对表达水平,验证其靶向关系;Western blot检测ROB细胞中ERK1/2、P-ERK蛋白的表达水平;碱性磷酸酶染色及茜素红染色观察ROB细胞内碱性磷酸酶活性及细胞钙化能力。
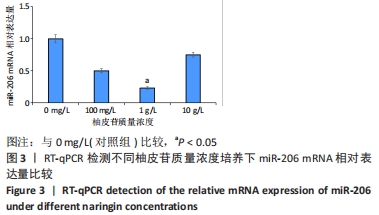
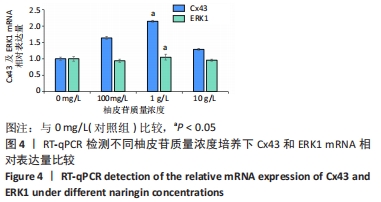
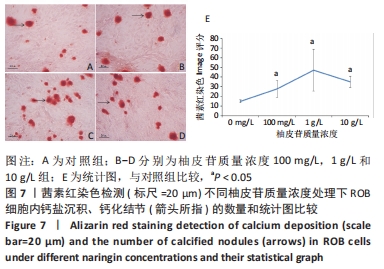
结果与结论:①柚皮苷能显著促进ROB细胞的增殖活性(P < 0.05),柚皮苷在一定质量浓度范围内,随着给药浓度升高,ROB细胞吸光度值和相对增殖率均相应升高,在质量浓度为1 g/L时细胞增殖活性最强;②柚皮苷能显著抑制ROB细胞内miR-206 mRNA的表达并靶向促进成骨分化指标缝隙连接蛋白43 mRNA及ERK1/2、P-ERK蛋白的表达(P < 0.05);③碱性磷酸酶染色及茜素红染色结果提示柚皮苷能显著促进ROB细胞内碱性磷酸酶活性和表达以及细胞钙化能力水平(P < 0.05),其中1 g/L质量浓度处理的效果最佳;④柚皮苷通过下调miR-206表达,靶向激活缝隙连接蛋白43/ERK1信号通路,进而促进ROB细胞增殖活性及成骨分化能力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4883-7331(吴晶晶)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: