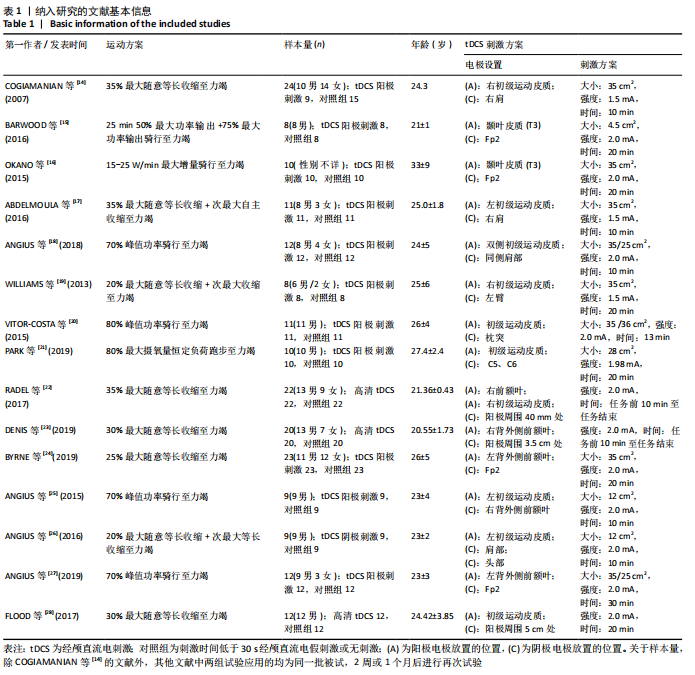
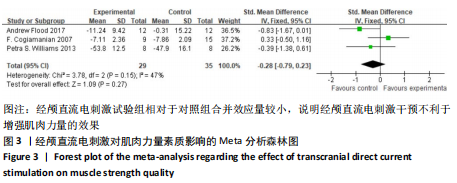
3.1 tDCS对肌肉力量的影响 神经-肌肉是人体运动的直接动力来源,是运动员取得优异运动成绩的基础条件[29]。肌肉力量作为影响人体运动表现的重要因素之一,其发展由形态学和神经学因素共同支持[30]。有研究认为,肌肉横截面积在肌力增长中可能占较小比重,而神经因素是肌肉力量快速增长的重要因素[31],这为tDCS通过刺激大脑皮质来调节脑区功能的应用提供了研究基础。tDCS通过刺激特定脑区,增加该区域神经元兴奋性和可塑性,募集更多的单元,从而提高肌肉性能。然而,通过所纳入3项研究(共44名受试者)的荟萃结果[14,19,28],遗憾的发现,仅1项研究呈阳性。COGIAMANIAN等[14]2007年的研究为首篇将tDCS应用于肌肉力量和耐力的文献,无屈肘肌健身或训练经历的受试者在接受35%最大随意等长收缩任务后,阳极和对照组标准化最大随意等长收缩分别为(-7.11±2.36)%和(-7.86±2.09)%,差异无显著性意义(P=0.77)。有2项研究的测试结果呈阴性,FLOOD等[28]采用高清tDCS用高环形配置电极对12名受试者进行干预,研究显示试验组与对照组间差异无显著性意义(P=0.083)。WILLIAMS等[19]选择8名受试者,在完成疲劳任务期间对受试者初级运动皮质分别进行了20 min tDCS阳极刺激和假刺激,在疲劳任务结束后,计算受试者最大随意等长收缩从基线下降的百分比,阳极tDCS条件下的最大随意等长收缩比对照组下降的幅度大,下降幅度超过6%。
综上,据总体合并效应来看,菱形图与无效线相交且落在无效线偏左侧,提示tDCS对增强肌肉力量的效果极其微弱,甚至不利于改善受试者的力量表现。鉴于纳入此次研究的项目较少、样本量较少、刺激方案不同等因素,且解释tDCS对力量改善的神经生理机制目前尚不清楚,需进行进一步的研究,以便深入探索tDCS刺激与肌肉力量间的关系。
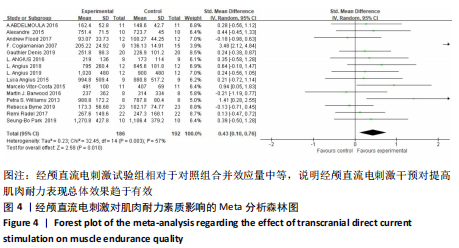
3.2 tDCS对耐力的影响 耐力素质是人体的基本素质之一。在周期性耐力项目(径赛、游泳、自行车等)中,耐力水平是决定运动员运动成绩的主要因素。在此次荟萃纳入的15项研究中[14-28],共201名受试者,有3项研究结果呈阴性。在BARWOOD等[15]的研究中,8名受试者在高温条件下完成高强度骑行任务,tDCS干预组耐力时间低于假刺激组。BYRNE等[24]在左背外侧前额叶皮质进行真、假tDCS刺激发现,试验组和对照组耐力时间分别为(173.30±56.68) s和(182.17±74.77) s,提示tDCS干预并未提高耐力表现(P=0.448)。FLOOD等[28]在另一项研究中发现,对初级运动皮质进行20 min 高清tDCS刺激,在疲劳任务后对照组耐力时间基于基线减少了(13.30±24.56)%,而试验组仅降低了(9.39±12.55)%。经分析发现,由于试验组与对照组耐力时间在基线存在极其微弱的差异(对照组略高于试验组,P=0.109),导致原本具有微弱干预效果的tDCS结果在此次荟萃研究中的结果呈阴性。
此次荟萃分析中12项研究结果呈阳性[14,16-23,25-27]。COGIAMANIAN等[14]在左肘曲肌疲劳任务前对右初级运动皮质进行tDCS刺激,之后测评发现,任务失败时间在阴极刺激和控制组无刺激后急剧下降[(-35.77±3.39)%,(-39.33±3.32)%],而阳极刺激后耐力时间减少相对较小(-21.11±5.52)%,该研究为非病理条件下阳极tDCS可减少肌肉疲劳与提高肌肉耐力开辟了道路。在随后的研究中,WILLIAMS等[19]利用阳极tDCS刺激条件下,受试者任务失败时间延长了31%;VITOR-COSTA等[20]证明了在没有生理变量(心率和肌电图)和感知变量变化的情况下,tDCS 能改善80%峰值功率骑行的任务失败时间;PARK等[21]在80%最大摄氧量恒定负荷跑步试验中,发现tDCS显著延长了任务失败时间[(21.18±7.13) min,(18.44±6.32) min,P=0.011];OKANO等[16]通过对10名国家级公路自行车运动员在实验室条件下完成最大增量骑行进行研究,发现在颞叶皮质上进行tDCS刺激最大输出功率改善了4%,降低了心率和感知变量,对调节运动表现具有至关重要的作用。该研究为tDCS在专业运动员中应用提供了证据,但针对临场比赛中的应用研究未来仍需进一步加强。
在荟萃中发现,关于tDCS对运动表现影响试验研究的作者较为分散,除FLOOD及其团队2项研究外[24,28],仅ANGIUS团队在2015至2019年间进行了4项持续追踪研究[18,25-27]。ANGIUS团队在最早的一项研究中发现,tDCS未引起骑行期间任务失败时间与生理参数的显著变化,分析认为任务失败时间未明显变化可能是tDCS蒙太奇所致,因为阳极电极对初级运动皮质的任何好处可能被右背外侧前额叶皮质上的阴极电极所抵消,建议全身运动应采用双侧tDCS蒙太奇[25]。在其随后的2项研究中支持了前面的推测,ANGIUS团队比较了2种蒙太奇对单腿伸肌任务失败时间的影响,发现阳极初级运动皮质和阴极同侧肩部的外部蒙太奇引起任务失败的时间显著改善了17%,而对皮质脊髓和周围参数未有影响,因此目前对任务失败时间改善的确切机制尚不清楚[26]。ANGIUS等[18]在进一步研究中发现,双侧初级运动皮质上的外侧阳极刺激对自行车运动期间的任务失败时间显著改善了23%。基于背外侧前额叶是抑制性控制的关键脑区,ANGIUS等[27]在最近的研究中,对健康个体左背外侧前额叶进行tDCS刺激,发现任务失败时间延长(P=0.029),心率(P=0.002)和感知变量(P < 0.001)明显较低,可同时改善抑制性控制和循环性能。
针对感兴趣区域焦点定位优化,与传统的tDCS相比,高清tDCS能避免因电极过大对其他脑区产生不必要的污染,此次荟萃研究共有3项随机对照试验使用高清tDCS进行干预。FLOOD等[28]研究发现,高清tDCS增加了止痛能力,但对提高肌肉耐力的效果不显著,对先前的研究观点,即对运动引起的内源性疼痛抑制与调节运动表现间的关系提出了质疑[32-33]。在最近的2项研究中,电极位置、刺激强度和时间均相同,分别测试肘屈肌和膝伸肌疲劳任务的时间,tDCS试验组任务失败时间下降的幅度均小于假刺激组[22-23]。RADEL等[22]采用近红外光谱和肌电图探究脑刺激对外周和中枢疲劳的影响;DENIS等[23]发现tDCS组与假刺激组无显著性主效应,但tDCS组耐力时间优于对照组。
针对目前tDCS的最佳电极放置不确定的问题,ANGIUS团队在2种tDCS蒙太奇会话随机对照试验中,将阳极电极置于左侧运动皮质,将阴极电极分别置于对侧前额和肩部,对2种不同tDCS电极蒙太奇对改善运动表现的影响进行分别测试,研究发现SHOULDER蒙太奇比HEAD蒙太奇能更有效地提高耐力性能[26]。初级运动皮质一直被认为是调节耐力的决定性皮质区域,已有多项研究针对初级运动皮质进行干 预[14,18-19,25]。针对近期研究认为初级运动皮质未增强皮质脊髓的兴奋性,RADEL等[22]采用近红外光谱监测在阴极初级运动皮质和前额叶分别运用高清tDCS对肘屈肌持续收缩任务氧合血红蛋白的影响,近红外光谱结果表明高清tDCS干预可有效调节前额叶的活性,但对于tDCS是否减少任务激活区域的O2HB仍需进一步研究验证。
基于上述观察结果,据总体合并效应量来看,tDCS干预对提高肌肉耐力表现效果总体趋于有效。鉴于tDCS改善任务失败时间的确切机制仍然未知、目前团队追踪研究较少、电极位置和感兴趣区域精准定位等因素,未来仍需进一步加强研究。
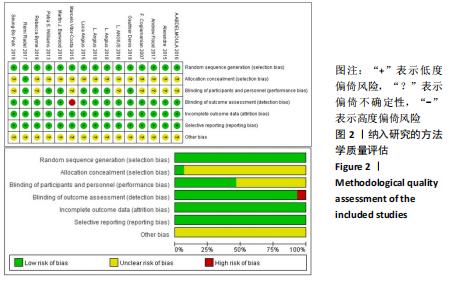
3.3 研究不足与局限性 目前tDCS对改善肌肉功能的确切机制尚存争议,COGIAMANIAN等[14]与WILLIAMS等[19]的团队认为tDCS能减轻脊髓上疲劳;而ABDELMOULA等[17]与FLOOD等[28]的团队研究认为运动表现的改善与皮质脊髓变化、内源性疼痛抑制无显著联系。因此,弄清确切的机制是当前急待解决的首要问题。其次,返回电极的位置、tDCS刺激的最佳剂量(刺激强度、刺激时间)、刺激脑区等控制变量仍在进一步的探索中。再次,连续性研究较少,样本量待加强,除ANGIUS[18]及其团队有持续追踪研究,其余研究均较为分散;部分研究样本较小可能会增加Ⅱ型统计误差。最后,神经兴奋的增补剂能使运动员在比赛中占据竞争优势,同时亦会引发人们对体育公平性与道德性的思考。
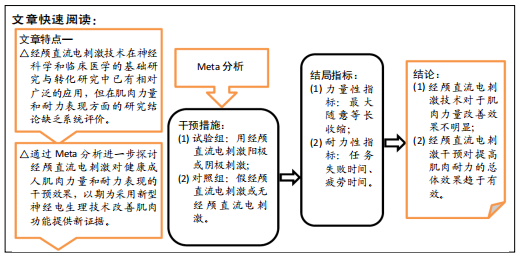
3.4 结论与建议 该系统评价与荟萃分析的结果提示,tDCS技术对于肌肉力量改善效果不明显,但对提高肌肉耐力效果显著。tDCS对于改善运动表现是一项极具前景的非侵入性脑刺激技术,未来将会受到生物医学、运动医学以及竞技体育领域的广泛关注。然而,鉴于目前确切机制尚不明晰、刺激剂量缺乏个性化参数、样本量相对较小、高质量连续性追踪研究较少、感兴趣区域精准定位不足等因素,未来应用与发展应注意以下几方面:
(1)加强tDCS神经生理机制探索:采用脑电图、功能MRI、功能近红外光谱多种神经影像学技术,监测tDCS对脑网络神经调节的影响。加强tDCS对肌肉功能影响的神经作用机制研究,进一步深入探索tDCS刺激与运动表现间的关系。
(2)实施更严格与广泛的试验研究:针对目前效用结果存在不一致性,刺激脑区和感兴趣区域聚焦性等问题、应加强高质量的试验研究,通过更大样本量测试,以期为tDCS改善肌肉功能提供更有效的刺激参数与有力的证据支持。
(3)对高水平竞技临场应用持期待与谨慎态度:在实践应用中,对于tDCS在高水平竞技临场应用,仍需保持期待与谨慎的态度。加强tDCS在竞技体育实践应用中的前期测试与监控,以tDCS为“脑-肌”沟通渠道,实现神经系统与运动系统光滑链接,以期为tDCS提高体育成绩、促进疲劳恢复与运动功能康复等提供有益的科技服务。
(4)设计个性化刺激方案:针对不同被试的个体差异,建立个性化刺激方案。借助基于脑结构和功能连接信息绘制的脑网络组图谱,通过高清tDCS刺激技术,精准定位皮质刺激区域,以便更有效地提高不同人群的运动表现。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程