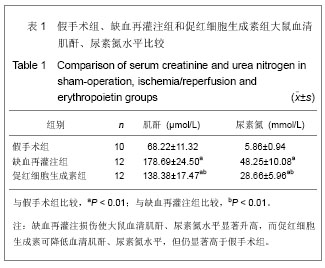
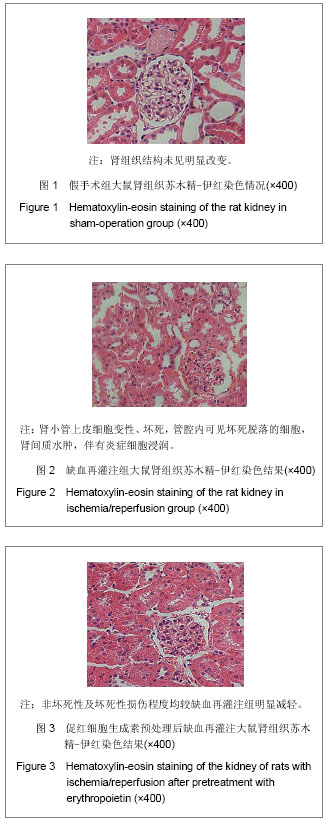
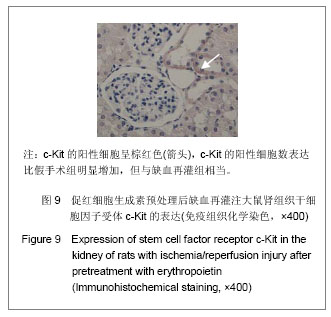
| [1] Ricci Z, Cruz D, Ronco C. The RIFLE criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: A systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008; 73(5):538-546.[2] Murugan R, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury: what's the prognosis? Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(4):209-217.[3] Madonna R, De Caterina R. Stem cells and growth factor delivery systems for cardiovascular disease. J Biotechnol. 2011;154(4):291-297.[4] Doycheva D, Shih G, Chen H, et al.Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in combination with stem cell factor confers greater neuroprotection after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the neonatal rats than a solitary treatment. Transl Stroke Res. 2013;4(2):171-178.[5] Geurt Stokman,Ingrid Stroo,Nike Claessen, et al .Stem Cell Factor Expression after Renal Ischemia Promotes Tubular Epithelial Survival. PLoS ONE.2012;5(12):e14386.[6] 刘窗溪,熊云彪,杨承勇,等.促红细胞生成素对兔局灶性脑缺血后干细胞因子及其受体表达的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2012, 29(4):305-308.[7] Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, et al. COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer. 2000;89(12):2637-2645.[8] 王光新,李朝芝,夏瑗瑜,等.大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注后IL-6变化及姜黄素预处理的影响[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2012,13(7): 617-619.[9] Coca SG, Singanamala S, Parikh CR. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012;81(5):442-448.[10] 陈颖,吴多江,杨亦彬,等. 促红细胞生成素干预肾缺血再灌注损伤后肾小管间质的纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(40): 7514-7519.[11] Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV, Papavassiliou AG. Selective modulation of the erythropoietic and tissue-protective effects of erythropoietin: time to reach the full therapeutic potential of erythropoietin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1776(1):1-9. [12] Pallet N,Rabant M,Legendre C.The nephroprotective properties of recombinant human erythropoietin in kidney transplantation:experiental facts and clinical proofs.Am J Transplant.2012;12(12):3184-3190.[13] Spandou E, Tsouchnikas I, Karkavelas G, et al. Erythropoietin attenuates renal injury in experimental acute renal failure ischaemic/reperfusion model. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21(2):330-336.[14] Yang CW, Li C, Jung JY, et al. Preconditioning with erythropoietin protects against subsequent ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat kidney. ASEB J. 2003; 17(12):1754-1755.[15] Westenfelder C, Biddle DL, Baranowski RL. Human, rat, and mouse kidney cells express functional erythropoietin receptors. Kidney Int. 1999;55(3):808-820.[16] Sharples EJ, Patel N, Brown P, et al. Erythropoietin protects the kidney against the injury and dysfunction caused by ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(8): 2115-2124.[17] Lennartsson J, Rönnstrand L. Stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit: from basic science to clinical implications. Physiol Rev. 2012; 92(4):1619-1649.[18] Liang J,Wu YL,Chen BJ, et al.The C-kit receptor-mediated signal transduction and tumor-related diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(5):435-443.[19] Smith MA, Pallister CJ, Smith JG. Stem cell factor: biology and relevance to clinical practice. Acta Haematol. 2001; 105(3):143-150.[20] Xiang FL, Lu X, Liu Y, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of human stem cell factor protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 2013 May 13.[21] Lu T, Luo Y,Sun H,et al. Electroacupuncture improves behavioral recovery and increases SCF/c-kit expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neurol Sci. 2013;34(4):487-495.[22] Kato N, Honma K, Hojo H, et al. KIT expression in normal and neoplastic renal tissues: immunohistochemical and molecular genetic analysis. Pathol Int. 2005;55(8):479-483.[23] Chen YT, Yang CC, Zhen YY, et al. Cyclosporine-assisted adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy to mitigate acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013; 4(3):62. [24] Gheisari Y, Azadmanesh K, Ahmadbeigi N, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells to overexpress CXCR4 and CXCR7 does not improve the homing and therapeutic potentials of these cells in experimental acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(16):2969-2980. [25] Bengatta S, Arnould C, Letavernier E, et al. MMP9 and SCF protect from apoptosis in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(4):787-797.[26] Tögel F, Isaac J, Hu Z, et al. Renal SDF-1 signals mobilization and homing of CXCR4-positive cells to the kidney after ischemic injury. Kidney Int. 2005;67(5):1772-1784. |