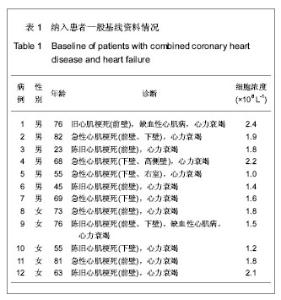
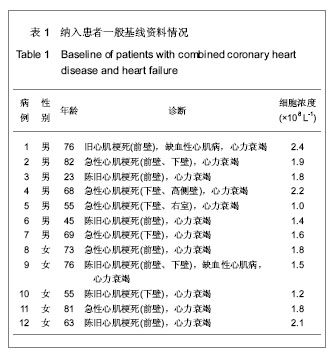
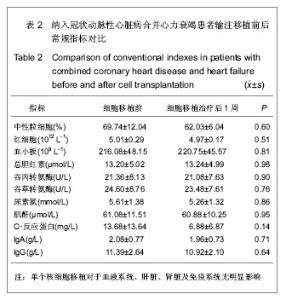
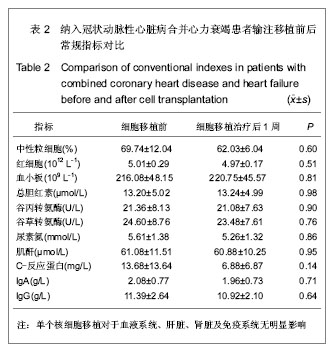
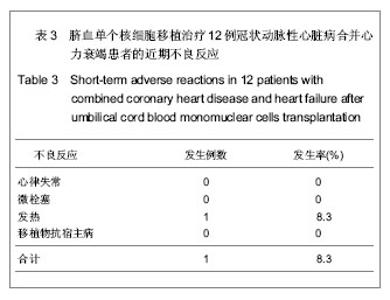
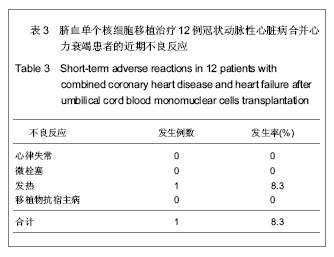
| [1] Eschalier R, Fertin M, Fay R, et al. Extracellular Matrix Turnover Biomarkers Predict Long-term Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction: Insights from the REVE-2 Study. Circ Heart Fail. 2013.[2] Esper SA, Subramaniam K. Heart failure and mechanical circulatory support. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2012; 26(2):91-104.[3] Tang XL, Rokosh G, Sanganalmath SK, et al. Intracoronary administration of cardiac progenitor cells alleviates left ventricular dysfunction in rats with a 30-day-old infarction. Circulation. 2010;121(2):293-305. [4] D'Amario D, Fiorini C, Campbell PM, et al. Functionally competent cardiac stem cells can be isolated from endomyocardial biopsies of patients with advanced cardiomyopathies. Circ Res. 2011;108(7):857-861.[5] D'Amario D, Cabral-Da-Silva MC, Zheng H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor identifies a pool of human cardiac stem cells with superior therapeutic potential for myocardial regeneration. Circ Res. 2011;108(12):1467-1481. [6] Flett AS, Hasleton J, Cook C, et al. Evaluation of techniques for the quantification of myocardial scar of differing etiology using cardiac magnetic resonance. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4(2):150-156.[7] 戴青原,汤亚明,胡家丽,等. 动脉硬化无创检测对冠心病的诊断价值[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2013,33(7):1500-1501.[8] 王岚峰,吴双,关秀茹,等. 脑钠素与急性心肌梗死预后关系的临床研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,2005,33(3):234-236.[9] 邓柳霞,余国龙,艾旗,等.人脐血单个核细胞静脉移植联合培哚普利对急性心肌梗死炎症反应的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(19):3481-3487.[10] 詹三华,张鲁峰,姚卫民,等. 人脐血间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠肝硬化模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19):3461-3466.[11] Hu S, Liu S, Zheng Z, et al. Isolated coronary artery bypass graft combined with bone marrow mononuclear cells delivered through a graft vessel for patients with previous myocardial infarction and chronic heart failure: a single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(24):2409-2415. [12] 巨亚萍,赵庆华. 三种来源于不同围产期组织间充质干细胞的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19):3546-3550. [13] Henning RJ, Abu-Ali H, Balis JU, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Transplant.2004;13(7-8):729-39. [14] 刘伦翠,邵华,卢林.人脐带血干细胞移植治疗大鼠心肌梗死的实验研究[J].中国全科医学;2008,11(15):1356-1357[15] Ichim TE, Solano F, Brenes R,et al.Placental mesenchymal and cord blood stem cell therapy for dilated cardiomyopathy. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;16(6):898-905.[16] Moelker AD, Baks T, Wever KM, et al. Intracoronary delivery of umbilical cord blood derived unrestricted somatic stem cells is not suitable to improve LV function after myocardial infarction in swine. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2007;42(4):735-45. [17] Miko?ajek W, Czajka R. Estimation of selected methods of separation of hematopoietic cells from human umbilical cord blood. Ginekol Pol. 2000;71(9):1235-1239. [18] Ingram DA,Mead LE, Tanaka H, et al. Identification of a novel hierarchy of endothelialp rogenitor cells using human peripheral and umbilical cord blood. B lood.2004;104(9): 2752-2760[19] IwatateM, Minra T, Ikeda Y, et al Effects of in vivo gene transfer of fibroblast growth factor-2 on cardiac function and collateral vessel formation in the microembolized rabbit heart.Jpn circ J.2001;65(3):226-231.[20] Wagner W , W ein F , S eckinger A , et al. C om parative characteristics of m esenchym al stem cels hum an bone m arrow , adipose tissue, and um bilicalcord blood. Exp Hem atoll. 2005;33(11):1402-1416.[21] 李占全,张明,金元哲,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死安全性观察[J].介入放射学杂志,2004,12(2):80-83.[22] 张书宁,孙爱军,葛俊波,等.经冠状动脉自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死安全性的系统评价[J].中华心血管病杂志,2008, 36(8):679-684.[23] Kogler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al. A new human somatic stem cell from placentalcord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004; 200(2 ):123 -135.[24] Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110.[25] Hanley PJ, Cruz CR, Shpall EJ, et al. Improving clinical outcomes using adoptively transferred immune cells from umbilical cord blood. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(6):713-720. [26] 董陆佳.现代造血干细胞移植治疗学[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社2001:5.[27] Ooi J,Iseki T,Nagayama H,et al.Unrelatedcordblood transplantation for adult patients with myelodysplastic syndrome related secondaryacutemyeloid leukaemia. BrJ Haematol. 2001;114(4):834-836.[28] Ma N, Stamm C, Kaminski A,et al. Humancordbloodcelsinduce angiogenesis folow ing m yocardial infarction in N OD /scid-m ice. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;66(1):45-54. [29] Hirata Y, Sata M, Motomura N, et al. Human umbilical cord blood cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;327(2): 609-614. [30] Vogel G. Rat brains respond to embryonic stem cells.Science. 2002;295:254-255.[31] Kim BO, Tian H, Prasongsukarn K, et al. Cell transplantation improves ventricular function after a myocardial infarction: a preclinical study of hum an unrestricted somatic stem cells in a porcine model. Circulation 2005;112( 9suppl):196-104.[32] Sell S.Stem cell origin of cancer and differentiation therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.2004;51(1):1-28. |