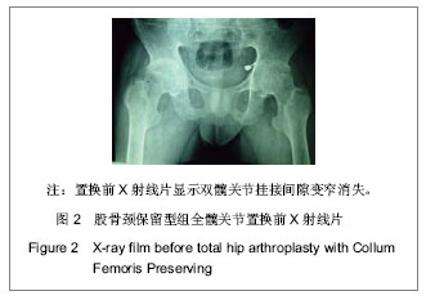
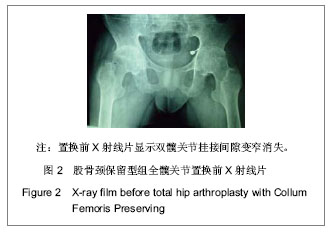
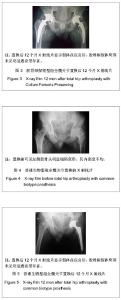
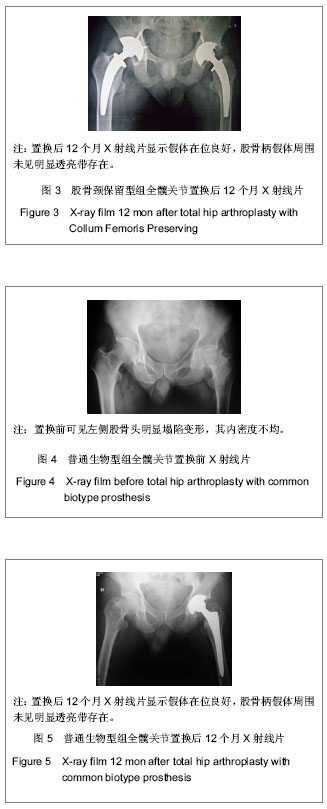
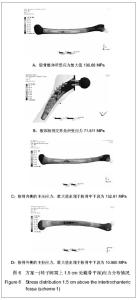
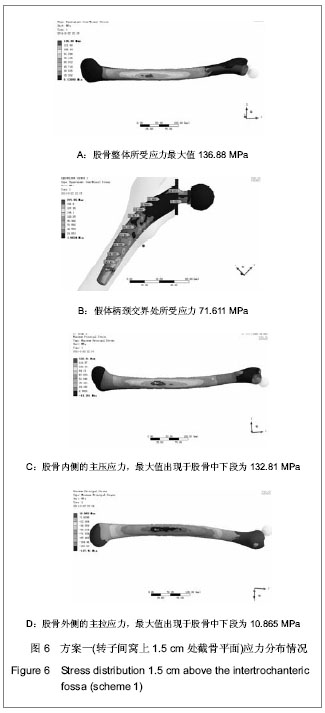
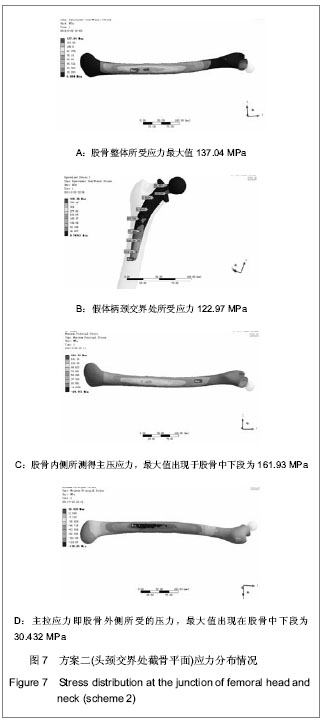
| [1] 周清,陈冉,俞晖.保留股骨颈全髋关节置换治疗年轻患者髋关节病[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(3):335-336.[2] 郑文忠,陈昆,刘爱刚,等.保留股骨颈型人工全髋关节置换术25例分析[J].临床军医杂志,2007,35(6):873-875.[3] 郑文忠,陈昆,潘永太,等.保留股骨颈型人工全髋关节置换术[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(6):592-594.[4] 陆晴友,吴岳嵩,王成焘.股骨近端解剖形态的CT三维重建与分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2005,26(9):1029-1033.[5] 左建林,柳林,应洪亮,等.基于三维CT多平面重建股骨近段髓腔的形态学实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(22): 4005-4009.[6] 郝跃峰,孙俊英,杨佩彦,等.髋关节旋转中心相关骨性参数的测量[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(5):413-416.[7] 朱建炜,董启榕,刘璠,等.正常国人股骨近端解剖参数的研究[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2008,28(4):582-585.[8] 单涛,刘芙蓉,王子轩.与关节置换相关的国人髋关节结构测量[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(13):2497-2500.[9] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.[10] Petersilge WJ, D'Lima DD, Walker RH,et al.Prospective study of 100 consecutive Harris-Galante porous total hip arthroplasties. 4- to 8-year follow-up study.J Arthroplasty. 1997;12(2):185-193.[11] Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH.Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1987; 69(1):45-55.[12] Lengsfeld M, Schmitt J, Alter P,et al.Comparison of geometry-based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation.Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(7): 515-522.[13] Bergmann G, Graichen F, Rohlmann A.Hip joint loading during walking and running, measured in two patients.J Biomech. 1993;26(8):969-990.[14] Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC."Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;(141): 17-27. [15] Davey JR, O'Connor DO, Burke DW,et al.Femoral component offset. Its effect on strain in bone-cement.J Arthroplasty. 1993;8(1):23-26.[16] Dearmin MG, Schulz KS.The effect of stem length on femoral component positioning in canine total hip arthroplasty.Vet Surg. 2004;33(3):272-278.[17] Kleemann RU, Heller MO, Stoeckle U,et al.THA loading arising from increased femoral anteversion and offset may lead to critical cement stresses.J Orthop Res. 2003;21(5): 767-774.[18] 成锋,朱镇佳,徐威,等.人工髋关节假体周围骨折中应力遮挡形成原因及预防[J].中医正骨,2010,22(7):35-36,40. [19] Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P,et al.Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register.J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7):857-865.[20] Rorabeck CH, Bourne BR. Soft tissue balancing of the hip: A concept which has come of age[C]. Presented at the 70th annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedie Surgeons,2003.[21] Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Northcut EJ,et al."In vivo" determination of hip joint separation and the forces generated due to impact loading conditions.J Biomech. 2001;34(5): 623-629.[22] Charles MN, Bourne RB, Davey JR,et al.Soft-tissue balancing of the hip: the role of femoral offset restoration.Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:131-141. |