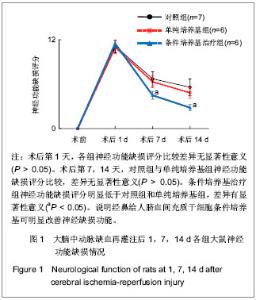
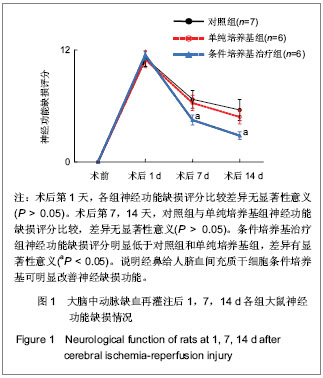
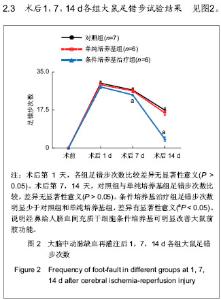
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intranasal administration of the conditioned medium of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
Shen Li-ping1, Wang Shuai-shuai1, Dong Li-guo1, Shen Xia1, Hua Fang1, Ye Xin-chun2, Cui Gui-yun2
- 1Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2013-08-17Online:2013-11-05Published:2013-11-05 -
Contact:Cui Gui-yun, M.D., Chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China cuiguiyun-js@163.com Corresponding author: Ye Xin-chun, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China xinchunye@foxmail.com -
About author:Shen Li-ping★, Studying for master’s degree, Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China shenliping1016@163.com -
Supported by:the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81201025*; the Major Science and Technology Research Program of Jiangxi Provincial Health Bureau, No. Z201208*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Li-ping, Wang Shuai-shuai, Dong Li-guo, Shen Xia, Hua Fang, Ye Xin-chun, Cui Gui-yun. Intranasal administration of the conditioned medium of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.45.011.
share this article
| [1] Veldhuis JD, Johnson ML, Iranmanesh A,et al.Temporal structure of in vivo adrenal secretory activity estimated by deconvolution analysis.J Biol Rhythms. 1990;5(3):247-255. [2] Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group.N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24): 1581-1587. [3] Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E,et al.Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke.N Engl J Med. 2008;359(13):1317-1329. [4] Seo JH, Cho SR.Neurorestoration induced by mesenchymal stem cells: potential therapeutic mechanisms for clinical trials.Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(6):1059-1067. [5] Bliss T, Guzman R, Daadi M, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for stroke.Stroke. 2007;38(2 Suppl):817-826. [6] Kurozumi K, Nakamura K, Tamiya T,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells that produce neurotrophic factors reduce ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model.Mol Ther. 2005;11(1):96-104. [7] Cui X, Chen J, Zacharek A,et al. Nitric oxide donor upregulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1/chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4 enhances bone marrow stromal cell migration into ischemic brain after stroke.Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2777-2785. [8] Egashira Y, Sugitani S, Suzuki Y,et al.The conditioned medium of murine and human adipose-derived stem cells exerts neuroprotective effects against experimental stroke model.Brain Res. 2012;1461:87-95. [9] Joannides A, Gaughwin P, Scott M,et al. Postnatal astrocytes promote neural induction from adult human bone marrow-derived stem cells.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003;12(6):681-688. [10] Li Y, Chen J, Chopp M. Adult bone marrow transplantation after stroke in adult rats.Cell Transplant. 2001;10(1):31-40. [11] Chen J, Zhang ZG, Li Y,et al. Intravenous administration of human bone marrow stromal cells induces angiogenesis in the ischemic boundary zone after stroke in rats.Circ Res. 2003;92(6):692-699. [12] Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J,et al.Intracarotid transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells increases axon-myelin remodeling after stroke.Neuroscience. 2006;137(2):393-399. [13] Zacharek A, Shehadah A, Chen J,et al.Comparison of bone marrow stromal cells derived from stroke and normal rats for stroke treatment.Stroke. 2010;41(3):524-530. [14] Shao H, Xu Q, Wu Q,et al. Defective CXCR4 expression in aged bone marrow cells impairs vascular regeneration.J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(10):2046-2056. [15] Shao P, Tang L, Li P,et al.Application of a vasculature model and standardization of the renal hilar approach in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for precise segmental artery clamping.Eur Urol. 2013;63(6):1072-1081. [16] Luo F, Lv Q, Zhao Y,et al. Quantification and Purification of Mangiferin from Chinese Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Cultivars and Its Protective Effect on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells under H(2)O(2)-induced Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(9):11260-11274. [17] Chopp M, Li Y.Treatment of neural injury with marrow stromal cells. Lancet Neurol. 2002;1(2):92-100. [18] Ma M, Ma Y, Yi X,et al. Intranasal delivery of transforming growth factor-beta1 in mice after stroke reduces infarct volume and increases neurogenesis in the subventricular zone.BMC Neurosci. 2008;9:117. [19] Zhu J, Jiang Y, Xu G,et al. Intranasal administration: a potential solution for cross-BBB delivering neurotrophic factors.Histol Histopathol. 2012;27(5):537-548. [20] Jiang Y, Zhu J, Xu G,et al. Intranasal delivery of stem cells to the brain.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(5):623-632. [21] Liu X.Clinical trials of intranasal delivery for treating neurological disorders--a critical review.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(12):1681-1690. [22] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L,et al.Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats.Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005-1011. [23] Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y,et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats.Stroke. 2001;32(11):2682-2688. [24] Liu F, McCullough LD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion model in rodents: methods and potential pitfalls. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:464701. [25] Cui X, Chopp M, Shehadah A,et al.Therapeutic benefit of treatment of stroke with simvastatin and human umbilical cord blood cells: neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and axon growth. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(5):845-856. [26] Chen J, Zacharek A, Zhang C,et al. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and neurogenesis after stroke in mice.J Neurosci. 2005;25(9):2366-2375. [27] Morris DC, Davies K, Zhang Z,et al.Measurement of cerebral microvessel diameters after embolic stroke in rat using quantitative laser scanning confocal microscopy.Brain Res. 2000;876(1-2):31-36. [28] Zhang ZG, Tsang W, Zhang L,et al.Up-regulation of neuropilin-1 in neovasculature after focal cerebral ischemia in the adult rat.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(5):541- 549. [29] Ohab JJ, Fleming S, Blesch A,et al. A neurovascular niche for neurogenesis after stroke.J Neurosci. 2006;26(50): 13007- 13016. [30] Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J,et al.One-year follow-up after bone marrow stromal cell treatment in middle-aged female rats with stroke.Stroke. 2007;38(7):2150-2156. [31] Teng H, Zhang ZG, Wang L,et al. Coupling of angiogenesis and neurogenesis in cultured endothelial cells and neural progenitor cells after stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008; 28(4):764-771. [32] Palmer TD, Willhoite AR, Gage FH.Vascular niche for adult hippocampal neurogenesis.J Comp Neurol. 2000;425(4): 479-494. [33] Shen Q, Wang Y, Kokovay E,et al. Adult SVZ stem cells lie in a vascular niche: a quantitative analysis of niche cell-cell interactions.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):289-300. [34] Tavazoie M, Van der Veken L, Silva-Vargas V,et al. A specialized vascular niche for adult neural stem cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):279-288. [35] Leventhal C, Rafii S, Rafii D,et al. Endothelial trophic support of neuronal production and recruitment from the adult mammalian subependyma.Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;13(6): 450-464. [36] Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S,et al. Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2001;22(3):147-184. [37] Rajadhyaksha M, Boyden T, Liras J,et al. Current advances in delivery of biotherapeutics across the blood-brain barrier.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2011;8(2):87-101. [38] Mistry A, Stolnik S, Illum L. Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs.Int J Pharm. 2009;379(1): 146-157. [39] Tian L, Guo R, Yue X,et al. Intranasal administration of nerve growth factor ameliorate β-amyloid deposition after traumatic brain injury in rats.Brain Res. 2012;1440:47-55. [40] Li L, Jiang Q, Zhang L,et al.Angiogenesis and improved cerebral blood flow in the ischemic boundary area detected by MRI after administration of sildenafil to rats with embolic stroke. Brain Res. 2007;1132(1):185-192. [41] Zhang L, Li Y, Romanko M,et al. Different routes of administration of human umbilical tissue-derived cells improve functional recovery in the rat after focal cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2012;1489:104-112. [42] Chen J, Shehadah A, Pal A,et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Human Placenta-derived Cell Treatment of Stroke in Rats.Cell Transplant. 2012. [Epub ahead of print] [43] Cui X, Chopp M, Zacharek A,et al. Combination treatment of stroke with sub-therapeutic doses of Simvastatin and human umbilical cord blood cells enhances vascular remodeling and improves functional outcome.Neuroscience. 2012;227: 223-231. [44] Chopp M, Zhang ZG, Jiang Q. Neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and MRI indices of functional recovery from stroke.Stroke. 2007;38(2 Suppl):827-831. [45] Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S,et al.Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis.Cell. 1996;87(7):1171-1180. [46] Metheny-Barlow LJ, Tian S, Hayes AJ,et al.Direct chemotactic action of angiopoietin-1 on mesenchymal cells in the presence of VEGF.Microvasc Res. 2004;68(3):221-230. [47] Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U,et al. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation.Nature. 1995;376(6535):70-74. [48] Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Croll SD,et al.Angiopoietin-1 reduces cerebral blood vessel leakage and ischemic lesion volume after focal cerebral embolic ischemia in mice.Neuroscience. 2002;113(3):683-687. [49] Thurston G, Rudge JS, Ioffe E,et al. Angiopoietin-1 protects the adult vasculature against plasma leakage.Nat Med. 2000; 6(4):460-463. [50] Chen JX,Stinnett A. Ang-1 gene therapy inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha)-prolyl-4- hydroxylase-2, stabilizes HIF-1alpha expression, and normalizes immature vasculature in db/db mice. Diabetes. 2008;57(12):3335-3343. [51] Pfister F, Feng Y, vom Hagen F,et al. Pericyte migration: a novel mechanism of pericyte loss in experimental diabetic retinopathy.Diabetes. 2008;57(9):2495-2502. [52] Iurlaro M, Scatena M, Zhu WH,et al. Rat aorta-derived mural precursor cells express the Tie2 receptor and respond directly to stimulation by angiopoietins.J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 17): 3635-3643. [53] Pfister F, Wang Y, Schreiter K,et al. Retinal overexpression of angiopoietin-2 mimics diabetic retinopathy and enhances vascular damages in hyperglycemia.Acta Diabetol. 2010; 47(1):59-64. [54] Zacharek A, Chen J, Cui X,et al. Angiopoietin1/Tie2 and VEGF/Flk1 induced by MSC treatment amplifies angiogenesis and vascular stabilization after stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(10):1684-1691. [55] Peters KG, Kontos CD, Lin PC,et al. Functional significance of Tie2 signaling in the adult vasculature.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:51-71. [56] Cui X, Chopp M, Zacharek A,et al. Angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway mediates type 2 diabetes induced vascular damage after cerebral stroke.Neurobiol Dis. 2011;43(1):285-292. [57] Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo D,et al. Inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke treatment.Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(14):1240-1260. [58] Zhang L, Li Y, Zhang C,et al. Delayed administration of human umbilical tissue-derived cells improved neurological functional recovery in a rodent model of focal ischemia.Stroke. 2011;42(5):1437-1444. [59] Doetsch F, García-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A.Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain.J Neurosci. 1997 ;17(13):5046-5061. [60] Chen J, Li Y, Zhang R,et al.Combination therapy of stroke in rats with a nitric oxide donor and human bone marrow stromal cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis.Brain Res. 2004; 1005(1-2):21-28. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279. |
| [3] | Zhang Shengmin, Liu Chao. Research progress in osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells induced by bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1107-1116. |
| [4] |
Wang Tiantian, Wang Jianzhong.
Application and prospect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the
treatment of early femoral head necrosis |
| [5] | Wang Zhangling, Yu Limei, Zhao Chunhua. Tissue repair using mesenchymal stem cells via mitochondrial transfer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1123-1129. |
| [6] | Deng Junhao, Li Miao, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Three-dimensional hanging-drop culture of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1101-1106. |
| [7] | Ren Chunmei, Liu Yufang, Xu Nuo, Shao Miaomiao, He Jianya, Li Xiaojie. Non-coding RNAs in human dental pulp stem cells: regulations and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1130-1137. |
| [8] | Huang Wenwen, Li Shuo, Hou Zongliu, Wang Wenju. Pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and mesenchymal stem cell therapy: therapeutic application and existing problems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1138-1143. |
| [9] | Liu Chundong, Shen Xiaoqing, Zhang Yanli, Zhang Xiaogen, Wu Buling. Effects of strontium-modified titanium surfaces on adhesion, migration and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of bone formation-related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1009-1015. |
| [10] | Lin Ming, Pan Jinyong, Zhang Huirong. Knockout of NIPBL gene down-regulates the abilities of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [11] | Zhang Wen, Lei Kun, Gao Lei, Li Kuanxin. Neuronal differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 985-990. |
| [12] | Wu Zhifeng, Luo Min. Biomechanical analysis of chemical acellular nerve allograft combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for repairing sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 991-995. |
| [13] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [14] | Qin Xinyu, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Gao Lianru, Cheng Tao, Wang Ze, Tong Shanshan, Chen Yu. Elabela promotes differentiation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1046-1051. |
| [15] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||