| [1]Ahmed TA, Hincke MT. Strategies for articular cartilage lesion repair and functional restoration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010; 16(3):305-329.
[2]Peretti GM, Pozzi A, Ballis R, et al. Current surgical options for articular cartilage repair. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011;108: 213-219.
[3]巩清波.关节软骨的损伤及其修复现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4491-4494.
[4]Stoltz JF, Huselstein C, Schiavi J, et al. Human stem cells and articular cartilage tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(15):2682-2691.
[5]Fini M, Pagani S, Giavaresi G, et al. Functional tissue engineering in articular cartilage repair: is there a role for electromagnetic biophysical stimulation. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(4):353-367.
[6]Johnstone B, Alini M, Cucchiarini M, et al. Tissue engineering for articular cartilage repair--the state of the art. Eur Cell Mater. 2013;25:248-267.
[7]Muhammad H, Schminke B, Miosge N. Current concepts in stem cell therapy for articular cartilage repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(4):541-548.
[8]赖建明,林建华.基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞修复关节软骨损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,(6):1107-1110.
[9]罗文,范建楠,叶川.软骨组织工程学方法修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(37):7009-7014.
[10]程越,田京.纳米支架与关节软骨重建[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(12):2265-2269.
[11]Luo W, Fan J, Ye C. Proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of precartilaginous stem cells in self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;26(12):1505-1511.
[12]You H, Chen A, Liu T, et al. Construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid of hTGF-beta3 and its inducing effect on differentiation of precartilaginous stem cells into chondroblasts. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(4):524-529.
[13]赵友,尹航,王昌兴,等.骨骺干细胞研究现状[J].中华中医药学刊, 2012,(2):346-348.
[14]Pan YS, Ding GX, Wang J. Research on repair strategies for articular cartilage defects. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(2): 175-178.
[15]Akiyama H. Transcriptional regulation in chondrogenesis by Sox-9. Clin Calcium. 2011;21(6):845-851.
[16]Tew SR, Clegg PD. Analysis of post transcriptional regulation of SOX-9 mRNA during in vitro chondrogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(13-14):1801-1807.
[17]Chen S, Tao J, Bae Y, et al. Notch gain of function inhibits chondrocyte differentiation via Rbpj-dependent suppression of Sox-9. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(3): 649-659.
[18]Sugimoto Y, Takimoto A, Akiyama H, et al. Scx+/Sox-9+ progenitors contribute to the establishment of the junction between cartilage and tendon/ligament. Development. 2013; 140(11):2280-2288.
[19]Cao L, Yang F, Liu G, et al. The promotion of cartilage defect repair using adenovirus mediated Sox-9 gene transfer of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(16):3910-3920.
[20]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[21]张衣北,陈安民,郭风劲,等.骨骺干细胞的体外培养及生长特性[J].中国康复,2006;21(1):3-5.
[22]游洪波,程浩.免疫磁性细胞分选技术分离纯化新生大鼠骨骺前软骨干细胞[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(10):33-35.
[23]Hu WH, Guo FJ, Li F, et al. Construction of Sox-9 gene eukaryotic expression vector and its inductive effects on directed differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells into precartilaginous stem cells in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009;(3):291-295.
[24]Hunziker EB, Rosenberg LC. Repair of partial-thickness defects in articular cartilage: cell recruitment from the synovial membrane. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(5):721-733.
[25]Gobbi A, Kon E, Berruto M, et al. Patellofemoral full-thickness chondral defects treated with second-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation: results at 5 years' follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(6):1083-1092.
[26]Hamanishi M, Nakasa T, Kamei N, et al. Treatment of cartilage defects by subchondral drilling combined with covering with atelocollagen membrane induces osteogenesis in a rat model. J Orthop Sci. 2013;19(4):353-367.
[27]Gao SJ, Wei JC, Lu B, et al. Experimental research on repairing full-thickness articular cartilage defects by transplantation of autologous uncultured bone-marrow- derived mononuclear cells in combination with micro-fracture. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012;92(35):2463-2467.
[28]Chahal J, Gross AE, Gross C, et al. Outcomes of osteochondral allograft transplantation in the knee. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(3):575-588.
[29]Zhang L, Hu J, Athanasiou KA. The role of tissue engineering in articular cartilage repair and regeneration. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;37(1-2):1-57.
[30]Guilak F, Butler DL, Goldstein SA. Functional tissue engineering: the role of biomechanics in articular cartilage repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(391 Suppl):S295-S305.
[31]El Sayed K, Marzahn U, John T, et al. PGA-associated heterotopic chondrocyte cocultures: implications of nasoseptal and auricular chondrocytes in articular cartilage repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(1):61-72.
[32]Singh M, Sandhu B, Scurto A, et al. Microsphere-based scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering: using subcritical CO(2) as a sintering agent. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(1):137-143.
[33]Raub CB, Hsu SC, Chan EF, et al. Microstructural remodeling of articular cartilage following defect repair by osteochondral autograft transfer. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(6):860- 868.
[34]Zhao Q, Wang S, Tian J, et al. Combination of bone marrow concentrate and PGA scaffolds enhance bone marrow stimulation in rabbit articular cartilage repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(3):793-801.
[35]Leijten JC, Georgi N, Wu L, et al. Cell sources for articular cartilage repair strategies: shifting from monocultures to cocultures. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(1):31-40.
[36]Kamei G, Kobayashi T, Ohkawa S, et al. Articular cartilage repair with magnetic mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(6):1255-1264.
[37]Robinson D, Hasharoni A, Cohen N, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 as a marker for precartilaginous stem cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(367 Suppl):S163-175.
[38]Cheng H, Chen AM , You HB. immunomagnetic indirect positive sorting of precartilaginous stem cells from neonatal rat. Huazhong Keji Daxue Xuebao (Yixue Yingdewen Ban). 2006;(6):723-724.
[39]丁然,张勇,游洪波,等.人转化生长因子β3基因转染KLD-12自组装纳米肽纤维支架三维培养前软骨干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(29):5339-5343.
[40]You HB, Chen AM, Liu T, et al. Construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid of htgf-β3 and its inducing effect on differentiation of precartilaginous stem cells into chondroblasts. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(4):524-529.
[41]You HB. Chondrogenesis of precartilaginous stem cells in KLD-12 self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffold loading TGF-β3 gene. Wuhan Ligong Daxue Xuebao:Cailiao Kexueban. 2011;(4):634-640.
[42]胡伟华,郭风劲,陈安民,等.新生大鼠前软骨干细胞株的体外培养分选、鉴定及永生化研究(英文)[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(43):8588-8592.
[43]张衣北,陈安民,郭风劲,等.Notch1信号系统对骨骺干细胞增殖与分化调控作用的初步观察[J].中华医学杂志,2005,85(48): 3430-3434.
[44]周治国,李丽,郭风劲.甲状旁腺相关肽调控骨骺干细胞后的stathmin表达[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2010,7(1):10- 15.
[45]赵守军,熊文化,郭宁峰.乏氧环境下骨骺干细胞株在软骨载体中的相容性、增殖和分化成软骨的实验研究[J].现代实用医学, 2012,24(4):375-377.
[46]Kupcsik L, Stoddart MJ, Li Z, et al. Improving chondrogenesis: potential and limitations of SOX-9 gene transfer and mechanical stimulation for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):1845-1855.
[47]Hattori T, Muller C, Gebhard S, et al. SOX-9 is a major negative regulator of cartilage vascularization, bone marrow formation and endochondral ossification. Development. 2010; 137(6):901-911.
[48]Nakamura Y, He X, Kato H, et al. Sox-9 is upstream of microRNA-140 in cartilage. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012; 166(1):64-71.
[49]Martinez-Sanchez A, Dudek KA, Murphy CL. Regulation of human chondrocyte function through direct inhibition of cartilage master regulator SOX-9 by microRNA-145 (miRNA-145). J Biol Chem. 2012;287(2):916-924.
[50]Park J, Zhang JJ, Moro A, et al. Regulation of Sox-9 by Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) is essential for patterning and formation of tracheal cartilage. Dev Dyn. 2010;239(2):514-526.
[51]Fanburg-Smith JC, Auerbach A, Marwaha JS, et al. Reappraisal of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: novel morphologic observations of the hyaline cartilage and endochondral ossification and beta-catenin, Sox-9, and osteocalcin immunostaining of 22 cases. Hum Pathol. 2010; 41(5):653-662.
[52]Cucchiarini M, Terwilliger EF, Kohn D, et al. Remodelling of human osteoarthritic cartilage by FGF-2, alone or combined with Sox9 via rAAV gene transfer. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13(8B): 2476-2488.
[53]张伟凯,陈安民,郭风劲,等.大鼠骨骺干细胞免疫纯化和Sox-9基因真核表达载体的克隆构建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12):2321-2325.
[54]张树威,金伟,祝少博,等.甲状旁腺素相关蛋白亚基因对骨骺干细胞的调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1814-1820.
[55]Cucchiarini M, Orth P, Madry H. Direct rAAV SOX-9 administration for durable articular cartilage repair with delayed terminal differentiation and hypertrophy in vivo. J Mol Med (Berl). 2013;91(5):625-636. |
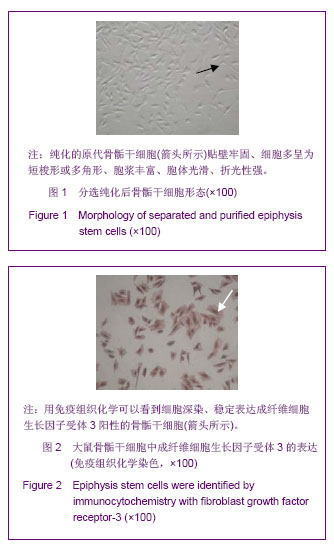
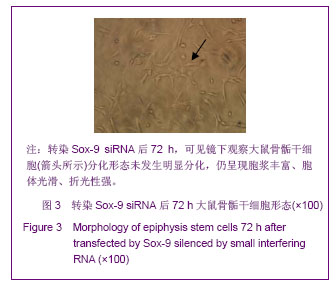
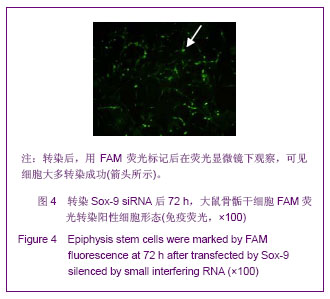
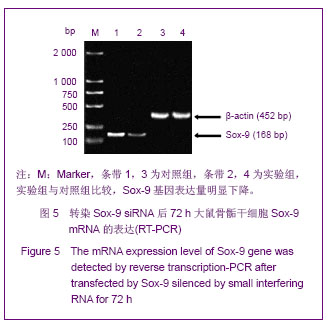
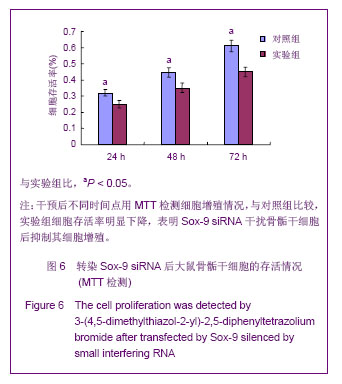
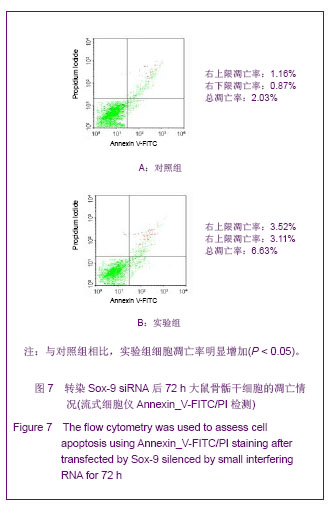
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg) Sox-9基因作为一个重要的转录激活因子,在骨骺干细胞增殖、凋亡及软骨分化过程中均起着非常重要的调控作用,相关的研究对软骨缺损损伤修复等组织再生工程发展具有十分重要的意义[46] 。目前的一些研究结果已显示很多的细胞生长因子可促进干细胞的增殖、分化,并且这种调控与Sox-9有密切的关系[47-52] ,这些生长因子可通过构建真核表达质粒转染进干细胞进行稳定表达促进增殖、分化,并可进一步联合新型材料支架用于软骨组织工程中修复软骨损伤。而相关的研究也显示Sox-9可以促进骨骺干细胞的增殖与成软骨分化[53] ,张树威等[54]研究显示PTHrP(107-139)可能是通过调控Sox-9、Ptc及骨形态发生蛋白6的表达来促进骨骺干细胞增殖并抑制其分化的。
Sox-9基因作为一个重要的转录激活因子,在骨骺干细胞增殖、凋亡及软骨分化过程中均起着非常重要的调控作用,相关的研究对软骨缺损损伤修复等组织再生工程发展具有十分重要的意义[46] 。目前的一些研究结果已显示很多的细胞生长因子可促进干细胞的增殖、分化,并且这种调控与Sox-9有密切的关系[47-52] ,这些生长因子可通过构建真核表达质粒转染进干细胞进行稳定表达促进增殖、分化,并可进一步联合新型材料支架用于软骨组织工程中修复软骨损伤。而相关的研究也显示Sox-9可以促进骨骺干细胞的增殖与成软骨分化[53] ,张树威等[54]研究显示PTHrP(107-139)可能是通过调控Sox-9、Ptc及骨形态发生蛋白6的表达来促进骨骺干细胞增殖并抑制其分化的。